Breathing Exercises
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Prashna Singh, Stella Constantinides, Robin Amel, Kim Jackson and Samuel Winter
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Breathing exercises are a form of exercise that can be used for a variety of health related reasons.eg: to enhance the respiratory system by improving ventilation; strengthening respiratory muscles; make breathing more efficient; and for stress reduction.[1][2].
Improper breathing can upset the oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange and contribute to anxiety, panic attacks, fatigue, and other physical and emotional disturbances.[3]
Deep Breathing[edit | edit source]
Deep breathing helps to relieve shortness of breath by preventing air from getting trapped in the lungs and helps inhalation of more fresh air into base of lungs. It may help help client to feel more relaxed and centered.
Technique:
- While standing or sitting, draw elbows back slightly to allow your chest to expand.
- Take a deep inhalation through the nose.
- Retain your breath for a count of 5.
- Slowly release your breath by exhaling through the nose[4].
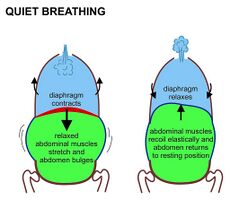
Diaphragmatic Breathing[edit | edit source]
Diaphragmatic breathing is a type of breathing exercise that helps strengthen the diaphragm, an important muscle that helps with breathing, as it represents 80% of breathing. Diaphragmatic exercises help to make people feel relaxed and rested.
This breathing exercise is also sometimes called belly breathing or abdominal breathing[5].
Pursed Lips Breathing[edit | edit source]
Pursed-lip breathing is a breathing technique that consists of exhaling through tightly pressed (pursed) lips and inhaling through the nose with the mouth closed. It is a simple breathing technique that helps with making deep breaths slower and more intentional. This technique has been found to benefit people who have anxiety associated lung conditions eg emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)[6]
Box Breathing[edit | edit source]
Box breathing can be helpful with relaxation. Box breathing is a breathing exercise to assist patients with stress management and can be implemented before, during, and/or after stressful experiences. Box breathing involves visualizing a journey around the four sides of a square, pausing while travelling horizontally and breathing in while travelling up the square and out while travelling down it. This exercise can be implemented in many environments, not requiring a calm environment to be effective.
- Step One: Breathe in through the nose for a count of 4.
- Step Two: Hold breath for a count of 4.
- Step Three: Breath out for a count of 4.
- Step Four: Hold breath for a count of 4.
- Repeat[7]
Pranayama[edit | edit source]
Pranayama is used as a technical term in yoga, it is often translated more specifically as "breath control".
Traditional pranayama was based on various aspects of physical and spiritual well being, practised from a seated position. In the modern world where everyone is at their desks for long durations proceeding with pranayama in motion is a good option, and has adaptions for this.
See Pranayama
Mindful Breathing[edit | edit source]
Mindfulness meditation involves focusing on your breathing and bringing attention to the present without allowing your mind to drift off to the past or future.
- A calming focus is chosen, including a sound ("om"), positive word ("peace"), or phrase ("breathe in calm, breathe out tension") to repeat silently as client inhales or exhales.
- The mind and body then let go and relax.
- When client notices the mind has drifted, they take a deep breath and gently return attention to the present.
Active Cycle of Breathing Techniques[edit | edit source]
The Active Cycle of Breathing Techniques (ACBT) is an active breathing technique performed by the patient and can be used to mobilize and clear excess pulmonary secretions and to generally improve lung function. Once ACBT has been taught, the patient can be encouraged to use it independently without the supervision of a physiotherapist. This exercise does not require the use of any special equipment.
Research Findings[edit | edit source]
Breathing affects all body systems; these systems in turn influence breathing. Optimal breathing patterns help to maintain homeostasis, but when breathing is disrupted, significant issues can arise.
Examples of how breathing can help in health outcomes shown below:
- Breathing exercises can improve pulmonary function, respiratory muscle strength, exercise capacity, dyspnea, and health-related quality of life in patients with COPD[8].
- Evidence suggests that diaphragmatic breathing may decrease stress as measured by physiologic biomarkers, as well psychological self-report tools[9]
- Evidence exists to support the use of breathing exercises in the treatment of chronic, nonspecific low back pain.[10]
- Breathing-based meditation decreases posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms in U.S. military veterans.[11]
- The way of breathing decisively influences autonomic and pain processing. Deep slow breathing in concert with relaxation are essential feature in the modulation of sympathetic arousal and pain perception. Thus can be useful in chronic pain management.[12]
- Breathing exercises for adults with asthma may have some positive effects on quality of life, hyperventilation symptoms, and lung function[13].
See The Science of Breathing Well
Give clients time to experiment with different types of breathing techniques, choosing appropriately.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Medical dictionary Breathing exercises Available: https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/breathing+exercise (accessed 11.3.2022)
- ↑ Lung Org Breathing exercises Available:https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/wellness/breathing-exercises (accessed 11.3.2022)
- ↑ Paulus MP. The breathing conundrum—interoceptive sensitivity and anxiety. Depression and anxiety. 2013 Apr;30(4):315-20.Available: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/da.22076(accessed 3.11.2022)
- ↑ Healthline 10 Breathing Techniques for Stress Relief and More Available:https://www.healthline.com/health/breathing-exercise (accessed 12.3.2022)
- ↑ Physiopedia Diaphragmatic breathing.
- ↑ Very well health 8 Deep Breathing Exercises for Anxiety Available: https://www.verywellmind.com/abdominal-breathing-2584115#citation-11 (accessed 11.3.2022)
- ↑ Norelli SK, Long A, Krepps JM. Relaxation Techniques.[Updated 2021 Jul 26]. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2021. Available;https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513238/ (accessed 11.3.2022)
- ↑ Lu Y, Li P, Li N, Wang Z, Li J, Liu X, Wu W. Effects of home-based breathing exercises in subjects with COPD. Respiratory care. 2020 Mar 1;65(3):377-87. Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31719191/(accessed 12.2.2022)
- ↑ Hopper SI, Murray SL, Ferrara LR, Singleton JK. Effectiveness of diaphragmatic breathing for reducing physiological and psychological stress in adults: a quantitative systematic review. JBI Evidence Synthesis. 2019 Sep 1;17(9):1855-76. Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31436595/(accessed 12.3.2022)
- ↑ Anderson BE, Bliven KC. The use of breathing exercises in the treatment of chronic, nonspecific low back pain. Journal of sport rehabilitation. 2017 Sep 1;26(5):452-8. Available: https://journals.humankinetics.com/view/journals/jsr/26/5/article-p452.xml(accessed 12.3.2022)
- ↑ Seppälä EM, Nitschke JB, Tudorascu DL, Hayes A, Goldstein MR, Nguyen DT, Perlman D, Davidson RJ. Breathing‐based meditation decreases posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms in US Military veterans: A randomized controlled longitudinal study. Journal of traumatic stress. 2014 Aug;27(4):397-405. Available:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25158633/ (accessed 12.3.2022)
- ↑ Busch V, Magerl W, Kern U, Haas J, Hajak G, Eichhammer P. The effect of deep and slow breathing on pain perception, autonomic activity, and mood processing—an experimental study. Pain Medicine. 2012 Feb 1;13(2):215-28. Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21939499/(accessed 12.3.2022)
- ↑ Santino TA, Chaves GS, Freitas DA, Fregonezi GA, Mendonça KM. Breathing exercises for adults with asthma. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020(3). Available:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32212422/ (accessed 12.3.2022)