Spinal Nerves
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson and Ahmed M Diab
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that send motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the CNS and the body, and belong to the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Humans have 31 left–right pairs of spinal nerves, each roughly corresponding to a segment of the vertebral column: eight cervical spinal nerve pairs, 12 thoracic pairs , five lumbar pairs, five sacral pairs, and one coccygeal pair.[1]
The spinal nerves have a variable course, horizontal in the cervical region and increasingly oblique in an inferolateral direction as the spinal cord descends (due of the growth discordance between the spinal cord and the spine).[2]
Spinal nerves can be impacted by a variety injuries, and cause pain, weakness, or decreased sensation. eg A nerve entrapment occurs when there is pressure or compression of a spinal nerve, and it is the most common spinal nerve disorder; a nerve can be lacerated resulting in cessation of function.[3]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
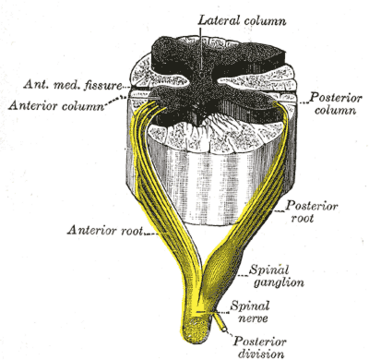
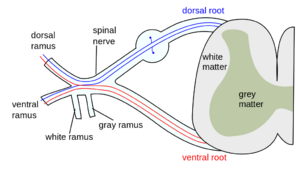
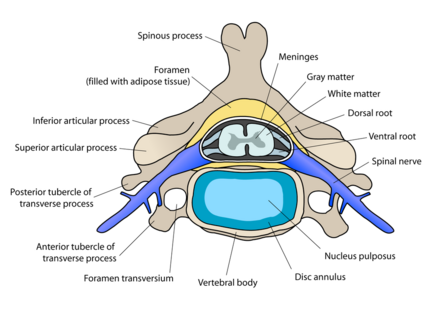
Near the spinal cord each spinal nerve branches into two roots.
- A sensory root containing sensory fibres, enters the spinal cord via the dorsal root; its cell bodies lie in a spinal ganglion that is outside the spinal cord.
- A motor root containing motor fibres, leaves the spinal cord via the ventral root; its cell bodies lie in specific areas of the spinal cord itself.[4]
Plexi[edit | edit source]
The spinal nerves form within a few centimeters of the spine on each side. Some groups of spinal nerves merge with each other to form a large plexus. Some spinal nerves divide into smaller branches, without forming a plexus.
A plexus is a group of nerves that combine with each other. There are five main plexi formed by the spinal nerves:
- Cervical Plexus
- Brachial Plexus
- Lumbar Plexus
- Sacral Plexus
- Coccygeal Plexus: Composed of the merging of nerves S4 through Co1, this plexus supplies motor and sensory control of the genitalia and the muscles that control defecation.[3]
Physiotherapy Relevance[edit | edit source]
Spinal nerves can be affected by a number of conditions. These situations can cause pain, sensory changes, and/or weakness. eg:
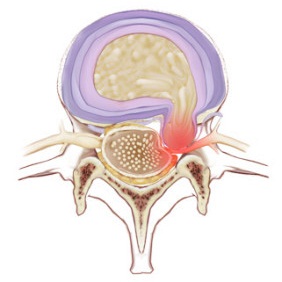
- Disc Herniation
- Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
- Guilliane Barre Disease
- Trauma eg falls, whiplash
- Multiple Sclerosis[3]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Lumen learning Spinal nerves Available: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-ap/chapter/spinal-nerves/(accessed 6.2.2022)
- ↑ Musculoskeletal key Spinal nerves Available: https://musculoskeletalkey.com/nerves-innervation-of-the-spine/(accessed 6.2.2022)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Very well health Spinal Nerves Available: https://www.verywellhealth.com/spinal-nerves-anatomy-4682599(accessed 6.2.2022)
- ↑ Britannica Spinal nerves Available: (accessed 6.2.2022)