Schizophrenia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editors '''- [[User:Meghan Shafer|Meghan Shafer]] from [[Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems|Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.]] | '''Original Editors '''- [[User:Meghan Shafer|Meghan Shafer]] from [[Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems|Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.]] | ||
''' | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Definition/Description | == Definition/Description == | ||
[[File:Cloth embroidery by schizophrenic.jpeg|thumb|Cloth embroidery by schizophrenic]] | |||
Schizophrenia is a psychiatric disorder that involves a range of [[Cognitive Impairments|cognitive]], behavioral, and [[Emotional Intelligence|emotional]] dysfunction. It is characterized by delusions (fixed false beliefs), hallucinations, disorganization, unusual behavior, and withdrawal. It usually begins during young adulthood. | |||
Schizophrenia is | * Schizophrenia is associated with alterations in the structure and function of the [[Brain Anatomy|brain]] and it is believed to be caused by [[Genetic Disorders|hereditary]], [[An Introduction to Environmental Physiotherapy|environmental]], and unknown factors.<ref name="APA" /> | ||
* It is possible to manage Schizophrenia with medication. | |||
* Symptoms often fluctuate throughout a person’s life, and may periodically require hospitalization, however many people who have schizophrenia are able to work and have satisfying relationships<ref name=":0">Very Well Health [https://www.verywellhealth.com/schizophrenia-5078641 Schizophrenia] Available:https://www.verywellhealth.com/schizophrenia-5078641 (accessed 19.3.2022)</ref>. | |||
== Etiology == | |||
[[File:Chromosome-DNA-gene copy.jpg|thumb|Chromosome-DNA-gene copy]] | |||
Genetics plays a fundamental role: there is a 46% concordance rate in monozygotic twins; 40% risk of developing schizophrenia if both parents are affected. | |||
[[ | Several studies postulate that the development of schizophrenia results from abnormalities in multiple [[neurotransmitters]], eg dopaminergic, serotonergic, and alpha-adrenergic hyperactivity or glutaminergic and GABA hypoactivity. | ||
== | The role of [[Substance Use Disorder|drug use]] and its contribution to schizophrenia has been suggested but it is often challenging to tease out to what degree drug use is a way to cope with the early effects of the condition before it is diagnosed or whether drug use contributes directly to schizophrenia.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1">Hany M, Rehman B, Azhar Y. Schizophrenia.[Updated 2020 Dec 8]. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2021.Available : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539864/ (accessed 19.3.20220</ref> | ||
== Epidemiology == | |||
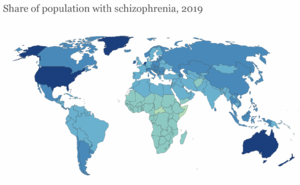
*It affects both males and females at an equal rate.<ref name="APA" /> | [[File:Schizophrenia epi.png|right|frameless]] | ||
*Average onset is in the late teens/early adult years. Males tend to start between the ages of 17-20. Women are generally diagnosed a little later in their twenties. <ref name="Kelly D">Kelly D. Treatment Considerations in Women with Schizophrenia. Journal of Women's Health. 2006; 15(10): 1132-1140.</ref> | Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population. <ref name="APA">American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV-TR. New York: APA; 2000.</ref> <ref name="Kelly D" /> | ||
*It affects both males and females at an equal rate.<ref name="APA" /> | |||
*Average onset is in the late teens/early adult years. Males tend to start between the ages of 17-20. Women are generally diagnosed a little later in their twenties. <ref name="Kelly D">Kelly D. Treatment Considerations in Women with Schizophrenia. Journal of Women's Health. 2006; 15(10): 1132-1140.</ref> | |||
*Childhood onset, before age 12, and late adulthood onset are not as common. <ref name="Foster et al.">Foster KA, Swartz L, Jager W. The Clinical Presentation of Childhood Onset Schizophrenia: A Literature Review. South African Journal of Psychology. 2006; 36(2): 299-318.</ref> | *Childhood onset, before age 12, and late adulthood onset are not as common. <ref name="Foster et al.">Foster KA, Swartz L, Jager W. The Clinical Presentation of Childhood Onset Schizophrenia: A Literature Review. South African Journal of Psychology. 2006; 36(2): 299-318.</ref> | ||
*The prevalence among older adults is slightly higher than in younger age groups.<ref>Folsom DP, Lebowitz BD, Lindamer LA, Palmer BW, Patterson TL, Jeste DV. Schizophrenia in late life: emerging issues. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience. 2022 Apr 1.</ref> | |||
== Characteristics/Clinical Presentation == | == Characteristics/Clinical Presentation == | ||
[[File:It's All In Your Head (2).png|right|frameless]] | |||
Schizophrenia can cause a variety of dysfunctions. A common feature is a lack of insight. It can be difficult for someone to recognize that they have the condition with family members, close friends, or coworkers identify the symptoms first. | |||
Schizophrenia usually begins when a person is in their 20’s, but it can start sooner during the teen years or later in adulthood. Symptoms can flare up, gradually becoming more severe over time. Loved ones etc may report eg agitation, neglect of personal hygiene, unusual appearance in the way a person dresses or grooms, withdrawal from others, delusional fear that others are conspiring or communicating in a secret way<ref name=":0" />. | |||
The diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) 6 is identified as the presence of two out of five (for at least six months) of the following: | |||
# Delusions | |||
# Auditory hallucinations | |||
# Catatonic symptoms | |||
# Negative symptoms (e.g. reduced emotional expression) | |||
# Disorganised speech<ref>Radiopedia Schizophrenia Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/schizophrenia (accessed 20.3.2022)</ref> | |||
== Associated Co-morbidities == | == Associated Co-morbidities == | ||
*Depression. <ref name="APA" / | *[[Depression]]. <ref name="APA" /> | ||
*Suicide risk. 50% of people with schizophrenia attempt suicide. <ref name="APA" /> | *Suicide risk. 50% of people with schizophrenia attempt suicide. <ref name="APA" /> | ||
*Diabetes Mellitus (as a result of the medication). <ref name="Sernyak et al.">Sernyak MJ, Leslie DL, Alarcon RD, Losonczy MF, Rosenbeck R. Association of Diabetes Mellitus with Use of Atypical Neuroleptics in the Treatment of Schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2002; 159(4): 561-566.</ref> | *[[Diabetes Mellitus Type 2|Diabetes Mellitus]] (as a result of the medication). <ref name="Sernyak et al.">Sernyak MJ, Leslie DL, Alarcon RD, Losonczy MF, Rosenbeck R. Association of Diabetes Mellitus with Use of Atypical Neuroleptics in the Treatment of Schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2002; 159(4): 561-566.</ref> | ||
*Attention Deficit Hyperactive | *[[Attention Deficit Disorders|Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder]] with childhood onset. <ref name="Foster et al." /> | ||
== Treatment / Management == | |||
A comprehensive plan required in the treatment of schizophrenia. It should include prescription antipsychotics, counseling, support from loved ones, and possibly hospitalization for flare-ups. There is no cure for the condition, but symptoms can be managed with treatment. | |||
The mainstay of treatment is antipsychotic medications; options vary between oral, as well as short or long acting IM therapy. Unfortunately antipsychotic therapy is not effective in the treatment of negative symptoms or cognitive dysfunction. | |||
[[Cognitive Behavioural Therapy|Cognitive behavioral therapy]] (CBT) and the use of art and drama therapies help counteract the negative symptoms of the disease, improve insight, and assist relapse prevention. | |||
If an organic cause for psychosis is identified, it must be treated accordingly. | |||
Treatment of co-existing disorders and with individual CBT ,family intervention and social support <ref>Soundy A, Freeman P, Stubbs B, Probst M, Vancampfort D. The value of social support to encourage people with schizophrenia to engage in physical activity: an international insight from specialist mental health physiotherapists. Journal of Mental Health. 2014 Oct 1;23(5):256-60.</ref>is advocated, although no long-term evidence exists regarding its efficacy in preventing a psychotic episode or reducing its severity<ref name=":0" />. | |||
< | == Physical Therapy Management == | ||
[[File:Physiotherapy Exercise and Physical Activity Image.png|thumb|Physical Activity]] | |||
Physical therapy can help manage any co-morbidities, side effects of medications, or help deal with the physical decline in function<ref>Stubbs B, Soundy A, Probst M, De Hert M, De Herdt A, Vancampfort D. Understanding the role of physiotherapists in schizophrenia: an international perspective from members of the International Organisation of Physical Therapists in Mental Health (IOPTMH). Journal of Mental Health. 2014 Jun 1;23(3):125-9</ref> as a part of multidisciplinary team MDT<ref>Andrew E, Briffa K, Waters F, Lee S, Fary R. Physiotherapists' views about providing physiotherapy services to people with severe and persistent mental illness: A mixed methods study. Journal of physiotherapy. 2019 Oct 1;65(4):222-9.</ref> . Physical therapy can also improve the patient's overall quality of life by increasing their mobility, strength, and independence in daily activities, which can positively impact their mental health.<ref>Probst M. Physiotherapy and mental health. Clinical physical therapy. 2017 May 31;230:59-68.</ref> It is important to incorporate physical therapy into the treatment plan for patients with Schizophrenia to address both their physical and mental health needs. | |||
A significant percentage of patients with schizophrenia die from cardiovascular disease, and diabetes affects 6% of people with schizophrenia. Educating patients on the importance of modifying risk factors such as increasing exercise, healthier diets, and smoking cessation will decrease their risk of cardiovascular problems and reduce the mortality rate.<ref name="Sernyak et al." /> <ref name=":1" />I | |||
In addition, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and medication management can help prevent and manage diabetes in patients with schizophrenia. This highlights the importance of addressing physical health concerns in addition to mental health treatment for individuals with schizophrenia. | |||
== Differential Diagnosis == | == Differential Diagnosis == | ||
*Differential diagnoses in children include: ADHD, conduct disorder, asperger's, borderline personality disorder, and childhood depression. <ref name="Foster et al." /> | *Differential diagnoses in children include: ADHD, conduct disorder, [[Asperger Syndrome|asperger's]], borderline personality disorder, and childhood depression. <ref name="Foster et al." /> | ||
*Differential diagnoses in adults include: bipolar disorder, depression, borderline personality disorder, mood disorders, schizoaffective disorder, | *Differential diagnoses in adults include: [[Bipolar Disorder|bipolar disorder]], depression, borderline personality disorder, mood disorders, schizoaffective disorder, schizophreniform, paranoia, and [[alcoholism]]. <ref name="Roberson C">Roberson C. Schizophrenia. The Alabama Nurse. August 2009: 6-8.</ref><ref name="APA" /> | ||
== Viewing == | |||
== | This 8 minute video outlines most aspects of Schizophrenia.{{#ev:youtube|PURvJV2SMso}}<ref>Schizophrenia-causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and pathology. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PURvJV2SMso</ref> | ||
< | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Bellarmine_Student_Project]] | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Mental Health]] | |||
[[Category:Mental Health - Conditions]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:49, 2 April 2023
Original Editors - Meghan Shafer from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.
Top Contributors - Meghan Shafer, Admin, Kim Jackson, Mariam Hashem, Lucinda hampton, Shaimaa Eldib, WikiSysop, 127.0.0.1, Elaine Lonnemann, Wendy Walker and Tolulope Adeniji
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
Schizophrenia is a psychiatric disorder that involves a range of cognitive, behavioral, and emotional dysfunction. It is characterized by delusions (fixed false beliefs), hallucinations, disorganization, unusual behavior, and withdrawal. It usually begins during young adulthood.
- Schizophrenia is associated with alterations in the structure and function of the brain and it is believed to be caused by hereditary, environmental, and unknown factors.[1]
- It is possible to manage Schizophrenia with medication.
- Symptoms often fluctuate throughout a person’s life, and may periodically require hospitalization, however many people who have schizophrenia are able to work and have satisfying relationships[2].
Etiology[edit | edit source]
Genetics plays a fundamental role: there is a 46% concordance rate in monozygotic twins; 40% risk of developing schizophrenia if both parents are affected.
Several studies postulate that the development of schizophrenia results from abnormalities in multiple neurotransmitters, eg dopaminergic, serotonergic, and alpha-adrenergic hyperactivity or glutaminergic and GABA hypoactivity.
The role of drug use and its contribution to schizophrenia has been suggested but it is often challenging to tease out to what degree drug use is a way to cope with the early effects of the condition before it is diagnosed or whether drug use contributes directly to schizophrenia.[2][3]
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the general population. [1] [4]
- It affects both males and females at an equal rate.[1]
- Average onset is in the late teens/early adult years. Males tend to start between the ages of 17-20. Women are generally diagnosed a little later in their twenties. [4]
- Childhood onset, before age 12, and late adulthood onset are not as common. [5]
- The prevalence among older adults is slightly higher than in younger age groups.[6]
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Schizophrenia can cause a variety of dysfunctions. A common feature is a lack of insight. It can be difficult for someone to recognize that they have the condition with family members, close friends, or coworkers identify the symptoms first.
Schizophrenia usually begins when a person is in their 20’s, but it can start sooner during the teen years or later in adulthood. Symptoms can flare up, gradually becoming more severe over time. Loved ones etc may report eg agitation, neglect of personal hygiene, unusual appearance in the way a person dresses or grooms, withdrawal from others, delusional fear that others are conspiring or communicating in a secret way[2].
The diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) 6 is identified as the presence of two out of five (for at least six months) of the following:
- Delusions
- Auditory hallucinations
- Catatonic symptoms
- Negative symptoms (e.g. reduced emotional expression)
- Disorganised speech[7]
Associated Co-morbidities[edit | edit source]
- Depression. [1]
- Suicide risk. 50% of people with schizophrenia attempt suicide. [1]
- Diabetes Mellitus (as a result of the medication). [8]
- Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder with childhood onset. [5]
Treatment / Management[edit | edit source]
A comprehensive plan required in the treatment of schizophrenia. It should include prescription antipsychotics, counseling, support from loved ones, and possibly hospitalization for flare-ups. There is no cure for the condition, but symptoms can be managed with treatment.
The mainstay of treatment is antipsychotic medications; options vary between oral, as well as short or long acting IM therapy. Unfortunately antipsychotic therapy is not effective in the treatment of negative symptoms or cognitive dysfunction.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and the use of art and drama therapies help counteract the negative symptoms of the disease, improve insight, and assist relapse prevention.
If an organic cause for psychosis is identified, it must be treated accordingly.
Treatment of co-existing disorders and with individual CBT ,family intervention and social support [9]is advocated, although no long-term evidence exists regarding its efficacy in preventing a psychotic episode or reducing its severity[2].
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
Physical therapy can help manage any co-morbidities, side effects of medications, or help deal with the physical decline in function[10] as a part of multidisciplinary team MDT[11] . Physical therapy can also improve the patient's overall quality of life by increasing their mobility, strength, and independence in daily activities, which can positively impact their mental health.[12] It is important to incorporate physical therapy into the treatment plan for patients with Schizophrenia to address both their physical and mental health needs.
A significant percentage of patients with schizophrenia die from cardiovascular disease, and diabetes affects 6% of people with schizophrenia. Educating patients on the importance of modifying risk factors such as increasing exercise, healthier diets, and smoking cessation will decrease their risk of cardiovascular problems and reduce the mortality rate.[8] [3]I
In addition, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and medication management can help prevent and manage diabetes in patients with schizophrenia. This highlights the importance of addressing physical health concerns in addition to mental health treatment for individuals with schizophrenia.
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- Differential diagnoses in children include: ADHD, conduct disorder, asperger's, borderline personality disorder, and childhood depression. [5]
- Differential diagnoses in adults include: bipolar disorder, depression, borderline personality disorder, mood disorders, schizoaffective disorder, schizophreniform, paranoia, and alcoholism. [13][1]
Viewing[edit | edit source]
This 8 minute video outlines most aspects of Schizophrenia.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV-TR. New York: APA; 2000.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Very Well Health Schizophrenia Available:https://www.verywellhealth.com/schizophrenia-5078641 (accessed 19.3.2022)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hany M, Rehman B, Azhar Y. Schizophrenia.[Updated 2020 Dec 8]. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2021.Available : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539864/ (accessed 19.3.20220
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kelly D. Treatment Considerations in Women with Schizophrenia. Journal of Women's Health. 2006; 15(10): 1132-1140.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Foster KA, Swartz L, Jager W. The Clinical Presentation of Childhood Onset Schizophrenia: A Literature Review. South African Journal of Psychology. 2006; 36(2): 299-318.
- ↑ Folsom DP, Lebowitz BD, Lindamer LA, Palmer BW, Patterson TL, Jeste DV. Schizophrenia in late life: emerging issues. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience. 2022 Apr 1.
- ↑ Radiopedia Schizophrenia Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/schizophrenia (accessed 20.3.2022)
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Sernyak MJ, Leslie DL, Alarcon RD, Losonczy MF, Rosenbeck R. Association of Diabetes Mellitus with Use of Atypical Neuroleptics in the Treatment of Schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2002; 159(4): 561-566.
- ↑ Soundy A, Freeman P, Stubbs B, Probst M, Vancampfort D. The value of social support to encourage people with schizophrenia to engage in physical activity: an international insight from specialist mental health physiotherapists. Journal of Mental Health. 2014 Oct 1;23(5):256-60.
- ↑ Stubbs B, Soundy A, Probst M, De Hert M, De Herdt A, Vancampfort D. Understanding the role of physiotherapists in schizophrenia: an international perspective from members of the International Organisation of Physical Therapists in Mental Health (IOPTMH). Journal of Mental Health. 2014 Jun 1;23(3):125-9
- ↑ Andrew E, Briffa K, Waters F, Lee S, Fary R. Physiotherapists' views about providing physiotherapy services to people with severe and persistent mental illness: A mixed methods study. Journal of physiotherapy. 2019 Oct 1;65(4):222-9.
- ↑ Probst M. Physiotherapy and mental health. Clinical physical therapy. 2017 May 31;230:59-68.
- ↑ Roberson C. Schizophrenia. The Alabama Nurse. August 2009: 6-8.
- ↑ Schizophrenia-causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and pathology. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PURvJV2SMso