Spinal Nerves: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[Brachial plexus|" to "[[Brachial Plexus|") |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
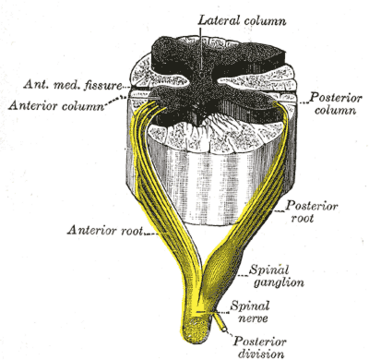
[[File:Spinal nerve formation.png|thumb|369x369px|Formation of spinal nerve from roots of spinal cord]] | [[File:Spinal nerve formation.png|thumb|369x369px|Formation of spinal nerve from roots of spinal cord]] | ||
Spinal [[Neurone|nerves]] are | Spinal [[Neurone|nerves]] are bundles of nerve fibers connected to the [[Spinal cord anatomy|spinal cord]] that carry information to and away from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves supply all the areas of the body except most head and neck region (see [[Cranial Nerves|cranial nerves]]) with a few exceptions eg [[Cervical Anatomy|neck muscles]] are supplied by the spinal nerves. | ||
Spinal [[Neurone|nerves]] are mixed nerves sending [[Motor Neurone|motor]], [[Sensation|sensory]], and autonomic signals between the [[Introduction to Neuroanatomy|CNS]] and the body and they belong to the peripheral nervous system (PNS).<ref name=":1">Lumen learning [https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-ap/chapter/spinal-nerves/ Spinal nerves] Available: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-ap/chapter/spinal-nerves/<nowiki/>(accessed 6.2.2022)</ref><ref name=":2">Musculoskeletal key Spinal nerves Available: https://musculoskeletalkey.com/nerves-innervation-of-the-spine/<nowiki/>(accessed 6.2.2022)</ref> | |||
Spinal nerves are essential for the control of body parts by the higher centres of the nervous system. | |||
* If the spinal nerve is cut, trapped, injured, or is involved in a disease process, the areas of the body supplied by that nerve escape the control of CNS. | |||
* If spinal nerves are impacted by injuries it will lose its functional ability and will cause pain, weakness and loss of sensation and may dies. eg A [[nerve entrapment]] occurs when there is pressure or compression of a spinal nerve, and it is the most common spinal nerve disorder; a [[Classification of Peripheral Nerve Injury|nerve can be lacerated]] resulting in cessation of function.<ref name=":0">Very well health Spinal Nerves Available: https://www.verywellhealth.com/spinal-nerves-anatomy-4682599<nowiki/>(accessed 6.2.2022)</ref> | |||
== Anatomy == | == Anatomy == | ||
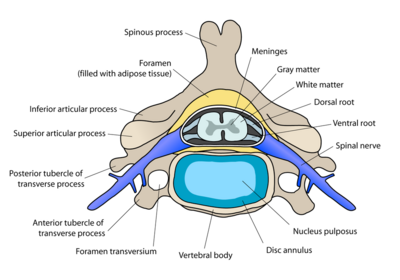
[[File: | Humans have 31 left–right pairs of spinal nerves, each roughly corresponding to a segment of the vertebral column: eight [[Cervical Anatomy|cervical]] spinal nerve pairs, 12 [[Thoracic Anatomy|thoracic]] pairs , five [[lumbar]] pairs, five [[Sacrum|sacral]] pairs, and one coccygeal pair.<ref>Brain made simple Spinal nerves Available: https://brainmadesimple.com/spinal-nerves/<nowiki/>(accessed 7.2.2022)</ref><ref name=":1" />.<ref name=":2" />[[File:Cervical spinal nerve.png|thumb|400x400px|Cervical vertebra, spinal nerve.|alt=]]Each spinal nerve is formed by the combination of nerve fibers from the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord. | ||
# | # The dorsal roots carry afferent sensory axons | ||
# The | # The ventral roots carry efferent motor axons. | ||
[[File: | The spinal nerve emerges from the spinal column through in the intervertebral foramen between adjacent vertebrae, where it is surrounded by the dura mater.<ref>Britannica Spinal nerves Available: (accessed 6.2.2022)</ref> | ||
Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve that contains afferent and efferent, somatic and autonomic fibers. | |||
== Rami == | |||
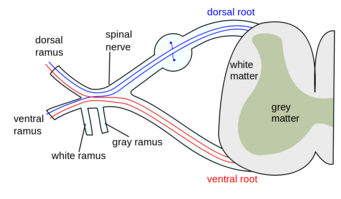
[[File:Spinal nerve.png|thumb|Spinal Nerve|alt=|341x341px]]Once outside the vertebral column, the nerve divides divides. | |||
# The Dorsal Ramus contains nerves that serve the dorsal portions of the trunk carrying visceral motor, somatic motor, and somatic sensory information to and from the [[skin]] and [[Back Muscles|muscles of the back]]. | |||
# The Ventral Ramus contains nerves that serve the remaining ventral parts of the trunk and the upper and lower limbs carrying visceral motor, somatic motor, and sensory information to and from the ventrolateral body surface, structures in the body wall, and the limbs. | |||
The meningeal branches branch from the spinal nerve to re-enter the intervertebral foramen to innervating the ligaments, dura, blood vessels, intervertebral discs, facet joints, and periosteum of the vertebrae.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
The spinal nerves have a variable course, horizontal in the cervical region and increasingly oblique in an inferolateral direction as the spinal cord descends (due of the growth discordance between the spinal cord and the spine). | |||
== Plexi == | |||
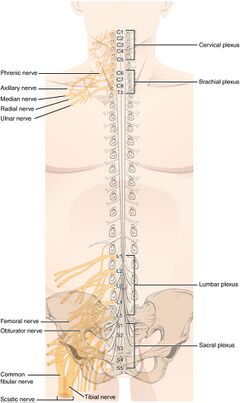
[[File:Spinal Nerve Plexuses.jpeg|thumb|404x404px|Spinal Nerve Plexi]] | |||
The spinal nerves form within a few centimeters of the spine on each side. Some groups of spinal nerves merge with each other to form a large plexus. Some spinal nerves divide into smaller branches, without forming a plexus. | The spinal nerves form within a few centimeters of the spine on each side. Some groups of spinal nerves merge with each other to form a large plexus. Some spinal nerves divide into smaller branches, without forming a plexus. | ||
A plexus is a group of nerves that combine with each other. There are five main plexi formed by the spinal nerves: | A plexus is a group of nerves that combine with each other. There are five main plexi formed by the spinal nerves: | ||
# [[Cervical Plexus]] | # [[Cervical Plexus|Cervical Plexus,]] provides nerve connections to the head, neck, and shoulder. | ||
# [[Brachial | # [[Brachial Plexus|Brachial Plexus,]] provides connections to the chest, shoulders, upper arms, forearms, and hands. | ||
# [[Lumbar Plexus]] | # [[Lumbar Plexus|Lumbar Plexus,]] provides connections to the back, abdomen, groin, thighs, knees, and calves. | ||
# [[Sacral Plexus]] | # [[Sacral Plexus]], provides connections for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg, the entire foot, and part of the pelvis. | ||
# Coccygeal Plexus: Composed of the merging of nerves S4 through Co1, this plexus supplies motor and sensory control of the genitalia and the muscles that control defecation.<ref name=":0" /> | # Coccygeal Plexus: Composed of the merging of nerves S4 through Co1, this plexus supplies motor and sensory control of the genitalia and the muscles that control defecation.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Physiotherapy Relevance == | == Physiotherapy Relevance == | ||
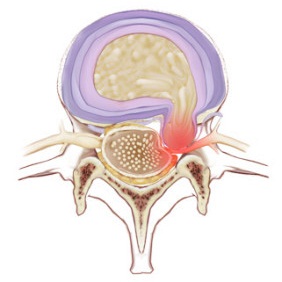
[[File:Disc extrusion.jpg|thumb|Disc Herniation]] | |||
Spinal nerves can be affected by a number of conditions. These situations can cause pain, sensory changes, and/or weakness. eg: | Spinal nerves can be affected by a number of conditions. These situations can cause pain, sensory changes, and/or weakness. eg: | ||
| Line 38: | Line 54: | ||
* [[Guillain-Barre Syndrome|Guilliane Barre Disease]] | * [[Guillain-Barre Syndrome|Guilliane Barre Disease]] | ||
* Trauma eg [[falls]], [[Whiplash Associated Disorders|whiplash]] | * Trauma eg [[falls]], [[Whiplash Associated Disorders|whiplash]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Neuropathies|Neuropathy]] | ||
*[[Oncology|Cancer]] in or near the spine can infiltrate/ compress the spinal nerves, causing dysfunction. eg [[Spinal Malignancy|Spinal malignancy]] <ref name=":0" /> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Nerves]] | |||
[[Category:Spinal Cord - Anatomy]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:00, 8 March 2024
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Ahmed M Diab and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Spinal nerves are bundles of nerve fibers connected to the spinal cord that carry information to and away from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves supply all the areas of the body except most head and neck region (see cranial nerves) with a few exceptions eg neck muscles are supplied by the spinal nerves.
Spinal nerves are mixed nerves sending motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the CNS and the body and they belong to the peripheral nervous system (PNS).[1][2]
Spinal nerves are essential for the control of body parts by the higher centres of the nervous system.
- If the spinal nerve is cut, trapped, injured, or is involved in a disease process, the areas of the body supplied by that nerve escape the control of CNS.
- If spinal nerves are impacted by injuries it will lose its functional ability and will cause pain, weakness and loss of sensation and may dies. eg A nerve entrapment occurs when there is pressure or compression of a spinal nerve, and it is the most common spinal nerve disorder; a nerve can be lacerated resulting in cessation of function.[3]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Humans have 31 left–right pairs of spinal nerves, each roughly corresponding to a segment of the vertebral column: eight cervical spinal nerve pairs, 12 thoracic pairs , five lumbar pairs, five sacral pairs, and one coccygeal pair.[4][1].[2]
Each spinal nerve is formed by the combination of nerve fibers from the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord.
- The dorsal roots carry afferent sensory axons
- The ventral roots carry efferent motor axons.
The spinal nerve emerges from the spinal column through in the intervertebral foramen between adjacent vertebrae, where it is surrounded by the dura mater.[5]
Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve that contains afferent and efferent, somatic and autonomic fibers.
Rami[edit | edit source]
Once outside the vertebral column, the nerve divides divides.
- The Dorsal Ramus contains nerves that serve the dorsal portions of the trunk carrying visceral motor, somatic motor, and somatic sensory information to and from the skin and muscles of the back.
- The Ventral Ramus contains nerves that serve the remaining ventral parts of the trunk and the upper and lower limbs carrying visceral motor, somatic motor, and sensory information to and from the ventrolateral body surface, structures in the body wall, and the limbs.
The meningeal branches branch from the spinal nerve to re-enter the intervertebral foramen to innervating the ligaments, dura, blood vessels, intervertebral discs, facet joints, and periosteum of the vertebrae.[1]
The spinal nerves have a variable course, horizontal in the cervical region and increasingly oblique in an inferolateral direction as the spinal cord descends (due of the growth discordance between the spinal cord and the spine).
Plexi[edit | edit source]
The spinal nerves form within a few centimeters of the spine on each side. Some groups of spinal nerves merge with each other to form a large plexus. Some spinal nerves divide into smaller branches, without forming a plexus.
A plexus is a group of nerves that combine with each other. There are five main plexi formed by the spinal nerves:
- Cervical Plexus, provides nerve connections to the head, neck, and shoulder.
- Brachial Plexus, provides connections to the chest, shoulders, upper arms, forearms, and hands.
- Lumbar Plexus, provides connections to the back, abdomen, groin, thighs, knees, and calves.
- Sacral Plexus, provides connections for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg, the entire foot, and part of the pelvis.
- Coccygeal Plexus: Composed of the merging of nerves S4 through Co1, this plexus supplies motor and sensory control of the genitalia and the muscles that control defecation.[3]
Physiotherapy Relevance[edit | edit source]
Spinal nerves can be affected by a number of conditions. These situations can cause pain, sensory changes, and/or weakness. eg:
- Disc Herniation
- Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
- Guilliane Barre Disease
- Trauma eg falls, whiplash
- Neuropathy
- Cancer in or near the spine can infiltrate/ compress the spinal nerves, causing dysfunction. eg Spinal malignancy [3]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Lumen learning Spinal nerves Available: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-ap/chapter/spinal-nerves/(accessed 6.2.2022)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Musculoskeletal key Spinal nerves Available: https://musculoskeletalkey.com/nerves-innervation-of-the-spine/(accessed 6.2.2022)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Very well health Spinal Nerves Available: https://www.verywellhealth.com/spinal-nerves-anatomy-4682599(accessed 6.2.2022)
- ↑ Brain made simple Spinal nerves Available: https://brainmadesimple.com/spinal-nerves/(accessed 7.2.2022)
- ↑ Britannica Spinal nerves Available: (accessed 6.2.2022)