Alzheimer's Disease: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (44 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== | == Introduction == | ||
[[File:Dementia -brain shrinkage.gif|thumb|260x260px|AD cause brain shrinkage]] | |||
Alzheimer's Disease (AD), a [[Neurodegenerative Disease|neurodegenerative disorder]], is the most common cause of [[dementia]] worldwide<ref>Anand, R., Gill, K.D. and Mahdi, A.A. (2014) 'Therapeutics of Alzheimers disease: past, present and future', Neuropharmacology, 76, 27-50</ref> <ref name=":4">Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.</ref> AD results from the of accumulation and deposition of cerebral amyloid-β (Aβ), and is the most frequent type of [[amyloidosis]] in humans.<ref name=":2">Ghiso J, Frangione B. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12453671/ Amyloidosis and Alzheimer’s disease]. Advanced drug delivery reviews. 2002 Dec 7;54(12):1539-51.Available:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12453671/ (accessed 17.1.2023)</ref> The symptoms of AD include emotional fluctuation, sleep disorders, behavior changes, and cognitive decline. In the advanced stages, it can cause severe symptoms such as malnutrition, multi-organ failure and brain death.<ref>Chen Ma, Fenfang Hong, and Shulong Yang [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8876037/ Amyloidosis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathogeny, Etiology, and Related] Therapeutic Directions Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8876037/ (accessed 16.1.2023) | |||
</ref> There is currently no cure for the disease, but treatments are available to slow down the progression<ref name=":1">Radiopedia [https://radiopaedia.org/articles/alzheimer-disease-1?lang=gb Alzheimer disease] Available:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/alzheimer-disease-1?lang=gb (accessed 16.1.2023)</ref><ref name=":4" />. | |||
[[ | == Epidemiology == | ||
[[File:Dementia-death-rates.png|right|frameless|487x487px|alt=]] | |||
Alzheimer disease is the most prevalent cause of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of all dementias. The prevalence is closely linked to age, >1% of 60-64-year-olds having the condition rising to 20-40%in the over 85-90 age bracket.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
Alzheimer's | First case of Alzheimer disease mentioned in 1907 by Alois.<ref>Hippius H, Neundörfer G. The discovery of Alzheimer's disease. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2003 Mar;5(1):101-8. </ref> According to the World Alzheimer Report 2018, a new case of dementia develops every 3 seconds around the globe with 66% of these people living in low‐ and middle‐income countries.<ref name=":0">Zhou X, Ashford JW. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6880670/ Advances in screening instruments for Alzheimer's disease]. Aging Medicine. 2019 Jun;2(2):88-93. Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6880670/ (accessed 16.1.2023)</ref> | ||
== Etiology == | |||
After years of research, scientists at first considered Alzheimer’s disease as a complex disease with genetic and age, family history, and Down syndrome all contributing to pathogenesis. But still, the actual pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease is still unclear. The amyloid cascade hypothesis is now the main model of AD pathogenesis.<ref name=":2" /> Genetics is a factor in some cases of early and late-onset AD. | |||
{{#ev:youtube.com/watch?v=nLdLfmFzLSo}}{{#ev:youtube|nLdLfmFzLSo|240}}<ref> Dementia - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options [Internet]. YouTube. YouTube; 2014 [cited /06/2014]. Available from: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nLdLfmFzLSo/ref https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nLdLfmFzLSo</ref> | |||
</ref | |||
Several risk factors (see also [[Dementia: Risk Factors|Dementia: Risk Factors)]] have been associated with AD including<ref name=":3">Kumar A, Sidhu J, Goyal A, Tsao JW. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499922/ Alzheimer disease.] Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499922/ (accessed 16.1.2023)</ref>: | |||
*Advancing age, >85 y/o risk increases by nearly 50%<ref>Alzheimer's & Dementia Testing Advances | Research Center [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr2]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/research/science/earlier_alzheimers_diagnosis.asp</ref> | |||
*Direct family member with the disease (mother, father, brother or sister) | |||
*Apolipoprotein E-e4 (APOE4) carries the strongest risk of developing Alzheimer’s Disease (a genetic mutation of APOE) <ref>Alzheimer's and Dementia Causes, Risk Factors | Research Center [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/research/science/alzheimers_disease_causes.asp#apoe</ref> | |||
*[[Overview of Traumatic Brain Injury|Traumatic brain injury]] | |||
*Deterministic genes have a direct cause of early-onset AD, however, they only account for less than 5% of cases: amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin-1 (PS-1), presenilin (PS-2) <ref>Alzheimer's and Dementia Causes, Risk Factors | Research Center [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/research/science/alzheimers_disease_causes.asp#apoe</ref> | |||
*[[Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)|Trisomy 21]] | |||
*Cardiovascular risk factors: mid-life [[obesity]], mid-life [[hypertension]], [[hyperlipidemia]], [[Diabetes|diabetes mellitus]]<ref>Latest Alzheimer's Facts and Figures [Internet]. Latest Facts; Figures Report | Alzheimer's Association. 2016 [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/facts/</ref> | |||
As well as the genetic and environmental factors above, the age when clinical signs show is affected by by socioeconomic factors: | |||
* Formal education | |||
* Income | |||
* Occupational status | |||
* Social network and family support<ref name=":1" /> | |||
People with higher function/supports prior to diagnosis are able to compensate for early disease changes more effectively and present later. When these people present, they tend to have more marked morphological changes on imaging.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Pathology == | |||
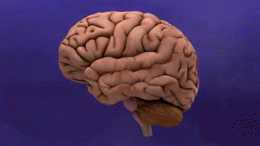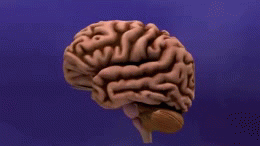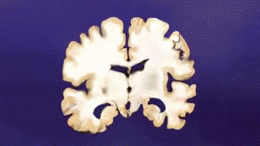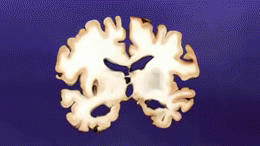
AD is distinguished by accumulation in the brain of [[Cerebral Cortex|cerebral]] amyloid-β (Aβ or Abeta), which progressively form neuritic plaques, neurofibrillary tangles and progressive neurone loss. Amyloid accumulation is caused by many factors, including impairment of cellular autophagy and low cerebral blood flow.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
Cerebral amyloid-β deposits occur predominantly | |||
* Entorhinal cortex in the [[hippocampus]] (important in spatial memory and navigation, and helps turn short-term memory into long-term memory)<ref name=":3" /><ref>Kiddle Hippocampus Available from:https://kids.kiddle.co/Hippocampus (accessed 17.1.2023)</ref><ref name=":3" /> | |||
* Association areas of the neocortex, | |||
* [[Limbic System|Limbic]] cortex | |||
The fundamental reason for the accumulation of neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles is not as yet understood. Evidence partially points to chronic inflammation having a role. This inflammatory state leads to prolonged activation of [[Glial Cells|microglial]] cells (phagocytose and remove foreign or damaged material, cells) which causes inflammatory mediators to be released resulting in neuronal damage and amyloid-induced neurodegeneration.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Clinical Presentation == | |||
[[File:Icon of a person with a question mark for a head for amnesia, forgetfulness or dementia.png|thumb|Icon: for amnesia or dementia]] | |||
The typical patient with AD will present initially with decreased ability to form/retain new [[Memory|memories]]. With time (often years), cognitive deficeits progresses, with eventual problems with attentional and executive processes, semantic memory, and visuoperceptual abilities. [[Mental Health|Mental health problems]] affect almost all patients eventually, including apathy, [[depression]], [[Generalized Anxiety Disorder|anxiety]], aggression/agitation, and psychosis (delusions and hallucinations).<ref name=":1" /> | |||
'''Stages of Alzheimer's Disease''' | |||
AD may progress through the following stages as follows<ref>Porth C. Pathopysiology Concepts of Altered Health States. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott and Wilkins; 2005.</ref><ref>Stages of Alzheimer's Symptoms [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/alzheimers_disease_stages_of_alzheimers.asp</ref>: | |||
# '''Mild Alzheimer’s Disease (Early Stage):''' May Function Independently: may drive, work or maybe apart of social activities. Memory Lapses: familiar words, location of objects, names of new people, recently read material. Difficulties noticed by family, friends and doctors: challenges performing activities at home or work, difficulty planning. Lack of spontaneity. Subtle personality changes. Disorientation to time and date | |||
# '''Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease (Middle Stage):''' Longest stage may last for years. Personality changes: moody or withdrawn, suspicious, delusions, compulsive, repetitive behavior. Increased memory loss: forgetfulness regarding personal history, unable to recall address, phone number, or high school they graduated from. Decreased independence: trouble controlling bowel and bladder, increased risk of wandering or becoming lost, dependence with choosing appropriate clothes for event or season, increased Confusion. Impaired cognition and abstract thinking. Restlessness and agitation. Wandering, "sundown syndrome". Inability to carry out activities of daily living. | |||
# '''Severe Alzheimer’s Disease (Late Stage):''' Decreased response to the environment: decreased ability to communicate and may speak in small phrases, decreased awareness of experiences & surroundings. Dependence on caregiver: decreased physical functioning: walking, sitting & swallowing; increased vulnerability to infections, incontinence. Emaciation, indifference to food | |||
== | == Diagnosis == | ||
Currently, the diagnosis of AD relies primarily on signs and symptoms of mental decline. Routine laboratory tests show no specific abnormality. [[CT Scans|CT]] brain reveal cerebral atrophy and widened third ventricles, a nonspecific finding as these abnormalities are also present in other illnesses and people with normal age-related changes. <ref>Alzheimer's & Dementia Testing Advances | Research Center [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr3]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/research/science/earlier_alzheimers_diagnosis.asp</ref> | |||
Tests include: | |||
* [[CSF Cerebrospinal Fluid|Cerebrospinal fluid]] (CSF) analysis for low beta-amyloid 42 and elevated tau helps at the pre-clinical stage. | |||
* EEG shows a slowing with no focal features, again nonspecific. | |||
* neuropsychological testing. including a psychiatric evaluation (looking for mental health conditions). | |||
* [[MRI Scans|MRI]] is the favoured modality as it shows great detail. | |||
* Molecular imaging with PET is gaining use in the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. PET is a form of [[Nuclear Medicine|Nuclear Medicine imaging]] | |||
* [[Genetic Conditions and Inheritance|Genetic]] Testing: Inheriting a single copy of the ApoE gene, encoding for apolipoprotein E, increases the chances of developing Alzheimer disease three times, whilst inheriting both copies increases one's risk eightfold.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Screening == | |||
AD screening is an important issue with various studies indicating that the first detectable cognitive changes related to AD development 10 years prior to clinical diagnosis. A measurement of AD from its preclinical phase through its progression to mild dementia is needed for identification of AD early, with no reliable tool yet existing <ref name=":0" />. | |||
Objective tools have been validated in order to screen for AD such as the [[Mini-Cog]], [[Mini-Mental State Examination|Mini-Mental State Exam]] (MMSE), Clock-Drawing, & Neurobehavioral Cognitive Status Exam.<ref>Cedervall Y, Stenberg AM, Åhman HB, Giedraitis V, Tinmark F, Berglund L, Halvorsen K, Ingelsson M, Rosendahl E, Åberg AC. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7084863/ Timed Up-and-Go Dual-Task Testing in the Assessment of Cognitive Function: A Mixed Methods Observational Study for Development of the UDDGait Protocol.] International journal of environmental research and public health. 2020 Jan;17(5):1715.</ref>. | |||
Objective tools have been validated | |||
== Systemic Involvement == | == Systemic Involvement == | ||
The most noticeable symptoms initially are the cognitive and memory-related symptoms. However, | The most noticeable symptoms initially are the cognitive and memory-related symptoms. However, AD can affect other parts of the body causing symptoms other than those affecting memory and cognition. Often abnormal motor signs can be apparent depending on the area of the brain affected by the disease. The presence of tremors can be associated with increased risk for cognitive decline, the presence of bradykinesia with increased risk for functional decline, and the presence of postural-gait impairments with increased risk of institutionalization and death. Additionally, patients may develop disorders of sleeping, eating, and sexual behaviour.<ref>Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.</ref> | ||
== Medical Management == | == Medical Management == | ||
There is currently no cure for | There is currently no cure for AD, so medical management is focused on maintaining the quality of life, maximizing function, enhancing cognition, fostering a safe environment and promoting self engagement<ref>Medical Management and Patient Care [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/health-care-professionals/medical-management-patient-care.asp</ref>. Maximizing dementia functioning involves monitoring the patient's health and cognition, patient and family education, initiation of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments. | ||
* Cognitive symptom treatment | * Cognitive symptom treatment | ||
** Although the disease progression cannot be altered, it may be slowed by the pharmacological medication listed above | ** Although the disease progression cannot be altered, it may be slowed by the pharmacological medication listed above | ||
* Behavioral and psychological symptom treatment | * Behavioral and psychological symptom treatment | ||
** Agitation, aggression, depression, and psychosis are the primary cause of assisted living or nursing home placement. | ** Agitation, aggression, [[depression]], and psychosis are the primary cause of assisted living or nursing home placement. | ||
** Assessment of behaviors occurring suddenly is important to increase patient comfort, security, and ease of mind. | ** Assessment of behaviors occurring suddenly is important to increase patient comfort, security, and ease of mind. | ||
* Monitoring Alzheimer’s disease | * Monitoring Alzheimer’s disease | ||
** Patients should return on a regular basis in order for the physician to monitor the course of Alzheimer’s disease (behavioral and cognitive changes). | ** Patients should return on a regular basis in order for the physician to monitor the course of Alzheimer’s disease (behavioral and cognitive changes). | ||
** Regular follow-up appointments allow for the adaptation of treatment styles to fit the needs of the patient. | ** Regular follow-up appointments allow for the adaptation of treatment styles to fit the needs of the patient. | ||
** | ** Non medical/social Issues the patients need to address: | ||
*** Need for ongoing support & information | *** Need for ongoing support & information | ||
*** A living will or power of attorney | *** A living will or power of attorney | ||
*** Review of finances/planning for future and end of life care | *** Review of finances/planning for future and end of life care | ||
* Alternative Treatment | * Alternative Treatment | ||
** There are concerns regarding alternative treatments in addition to physician-prescribed medicine. If any concerns are questions brought to attention, the physician should be notified. | ** There are concerns regarding alternative treatments in addition to physician-prescribed medicine. If any concerns are questions brought to attention, the physician should be notified. | ||
** Aerobic and strengthening exercise might slow cognitive impairment in dementia has gained widespread popularity. Many studies describe plausible mechanisms using mammalian models, but there are fewer studies using human participants.<ref>Lamb SE, Sheehan B, Atherton N, Nichols V, Collins H, Mistry D, Dosanjh S, Slowther AM, Khan I, Petrou S, Lall R; DAPA Trial Investigators. Dementia And Physical Activity (DAPA) trial of moderate to high intensity exercise training for people with dementia: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2018 May 16;361:k1675. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k1675. PMID: 29769247; PMCID: PMC5953238.</ref> | |||
** Some researchers consider exercise replacement for drugs to decrease the negative effect of dementia on cognitive function as memory, executive and physical function as strength, balance and endurance.<ref>Sanders, L. M. J., Hortobágyi, T., Karssemeijer, E. G. A., Van der Zee, E. A., Scherder, E. J. A., & van Heuvelen, M. J. G. (2020). Effects of low- and high-intensity physical exercise on physical and cognitive function in older persons with dementia: a randomized controlled trial. ''Alzheimer's research & therapy'', ''12''(1), 28. </ref> | |||
** Effect on dementia have conflicted one review observed exercise has a positive effect on physical status not cognitive, while another review concluded aerobic exercise affects physical and cognitive functions.<ref name=":5">Lamb SE, Sheehan B, Atherton N, Nichols V, Collins H, Mistry D, Dosanjh S, Slowther AM, Khan I, Petrou S, Lall R; DAPA Trial Investigators. Dementia And Physical Activity (DAPA) trial of moderate to high intensity exercise training for people with dementia: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2018 May 16;361:k1675. </ref>. | |||
** Positive effects of exercise are increase of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), insulin-like growth factor-type I (IGF-1), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and homocysteine [15–23] that is enhance memory and executive function.<ref name=":5" /> | |||
** Music therapy treatment may enhance both psychological and physical by lowering stress levels, and reduction of plasma cortisol levels. some researcher measured salivary cortisol samples with moderate or severe dementia. limited number of studies explained effect of music therapy on dementia <ref>Takahashi, T., & Matsushita, H. (2006). Long-term effects of music therapy on elderly with moderate/severe dementia. ''Journal of music therapy'', ''43''(4), 317–333. </ref> | |||
* Importance of Caregiver | * Importance of Caregiver | ||
** Many caregivers seek to meet the needs of the physician and the patient which increases rates of stress and depression. Physicians should continue to monitor the status of the caregivers watching out for burnout and providing them with resources as well. | ** Many caregivers seek to meet the needs of the physician and the patient which increases rates of stress and depression. Physicians should continue to monitor the status of the caregivers watching out for burnout and providing them with resources as well. | ||
== | == Medications == | ||
Below is a list of some commonly used medications use in the treatments of the symptoms of Alzheimer's. There is also the use of other treatments such as antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, and estrogen replacement therapy in women to prevent or delay the onset of the disease.<ref>Porth C. Pathopysiology Concepts of Altered Health States. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott and Wilkins; 2005.</ref><ref>Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.</ref> | |||
* Cholinesterase inhibitors e.g. donepezil | |||
* Partial NMDA receptor antagonists | |||
* Medications for behavioural symptoms | |||
* Antidepressants | |||
* Anxiolytics | |||
* Antiparkinsonian (movement symptoms) | |||
* Anticonvulsants/sedatives (behavioural) | |||
* Recently Aduhelm (aducanumab) has been approved by the FDA, professed to reduce amyloid-beta plaque in people, however its efficacy and long-term benefits remain controversial.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Physical Therapy Management == | |||
In the early and middle stages of AD, physical therapists can assist people stay mobile. This helps them maintain a degree of independence, and continue to perform their roles in the family and in the community. | |||
Later as AD progresses physical therapists assist in keeping them able to perform daily activities for as long as possible, reducing the load on family members and caregivers. Physical therapists can perform a home assessment to ensure help the home is a safe environment and possibly delay the need for facility-based care. | |||
* [[Physical Activity|Physical activity]] is important to incorporate in a patient’s with Alzheimer’s disease life. Problems with balance and gait can often be lessened by regular physical therapy sessions, thereby reducing the risk of falls, fractures, and other injuries.<ref>Phillips, C. et al. "The Link Between Physical Activity And Cognitive Dysfunction In Alzheimer Disease". Physical Therapy 95.7 (2015): 1046-1060. Web. 1 Apr. 2017.</ref><ref>Lin TW, Tsai SF, Kuo YM. Physical exercise enhances neuroplasticity and delays Alzheimer’s disease. Brain plasticity. 2018 Jan 1;4(1):95-110.</ref> | |||
* A community-based exercise program has been shown to improve multiple domains of life for individuals with Alzheimer's. Studies show that those participating in such exercise groups improved cognition, mobility, and instrumental activities of daily living<ref>Vreugdenhil, Anthea et al. "A Community-Based Exercise Programme To Improve Functional Ability In People With Alzheimer’S Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial". Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences 26.1 (2011): 12-19. Web. 1 Apr. 2017.</ref>. See [[Preventing Dementia and Cognitive Decline]] | |||
Individuals with dementia are at an increased risk for falling compared to the average population of community-dwelling older adults. <ref>Renfro M, Bainbridge D, Smith M. Validation of Evidence-Based Fall Prevention Programs for Adults with Intellectual and/or Developmental Disorders: A Modified Otago Exercise Program. Frontiers in Public Health. 2016;4. Web. 1 Apr. 2017.</ref> A research study suggests that poor visual acuity resulted in poorer executive function, which further caused more inadequate balance control, thus demonstrating the importance of assessing executive functions besides vision and balance in older individuals living with Alzheimer's dementia.<ref>Hunter SW, Divine A, Madou E, Omana H, Hill KD, Johnson AM, Holmes JD, Wittich W. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32388070/ Executive function as a mediating factor between visual acuity and postural stability in cognitively healthy adults and adults with Alzheimer’s dementia]. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2020 Apr 19:104078.</ref> | * Individuals with dementia are at an increased risk for falling compared to the average population of community-dwelling older adults. <ref>Renfro M, Bainbridge D, Smith M. Validation of Evidence-Based Fall Prevention Programs for Adults with Intellectual and/or Developmental Disorders: A Modified Otago Exercise Program. Frontiers in Public Health. 2016;4. Web. 1 Apr. 2017.</ref> A research study suggests that poor visual acuity resulted in poorer executive function, which further caused more inadequate balance control, thus demonstrating the importance of assessing executive functions besides vision and [[balance]] in older individuals living with Alzheimer's dementia.<ref>Hunter SW, Divine A, Madou E, Omana H, Hill KD, Johnson AM, Holmes JD, Wittich W. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32388070/ Executive function as a mediating factor between visual acuity and postural stability in cognitively healthy adults and adults with Alzheimer’s dementia]. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2020 Apr 19:104078.</ref> See [[Falls and Dementia]] | ||
* Group therapy is also successful with patients with Alzheimer's disease, but the session must not provide more stimulation than the patient is able to tolerate. Repetition and encouragement are also very important to help keep the patient's confidence high and to help with remembering the exercises.<ref>Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.</ref> | |||
This 4 minute video outlines the role of Physiotherapy may play in AD.{{#ev:youtube|rW3rQ73rQFE|200}}<ref>Pollom E, Little J. PT Management of Alzheimer's Disease [Internet]. YouTube. YouTube; 2017 [cited 2017Apr2]. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rW3rQ73rQFE&t=8s</ref> | |||
Group therapy is also successful with patients with Alzheimer's disease, but the session must not provide more stimulation than the patient is able to tolerate. Repetition and encouragement are also very important to help keep the patient's confidence high and to help with remembering the exercises. | |||
== Dietary Management == | == Dietary Management == | ||
It has been found that maintaining a healthy diet may help to prevent or slow the progression of Alzheimer's. It is suggested that the diet be low in fat, high in omega-3 oils, and high in dark vegetables and fruits, also adding vitamin C to the diet along with coenzyme Q10, and folate may work to lower the risk of Alzheimer's. There does not seem to be one single aspect of diet that provides neuroprotection, rather | It has been found that maintaining a healthy diet may help to prevent or slow the progression of Alzheimer's. It is suggested that the diet be low in fat, high in omega-3 oils, and high in dark vegetables and fruits, also adding vitamin C to the diet along with coenzyme Q10, and folate may work to lower the risk of Alzheimer's. There does not seem to be one single aspect of diet that provides neuroprotection, rather than the items work together to decrease the risk of AD.<ref>Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.</ref>There is also some interest in the use of antioxidants such as vitamin E and ginkgo, along with anti-inflammatory agents, and estrogen replacement therapy for women.<ref>Porth C. Pathopysiology Concepts of Altered Health States. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott and Wilkins; 2005.</ref> | ||
== Differential Diagnosis == | == Differential Diagnosis == | ||
*Pick's Disease | *[[Pick's Disease]] | ||
*[[Lewy Body Disease|Lewy Body Dementia]] | *[[Lewy Body Disease|Lewy Body Dementia]] | ||
*Frontotemporal Dementia | *[[Frontotemporal Dementia]] | ||
*Dementia from multiple medications | *Dementia from multiple medications | ||
*Other potentially reversible causes of dementia | *Other potentially reversible causes of dementia | ||
== | == Low Resource Health Settings == | ||
More than half of all people with dementia are from low and middle-income countries. Alzheimer’s disease, other dementias, and non-communicable diseases are expected to continue to be a burden on health systems throughout sub-Saharan Africa, as country populations age and communicable disease mortality and morbidity go down <ref>Mubangizi V, Maling S, Obua C, Tsai AC. Prevalence and correlates of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias in rural Uganda: cross-sectional, population-based study. BMC geriatrics. 2020 Dec;20(1):1-7.</ref>. The number of people with Alzheimer's disease and dementia in general is estimated to increase far more rapidly in the upper middle, lower middle and low-income countries (LMICs) than in the high-income countries <ref>Global Prevalence. Available from:https://www.dementiastatistics.org/statistics/global-prevalence/( Accessed, 20/09/2021).</ref>. There is a general lack of awareness of the disease among the population, therefore patients don't seek for medical care and do not get the treatment they need. Hence, it is under-recognized, underdisclosed, undertreated, and undermanaged, particularly in LMICs<ref>Ferri CP, Jacob KS. Dementia in low-income and middle-income countries: different realities mandate tailored solutions. PLoS medicine. 2017 Mar 28;14(3):e1002271. | |||
</ref>. The living environment also often poses little cognitive challenge because families may not understand their relative’s behavior <ref>George-Carey R, Adeloye D, Chan KY, Paul A, Kolčić I, Campbell H, Rudan I. An estimate of the prevalence of dementia in Africa: a systematic analysis. Journal of global health. 2012 Dec;2(2).</ref>. Many of the cognitive and functional assessment tools used in LMICs were originally developed and validated in High Income Countries. There is a need to adapt it to be used more effectively in LMICs <ref>Sexton C, Snyder HM, Chandrasekaran L, Worley S, Carrillo MC. Expanding Representation of Low and Middle Income Countries in Global Dementia Research: Commentary From the Alzheimer's Association. Frontiers in Neurology. 2021 Mar 15;12:271.</ref>. | |||
== Resources == | |||
See also [[:Category:Dementia|Category:Dementia]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Conditions]] | [[Category:Conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Dementia]] | [[Category:Dementia]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:51, 1 May 2023
Original Editors - Students from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project. Top Contributors - Josie Little, Stephanie Schwebler, Laura Ritchie, Admin, Lucinda hampton, Elaine Lonnemann, Kim Jackson, Hayaa Yousri, Emily Pollom, Dave Pariser, Vidya Acharya, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane, Nikhil Benhur Abburi, Lauren Lopez, 127.0.0.1, Shaimaa Eldib, Joseph Ayotunde Aderonmu, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop, Tolulope Adeniji, Safiya Naz, Wendy Walker and Naomi O'Reilly
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Alzheimer's Disease (AD), a neurodegenerative disorder, is the most common cause of dementia worldwide[1] [2] AD results from the of accumulation and deposition of cerebral amyloid-β (Aβ), and is the most frequent type of amyloidosis in humans.[3] The symptoms of AD include emotional fluctuation, sleep disorders, behavior changes, and cognitive decline. In the advanced stages, it can cause severe symptoms such as malnutrition, multi-organ failure and brain death.[4] There is currently no cure for the disease, but treatments are available to slow down the progression[5][2].
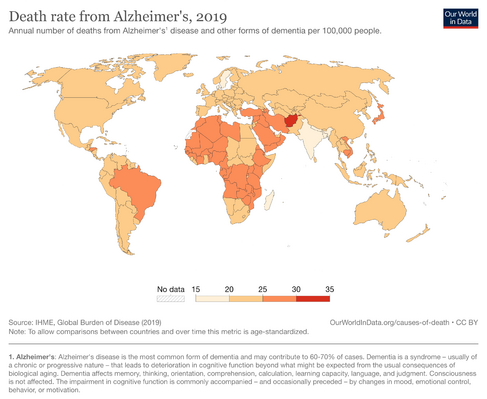
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Alzheimer disease is the most prevalent cause of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of all dementias. The prevalence is closely linked to age, >1% of 60-64-year-olds having the condition rising to 20-40%in the over 85-90 age bracket.[5]
First case of Alzheimer disease mentioned in 1907 by Alois.[6] According to the World Alzheimer Report 2018, a new case of dementia develops every 3 seconds around the globe with 66% of these people living in low‐ and middle‐income countries.[7]
Etiology[edit | edit source]
After years of research, scientists at first considered Alzheimer’s disease as a complex disease with genetic and age, family history, and Down syndrome all contributing to pathogenesis. But still, the actual pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease is still unclear. The amyloid cascade hypothesis is now the main model of AD pathogenesis.[3] Genetics is a factor in some cases of early and late-onset AD.
Several risk factors (see also Dementia: Risk Factors) have been associated with AD including[9]:
- Advancing age, >85 y/o risk increases by nearly 50%[10]
- Direct family member with the disease (mother, father, brother or sister)
- Apolipoprotein E-e4 (APOE4) carries the strongest risk of developing Alzheimer’s Disease (a genetic mutation of APOE) [11]
- Traumatic brain injury
- Deterministic genes have a direct cause of early-onset AD, however, they only account for less than 5% of cases: amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin-1 (PS-1), presenilin (PS-2) [12]
- Trisomy 21
- Cardiovascular risk factors: mid-life obesity, mid-life hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus[13]
As well as the genetic and environmental factors above, the age when clinical signs show is affected by by socioeconomic factors:
- Formal education
- Income
- Occupational status
- Social network and family support[5]
People with higher function/supports prior to diagnosis are able to compensate for early disease changes more effectively and present later. When these people present, they tend to have more marked morphological changes on imaging.[5]
Pathology[edit | edit source]
AD is distinguished by accumulation in the brain of cerebral amyloid-β (Aβ or Abeta), which progressively form neuritic plaques, neurofibrillary tangles and progressive neurone loss. Amyloid accumulation is caused by many factors, including impairment of cellular autophagy and low cerebral blood flow.[3]
Cerebral amyloid-β deposits occur predominantly
- Entorhinal cortex in the hippocampus (important in spatial memory and navigation, and helps turn short-term memory into long-term memory)[9][14][9]
- Association areas of the neocortex,
- Limbic cortex
The fundamental reason for the accumulation of neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles is not as yet understood. Evidence partially points to chronic inflammation having a role. This inflammatory state leads to prolonged activation of microglial cells (phagocytose and remove foreign or damaged material, cells) which causes inflammatory mediators to be released resulting in neuronal damage and amyloid-induced neurodegeneration.[5]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
The typical patient with AD will present initially with decreased ability to form/retain new memories. With time (often years), cognitive deficeits progresses, with eventual problems with attentional and executive processes, semantic memory, and visuoperceptual abilities. Mental health problems affect almost all patients eventually, including apathy, depression, anxiety, aggression/agitation, and psychosis (delusions and hallucinations).[5]
Stages of Alzheimer's Disease
AD may progress through the following stages as follows[15][16]:
- Mild Alzheimer’s Disease (Early Stage): May Function Independently: may drive, work or maybe apart of social activities. Memory Lapses: familiar words, location of objects, names of new people, recently read material. Difficulties noticed by family, friends and doctors: challenges performing activities at home or work, difficulty planning. Lack of spontaneity. Subtle personality changes. Disorientation to time and date
- Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease (Middle Stage): Longest stage may last for years. Personality changes: moody or withdrawn, suspicious, delusions, compulsive, repetitive behavior. Increased memory loss: forgetfulness regarding personal history, unable to recall address, phone number, or high school they graduated from. Decreased independence: trouble controlling bowel and bladder, increased risk of wandering or becoming lost, dependence with choosing appropriate clothes for event or season, increased Confusion. Impaired cognition and abstract thinking. Restlessness and agitation. Wandering, "sundown syndrome". Inability to carry out activities of daily living.
- Severe Alzheimer’s Disease (Late Stage): Decreased response to the environment: decreased ability to communicate and may speak in small phrases, decreased awareness of experiences & surroundings. Dependence on caregiver: decreased physical functioning: walking, sitting & swallowing; increased vulnerability to infections, incontinence. Emaciation, indifference to food
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Currently, the diagnosis of AD relies primarily on signs and symptoms of mental decline. Routine laboratory tests show no specific abnormality. CT brain reveal cerebral atrophy and widened third ventricles, a nonspecific finding as these abnormalities are also present in other illnesses and people with normal age-related changes. [17]
Tests include:
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis for low beta-amyloid 42 and elevated tau helps at the pre-clinical stage.
- EEG shows a slowing with no focal features, again nonspecific.
- neuropsychological testing. including a psychiatric evaluation (looking for mental health conditions).
- MRI is the favoured modality as it shows great detail.
- Molecular imaging with PET is gaining use in the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. PET is a form of Nuclear Medicine imaging
- Genetic Testing: Inheriting a single copy of the ApoE gene, encoding for apolipoprotein E, increases the chances of developing Alzheimer disease three times, whilst inheriting both copies increases one's risk eightfold.[5]
Screening[edit | edit source]
AD screening is an important issue with various studies indicating that the first detectable cognitive changes related to AD development 10 years prior to clinical diagnosis. A measurement of AD from its preclinical phase through its progression to mild dementia is needed for identification of AD early, with no reliable tool yet existing [7].
Objective tools have been validated in order to screen for AD such as the Mini-Cog, Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE), Clock-Drawing, & Neurobehavioral Cognitive Status Exam.[18].
Systemic Involvement[edit | edit source]
The most noticeable symptoms initially are the cognitive and memory-related symptoms. However, AD can affect other parts of the body causing symptoms other than those affecting memory and cognition. Often abnormal motor signs can be apparent depending on the area of the brain affected by the disease. The presence of tremors can be associated with increased risk for cognitive decline, the presence of bradykinesia with increased risk for functional decline, and the presence of postural-gait impairments with increased risk of institutionalization and death. Additionally, patients may develop disorders of sleeping, eating, and sexual behaviour.[19]
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
There is currently no cure for AD, so medical management is focused on maintaining the quality of life, maximizing function, enhancing cognition, fostering a safe environment and promoting self engagement[20]. Maximizing dementia functioning involves monitoring the patient's health and cognition, patient and family education, initiation of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments.
- Cognitive symptom treatment
- Although the disease progression cannot be altered, it may be slowed by the pharmacological medication listed above
- Behavioral and psychological symptom treatment
- Agitation, aggression, depression, and psychosis are the primary cause of assisted living or nursing home placement.
- Assessment of behaviors occurring suddenly is important to increase patient comfort, security, and ease of mind.
- Monitoring Alzheimer’s disease
- Patients should return on a regular basis in order for the physician to monitor the course of Alzheimer’s disease (behavioral and cognitive changes).
- Regular follow-up appointments allow for the adaptation of treatment styles to fit the needs of the patient.
- Non medical/social Issues the patients need to address:
- Need for ongoing support & information
- A living will or power of attorney
- Review of finances/planning for future and end of life care
- Alternative Treatment
- There are concerns regarding alternative treatments in addition to physician-prescribed medicine. If any concerns are questions brought to attention, the physician should be notified.
- Aerobic and strengthening exercise might slow cognitive impairment in dementia has gained widespread popularity. Many studies describe plausible mechanisms using mammalian models, but there are fewer studies using human participants.[21]
- Some researchers consider exercise replacement for drugs to decrease the negative effect of dementia on cognitive function as memory, executive and physical function as strength, balance and endurance.[22]
- Effect on dementia have conflicted one review observed exercise has a positive effect on physical status not cognitive, while another review concluded aerobic exercise affects physical and cognitive functions.[23].
- Positive effects of exercise are increase of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), insulin-like growth factor-type I (IGF-1), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and homocysteine [15–23] that is enhance memory and executive function.[23]
- Music therapy treatment may enhance both psychological and physical by lowering stress levels, and reduction of plasma cortisol levels. some researcher measured salivary cortisol samples with moderate or severe dementia. limited number of studies explained effect of music therapy on dementia [24]
- Importance of Caregiver
- Many caregivers seek to meet the needs of the physician and the patient which increases rates of stress and depression. Physicians should continue to monitor the status of the caregivers watching out for burnout and providing them with resources as well.
Medications[edit | edit source]
Below is a list of some commonly used medications use in the treatments of the symptoms of Alzheimer's. There is also the use of other treatments such as antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, and estrogen replacement therapy in women to prevent or delay the onset of the disease.[25][26]
- Cholinesterase inhibitors e.g. donepezil
- Partial NMDA receptor antagonists
- Medications for behavioural symptoms
- Antidepressants
- Anxiolytics
- Antiparkinsonian (movement symptoms)
- Anticonvulsants/sedatives (behavioural)
- Recently Aduhelm (aducanumab) has been approved by the FDA, professed to reduce amyloid-beta plaque in people, however its efficacy and long-term benefits remain controversial.[5]
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
In the early and middle stages of AD, physical therapists can assist people stay mobile. This helps them maintain a degree of independence, and continue to perform their roles in the family and in the community.
Later as AD progresses physical therapists assist in keeping them able to perform daily activities for as long as possible, reducing the load on family members and caregivers. Physical therapists can perform a home assessment to ensure help the home is a safe environment and possibly delay the need for facility-based care.
- Physical activity is important to incorporate in a patient’s with Alzheimer’s disease life. Problems with balance and gait can often be lessened by regular physical therapy sessions, thereby reducing the risk of falls, fractures, and other injuries.[27][28]
- A community-based exercise program has been shown to improve multiple domains of life for individuals with Alzheimer's. Studies show that those participating in such exercise groups improved cognition, mobility, and instrumental activities of daily living[29]. See Preventing Dementia and Cognitive Decline
- Individuals with dementia are at an increased risk for falling compared to the average population of community-dwelling older adults. [30] A research study suggests that poor visual acuity resulted in poorer executive function, which further caused more inadequate balance control, thus demonstrating the importance of assessing executive functions besides vision and balance in older individuals living with Alzheimer's dementia.[31] See Falls and Dementia
- Group therapy is also successful with patients with Alzheimer's disease, but the session must not provide more stimulation than the patient is able to tolerate. Repetition and encouragement are also very important to help keep the patient's confidence high and to help with remembering the exercises.[32]
This 4 minute video outlines the role of Physiotherapy may play in AD.
Dietary Management[edit | edit source]
It has been found that maintaining a healthy diet may help to prevent or slow the progression of Alzheimer's. It is suggested that the diet be low in fat, high in omega-3 oils, and high in dark vegetables and fruits, also adding vitamin C to the diet along with coenzyme Q10, and folate may work to lower the risk of Alzheimer's. There does not seem to be one single aspect of diet that provides neuroprotection, rather than the items work together to decrease the risk of AD.[34]There is also some interest in the use of antioxidants such as vitamin E and ginkgo, along with anti-inflammatory agents, and estrogen replacement therapy for women.[35]
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- Pick's Disease
- Lewy Body Dementia
- Frontotemporal Dementia
- Dementia from multiple medications
- Other potentially reversible causes of dementia
Low Resource Health Settings[edit | edit source]
More than half of all people with dementia are from low and middle-income countries. Alzheimer’s disease, other dementias, and non-communicable diseases are expected to continue to be a burden on health systems throughout sub-Saharan Africa, as country populations age and communicable disease mortality and morbidity go down [36]. The number of people with Alzheimer's disease and dementia in general is estimated to increase far more rapidly in the upper middle, lower middle and low-income countries (LMICs) than in the high-income countries [37]. There is a general lack of awareness of the disease among the population, therefore patients don't seek for medical care and do not get the treatment they need. Hence, it is under-recognized, underdisclosed, undertreated, and undermanaged, particularly in LMICs[38]. The living environment also often poses little cognitive challenge because families may not understand their relative’s behavior [39]. Many of the cognitive and functional assessment tools used in LMICs were originally developed and validated in High Income Countries. There is a need to adapt it to be used more effectively in LMICs [40].
Resources[edit | edit source]
See also Category:Dementia
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Anand, R., Gill, K.D. and Mahdi, A.A. (2014) 'Therapeutics of Alzheimers disease: past, present and future', Neuropharmacology, 76, 27-50
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Ghiso J, Frangione B. Amyloidosis and Alzheimer’s disease. Advanced drug delivery reviews. 2002 Dec 7;54(12):1539-51.Available:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12453671/ (accessed 17.1.2023)
- ↑ Chen Ma, Fenfang Hong, and Shulong Yang Amyloidosis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathogeny, Etiology, and Related Therapeutic Directions Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8876037/ (accessed 16.1.2023)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Radiopedia Alzheimer disease Available:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/alzheimer-disease-1?lang=gb (accessed 16.1.2023)
- ↑ Hippius H, Neundörfer G. The discovery of Alzheimer's disease. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2003 Mar;5(1):101-8.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Zhou X, Ashford JW. Advances in screening instruments for Alzheimer's disease. Aging Medicine. 2019 Jun;2(2):88-93. Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6880670/ (accessed 16.1.2023)
- ↑ Dementia - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options [Internet]. YouTube. YouTube; 2014 [cited /06/2014]. Available from: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nLdLfmFzLSo/ref https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nLdLfmFzLSo
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Kumar A, Sidhu J, Goyal A, Tsao JW. Alzheimer disease. Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499922/ (accessed 16.1.2023)
- ↑ Alzheimer's & Dementia Testing Advances | Research Center [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr2]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/research/science/earlier_alzheimers_diagnosis.asp
- ↑ Alzheimer's and Dementia Causes, Risk Factors | Research Center [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/research/science/alzheimers_disease_causes.asp#apoe
- ↑ Alzheimer's and Dementia Causes, Risk Factors | Research Center [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/research/science/alzheimers_disease_causes.asp#apoe
- ↑ Latest Alzheimer's Facts and Figures [Internet]. Latest Facts; Figures Report | Alzheimer's Association. 2016 [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/facts/
- ↑ Kiddle Hippocampus Available from:https://kids.kiddle.co/Hippocampus (accessed 17.1.2023)
- ↑ Porth C. Pathopysiology Concepts of Altered Health States. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott and Wilkins; 2005.
- ↑ Stages of Alzheimer's Symptoms [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/alzheimers_disease_stages_of_alzheimers.asp
- ↑ Alzheimer's & Dementia Testing Advances | Research Center [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr3]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/research/science/earlier_alzheimers_diagnosis.asp
- ↑ Cedervall Y, Stenberg AM, Åhman HB, Giedraitis V, Tinmark F, Berglund L, Halvorsen K, Ingelsson M, Rosendahl E, Åberg AC. Timed Up-and-Go Dual-Task Testing in the Assessment of Cognitive Function: A Mixed Methods Observational Study for Development of the UDDGait Protocol. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2020 Jan;17(5):1715.
- ↑ Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.
- ↑ Medical Management and Patient Care [Internet]. Alzheimer's Association. [cited 2017Apr1]. Available from: http://www.alz.org/health-care-professionals/medical-management-patient-care.asp
- ↑ Lamb SE, Sheehan B, Atherton N, Nichols V, Collins H, Mistry D, Dosanjh S, Slowther AM, Khan I, Petrou S, Lall R; DAPA Trial Investigators. Dementia And Physical Activity (DAPA) trial of moderate to high intensity exercise training for people with dementia: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2018 May 16;361:k1675. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k1675. PMID: 29769247; PMCID: PMC5953238.
- ↑ Sanders, L. M. J., Hortobágyi, T., Karssemeijer, E. G. A., Van der Zee, E. A., Scherder, E. J. A., & van Heuvelen, M. J. G. (2020). Effects of low- and high-intensity physical exercise on physical and cognitive function in older persons with dementia: a randomized controlled trial. Alzheimer's research & therapy, 12(1), 28.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Lamb SE, Sheehan B, Atherton N, Nichols V, Collins H, Mistry D, Dosanjh S, Slowther AM, Khan I, Petrou S, Lall R; DAPA Trial Investigators. Dementia And Physical Activity (DAPA) trial of moderate to high intensity exercise training for people with dementia: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2018 May 16;361:k1675.
- ↑ Takahashi, T., & Matsushita, H. (2006). Long-term effects of music therapy on elderly with moderate/severe dementia. Journal of music therapy, 43(4), 317–333.
- ↑ Porth C. Pathopysiology Concepts of Altered Health States. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott and Wilkins; 2005.
- ↑ Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.
- ↑ Phillips, C. et al. "The Link Between Physical Activity And Cognitive Dysfunction In Alzheimer Disease". Physical Therapy 95.7 (2015): 1046-1060. Web. 1 Apr. 2017.
- ↑ Lin TW, Tsai SF, Kuo YM. Physical exercise enhances neuroplasticity and delays Alzheimer’s disease. Brain plasticity. 2018 Jan 1;4(1):95-110.
- ↑ Vreugdenhil, Anthea et al. "A Community-Based Exercise Programme To Improve Functional Ability In People With Alzheimer’S Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial". Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences 26.1 (2011): 12-19. Web. 1 Apr. 2017.
- ↑ Renfro M, Bainbridge D, Smith M. Validation of Evidence-Based Fall Prevention Programs for Adults with Intellectual and/or Developmental Disorders: A Modified Otago Exercise Program. Frontiers in Public Health. 2016;4. Web. 1 Apr. 2017.
- ↑ Hunter SW, Divine A, Madou E, Omana H, Hill KD, Johnson AM, Holmes JD, Wittich W. Executive function as a mediating factor between visual acuity and postural stability in cognitively healthy adults and adults with Alzheimer’s dementia. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2020 Apr 19:104078.
- ↑ Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.
- ↑ Pollom E, Little J. PT Management of Alzheimer's Disease [Internet]. YouTube. YouTube; 2017 [cited 2017Apr2]. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rW3rQ73rQFE&t=8s
- ↑ Goodman CC, Fuller KS. Pathology: implications for the physical therapist. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2015.
- ↑ Porth C. Pathopysiology Concepts of Altered Health States. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott and Wilkins; 2005.
- ↑ Mubangizi V, Maling S, Obua C, Tsai AC. Prevalence and correlates of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias in rural Uganda: cross-sectional, population-based study. BMC geriatrics. 2020 Dec;20(1):1-7.
- ↑ Global Prevalence. Available from:https://www.dementiastatistics.org/statistics/global-prevalence/( Accessed, 20/09/2021).
- ↑ Ferri CP, Jacob KS. Dementia in low-income and middle-income countries: different realities mandate tailored solutions. PLoS medicine. 2017 Mar 28;14(3):e1002271.
- ↑ George-Carey R, Adeloye D, Chan KY, Paul A, Kolčić I, Campbell H, Rudan I. An estimate of the prevalence of dementia in Africa: a systematic analysis. Journal of global health. 2012 Dec;2(2).
- ↑ Sexton C, Snyder HM, Chandrasekaran L, Worley S, Carrillo MC. Expanding Representation of Low and Middle Income Countries in Global Dementia Research: Commentary From the Alzheimer's Association. Frontiers in Neurology. 2021 Mar 15;12:271.