Supraspinatus Tear: Difference between revisions
Leana Louw (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Definition/Description == | |||
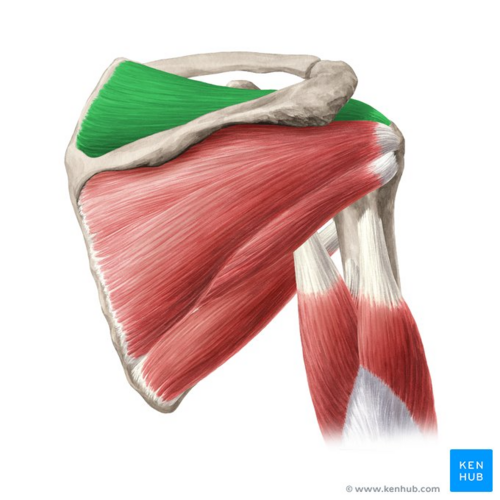
[[File:Supraspinatus muscle - Kenhub.png|alt=Supraspinatus muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view|right|frameless|500x500px|Supraspinatus muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view]] | |||
A supraspinatus tear is a tear or rupture of the tendon of the [[supraspinatus]] muscle. The supraspinatus is part of the [[Rotator Cuff|rotator cuff]] of the shoulder. Most of the time, it is accompanied by another [[Rotator Cuff Tears|rotator cuff muscle tear]]. This can occur due to trauma or repeated micro-trauma and present as a partial or full-thickness tear.<ref name=":0">American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons, Ortho Info. Rotator cuff tears, http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=a00064 (accessed 29/08/2018).</ref> Quite often, the tear occurs in the tendon or as an avulsion from the greater tuberosity.<ref name=":6">Benazzo F, Marullo M, Pietrobono L. [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10195-013-0271-x Supraspinatus rupture at the musculotendinous junction in a young woman.] Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology 2014;15(3):231-4.</ref> | |||
Image: Supraspinatus muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view<ref >Supraspinatus muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view image - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/supraspinatus-muscle</ref> | |||
== Clinical | == Clinical Relevant Anatomy == | ||
The [[Shoulder|shoulder joint]] is made up of three bones: the [[humerus]], [[scapula]] and clavicle. The head of the humerus and the glenoid of the scapula form a ball-and-socket joint<ref name=":0" />. The supraspinatus muscle is located on the back of the shoulder, forming part of the [[Rotator Cuff|rotator cuff]]. The rotator cuff consists of [[Supraspinatus|Supraspinatus,]] [[Infraspinatus]], [[Subscapularis]] and [[Teres Minor|teres minor]]. The rotator cuff covers the head of the humerus and keeps it in place. These muscles help to lift and rotate the arm. Visit the [[shoulder]] for more detailed information. | |||
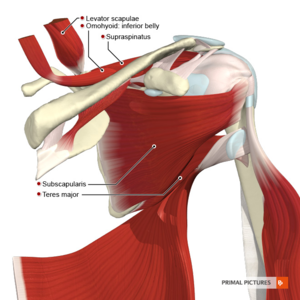
The [[Shoulder|shoulder joint]] is made up of three bones: the [[humerus]], [[scapula]] and clavicle. The head of humerus and glenoid of the scapula form a ball-and-socket joint<ref name=":0" />. The supraspinatus muscle is located on the back of the shoulder, forming part of the [[Rotator Cuff|rotator cuff]]. The rotator cuff consists of [[Supraspinatus]] | [[File:Muscles of the scapular region anterior aspect Primal.png|thumb]] | ||
=== Supraspinatus === | === Supraspinatus === | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* '''Insertion''': Greater tubercle of the humerus | * '''Insertion''': Greater tubercle of the humerus | ||
* '''Innervation''': Supraspinatus nerve (C5-C6) | * '''Innervation''': Supraspinatus nerve (C5-C6) | ||
* '''Function''': Abduction of the glenohumeral joint; assists the rotator cuff in stabilizing, control and movement the shoulder; assists in preventing | * '''Function''': Abduction of the glenohumeral joint; assists the rotator cuff in stabilizing, control and movement the shoulder; assists in preventing subluxation at the shoulder | ||
<ref name=":0" /><ref>Schünke M, Schulte E, Schumacher U, Voll M, Wesker K. Prometheus: Algemene anatomie en bewegingsapparaat, 2010. p600.</ref><ref>Physioworks, Rotator Cuff Tear.http://physioworks.com.au/injuries-conditions-1/rotator-cuff-tears (accessed 29/08/2018).</ref> <u></u> | <ref name=":0" /><ref>Schünke M, Schulte E, Schumacher U, Voll M, Wesker K. Prometheus: Algemene anatomie en bewegingsapparaat, 2010. p600.</ref><ref>Physioworks, Rotator Cuff Tear.http://physioworks.com.au/injuries-conditions-1/rotator-cuff-tears (accessed 29/08/2018).</ref> <u></u> | ||
== Epidemiology/ | == Epidemiology/Aetiology == | ||
The | The aetiology of supraspinatus tears is multifactorial, consisting of age-related degeneration, microtrauma, and macrotrauma. It mostly affects the dominant arm with about 50% of people in their 80s experiencing this condition. <ref name=":10">Tashjian RZ. [https://www.sportsmed.theclinics.com/article/S0278-5919(12)00044-0/abstract Epidemiology, natural history and indications for treatment of rotator cuff tears]. Clinics in Sports Medicine 2012:31(4):589-604.</ref><ref name=":11">Yamamoto A, Takagishi K, Osawa T, Yanagawa T, Nakajima D, Shitara H, Kobayashi T. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1058274609002043 Prevalence and risk factors of a rotator cuff tear in the general population.] Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery 2010:19(1):116-20.</ref> Injury and degeneration are the two main causes of rotator cuff tears. Rotator cuff tears are associated with older patients, those with a history of trauma and mostly affect the dominant arm. | ||
=== Mechanism of | === Mechanism of Injury === | ||
Acute tear: Can occur with other shoulder injuries (e.g. clavicle fracture of [[Shoulder Dislocation|shoulder dislocation]]) | |||
* Fall on an outstretched arm | |||
* | * Lifting something too heavy | ||
Degenerative: Wear and tear of the tendon slowly over time | |||
* Increases with the age | |||
* More common in the dominant arm | |||
* When you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, you have a greater risk for a tear in the opposite shoulder, even if you have no pain in the opposite shoulder. | |||
=== Risk Factors === | |||
=== Risk | |||
* > 40 years old | * > 40 years old | ||
* Male > Female | * Male > Female | ||
| Line 45: | Line 44: | ||
* Lack of blood supply | * Lack of blood supply | ||
* Bony spurs | * Bony spurs | ||
* Overhead activities and other people who do overhead work: | * Overhead activities and other people who do overhead work: Tennis players, Baseball pitchers, Painters, Carpenters, and Plumbers. | ||
* Traumatic injury e.g. fall (more common cause in younger individuals)<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Characteristics/Clinical presentation == | |||
Supraspinatus tears are normally present as partial or full-thickness tears. It can be asymptomatic or symptomatic. | |||
'''Partial thickness''': | |||
* Traumatic injury e.g. fall (more common cause in younger individuals) | * Incomplete disruption of muscle fibres<ref name=":0" /> | ||
<ref name=":0" /> | * Can progress to complete tear - Increasing pain is normally the first sign of the progression of a tear | ||
'''Full thickness''': Complete disruption of muscle fibres | |||
* Large tears (1-1,5cm) have a high rate of progression | |||
* If progression is suspected in conservatively managed cases - further investigation is warranted | |||
* Smaller tears (<1cm) progress slower | |||
<ref name=":10" /><ref name=":11" /> | |||
=== Signs and Symptoms === | |||
Patients normally present with:<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":11" /><ref name=":13">Mayo Clinic Rotator cuff injury. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rotator-cuff-injury/symptoms-causes/dxc-20126923 (accessed 30/08/2018).</ref> | |||
* Pain/worsening pain (in cases where tears are progressing), the most common symptoms are: | |||
:* Pain when lifting and lowering your arm or with specific movement | |||
:* Pain at rest | |||
:* Pain at night, predominantly when you lie on the affected shoulder | |||
:* Traumatic tears: Sudden, intense pain often accompanied by a snapping sensation and immediate weakness in the upper arm | |||
:* Located anterolaterally and superiorly | |||
:* Referred to the level of the [[deltoid]] insertion with full-thickness tears | |||
:* Repetitive strain tear: Starts off mild and only when lifting your arm; over time the pain can become more noticeable at rest | |||
:* Aggravated in overhead or forward-flexed position | |||
* Limited range of motion | |||
:* Reduced forward elevation, external rotation and abduction | |||
:* Struggle with activities like reaching behind back, combing hair and overhead activities | |||
:* Stiffness | |||
* Weakness when rotating or lifting your arm | * Weakness when rotating or lifting your arm | ||
* Crepitus, Clicking, and Instability | |||
=== Differential | === Differential Diagnosis === | ||
* [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Acromioclavicular_Joint_Disorders Acromioclavicular | * [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Acromioclavicular_Joint_Disorders Acromioclavicular joint injury] | ||
* [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Brachial_plexus_injury Brachial | * [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Brachial_plexus_injury Brachial plexus injury] | ||
* Bicipital | * Bicipital tendinopathy | ||
* [[Cervical Radiculopathy]] | * [[Cervical Radiculopathy|Cervical radiculopathy]] | ||
* Cervical | * Cervical spine sprain | ||
* Cervical | * Cervical strain injuries | ||
* [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Disc_Herniation Cervical | * [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Disc_Herniation Cervical disc injuries] | ||
* [[Cervical Radiculopathy|Cervical | * [[Cervical Radiculopathy|Cervical nerve root injury]] | ||
* [[Cervical Spondylosis]] | * [[Cervical Spondylosis]] | ||
* Cervical | * Cervical discogenic pain syndrome | ||
* [[Clavicula fracture|Clavicular | * [[Clavicula fracture|Clavicular fracture]] | ||
* [[Sternoclavicular Joint Disorders]] | * [[Sternoclavicular Joint Disorders|Sternoclavicular joint disorders]] | ||
* Infraspinatus | * Infraspinatus syndrome | ||
* Contusions | * Contusions | ||
* [[Rotator Cuff Tears|Rotator | * [[Rotator Cuff Tears|Rotator cuff tear]] | ||
* [[Shoulder Dislocation]] | * [[Shoulder Dislocation|Shoulder dislocation]] | ||
* [[Myofascial pain|Myofascial | * [[Myofascial pain|Myofascial pain]] | ||
* [[Internal Impingement of the Shoulder|Shoulder | * [[Internal Impingement of the Shoulder|Shoulder impingement syndrome]] | ||
* [[SLAP Lesion|Superior | * [[SLAP Lesion|Superior labrum lesions]] | ||
* [[Shoulder | * [[Shoulder Subluxation|Shoulder subluxation]] | ||
* Angina | * Angina pectoris | ||
* [[Myocardial Infarction]] | * [[Myocardial Infarction|Myocardial infarction]] | ||
* [[Subacromial Impingement]] | * [[Subacromial Impingement|Subacromial impingement]] | ||
* [[Osteoarthritis]] | * [[Osteoarthritis]] | ||
* [[Rheumatoid Arthritis]] | * [[Rheumatoid Arthritis|Rheumatoid arthritis]] | ||
* Subscapular | * Subscapular nerve entrapment | ||
* [[Shoulder Instability]] | * [[Shoulder Instability|Shoulder instability]] | ||
** [[Anterior Shoulder Instability|Anterior | ** [[Anterior Shoulder Instability|Anterior instability]] | ||
** [[Posterior Shoulder Instability|Posterior | ** [[Posterior Shoulder Instability|Posterior instability]] | ||
<ref name=":1">Medscape. Supraspinatus tendonitis: Differential diagnoses, http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/93095-differential (Accessed 20/03/2015).</ref><ref name=":2">Medscape. Rotator cuff injury: Differential diagnoses, http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/92814-differential, (Accessed 25/03/2015).</ref> | |||
== Diagnostic | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
=== Physical Examination === | |||
=== | ==== Subjective interview: ==== | ||
* Duration of | * Onset: Spontaneous or after injury | ||
* Pain | * Duration of pain | ||
* Night | * Pain provocation/aggravating factors | ||
* Night rest | |||
* Same problems in the past? | * Same problems in the past? | ||
* Activity limitations | |||
* Localize pain | |||
* Past medical history | |||
* Recreational or sport activities (possible overhead activities) | |||
=== | ==== Observation: ==== | ||
* | ** Any atrophy present | ||
* | |||
=== | ==== Range of motion: ==== | ||
* | * Expect reductions in flexion, abduction and external rotation | ||
* If passive abduction range is more than active range, it is an indication of a rotator cuff tear | |||
== | ==== Muscle power: ==== | ||
* Test supraspinatus by resisting abduction at 90° and internal rotation | |||
* Scapular movement may be affected | |||
==== Palpation: ==== | |||
* Forearm behind back to palpate rotator cuff just anterior and below the acromion | |||
** Muscle atrophy present | |||
** Tenderness | |||
< | ==== Special tests: ==== | ||
</ref>< | * Drop-arm test: Active shoulder abduction to 90°, then return <ref name=":4">Hughers PC, Taylor NF, Green RA. [https://ac.els-cdn.com/S0004951408700229/1-s2.0-S0004951408700229-main.pdf?_tid=8b887d9e-8135-4347-a25d-3c50c63efd54&acdnat=1535600075_4f552aaa403df67a5cac32ef4184113d Most clinical tests cannot accurately diagnose rotator cuff pathology: a systematic review.] Aust J Physiother 2008;54(3):159-70.</ref> | ||
** Positive: Dropping the arm down with pain indicates a positive test | |||
{{#ev:youtube|6AUlMbdzaDE}} | |||
<clinicallyrelevant id="83864746" title="Drop Arm Test" /><br> | |||
:* Jobe/supraspinatus/empty can test: Resist shoulder abduction and internal rotation<ref name=":4" /> | |||
:** Positive: Pain/weakness | |||
{{#ev:youtube|nSlrWoCfs4w}} | |||
<clinicallyrelevant id="83864751" title="Empty Can Test" /> | |||
:* Full can test: Resisted shoulder abduction in external rotation | |||
:** Positive: Pain/weakness | |||
{{#ev:youtube|05TCh3VXMOU}} | |||
<clinicallyrelevant id="83864778" title="Full Can Test" /> | |||
:* Subacromial grind test: Patient standing and examiner standing facing the patient, the examiner grasps the patient's flexed elbow. The shoulder is passively abducted in the scapular plane to 90°. The examiner's other hand is placed over the patient's shoulder overlying the anterior acromion and greater tuberosity. The examiner passively internally and externally rotates the shoulder detecting the presence of palpable crepitus. | |||
:** Positive: Palpable crepitus.<ref name=":12">Sawalha S, Fischer J. The accuracy of “subacromial grind test” in diagnosis of supraspinatus rotator cuff tears. International journal of shoulder surgery 2015;9(2):43-46.</ref> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|f5yOT2hpTac}} | |||
<ref>Walters J, editor. Orthopaedics - A guide for practitioners. 4th Edition. Cape Town: University of Cape Town, 2010.</ref><ref name=":5">Orthop J. Rotator cuff tear: physical examination and conservative treatment. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tohoku University, 2013:197–204.</ref> | |||
== | === Special Investigations === | ||
=== X-rays === | |||
* Excluding sclerosis and osteophyte formation on the acromion | |||
* [[X-Rays|X-ray]]s measure the size of the subacromial space | |||
* Unable to see the tendon | |||
[[File:Tear of supraspinatus tendon.png|thumb|Supraspinatus tear as seen in radiographics]] | |||
==== MRI ==== | |||
* [[MRI Scans|MRI]] Scan shows partial or full tears in the tendons of the rotator cuff, inflammation to weak structures and cracks in the capsule | |||
== | ==== CT Scan ==== | ||
* [[CT Scans|CT scan]] is able to localize tendon when patient positioned with forearm behind the back | |||
==== Ultrasound ==== | |||
* '''[[Ultrasound Scans|Ultrasound]] helps in''' localising tendon | |||
== Outcome Measures == | |||
* [[36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36)|Short Form-36]] (SF-36) | |||
* Rotator Cuff Quality of Life (RC-QOL) scale | |||
* [[Western Ontario Rotator Cuff (WORC) Index|Western Ontario Rotator Cuff (WORC) index]] | |||
* [https://www.physio-pedia.com/DASH_Outcome_Measure Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH)]<ref name=":0" /><sup></sup><u></u><sup></sup> | |||
== Medical Management == | |||
=== Conservative Management === | |||
Indications:<ref name=":10" /><ref name=":11" /> | |||
* Older (>70 years) patients with a chronic tear | |||
* Patients with irreparable tears with irreversible changes | |||
* Patients of any age with small (<1 cm) full-thickness tears | |||
** As a result of the slow rate of progression of these tears | |||
* Patients without a full-thickness tear | |||
Management includes:<ref>Björkenheim JM, Paavolainen P, Ahovuo J, Slätis P. [https://europepmc.org/abstract/med/3180567 Surgical repair of the rotator cuff and surrounding tissues. Factors influencing the results.] Clinical orthopaedics and related research 1988;(236):148-53.</ref> | |||
NSAID's: | |||
* Ibuprofen | |||
Corticosteroid injections: | |||
* Eliminate pain for a period of time, making physiotherapy management easier | |||
* Tendon tissue can be weakened by these injections (which would have an adverse effect on the outcome of a possible surgery) | |||
* Limited to 2 injections | |||
* Physiotherapy (see Physiotherapy management below) | |||
< | === Surgical Management === | ||
'''Indications''':<ref name=":10" /><ref name=":11" /><ref name=":3" /> | |||
* Failed conservative management | |||
* Larger symptomatic full-thickness tears (1-1,5cm) as a result of the high rate of progression. Should be considered for earlier surgical repair in younger patients if the tear is repairable and the muscle degeneration is limited | |||
* Acute large tears (>1 cm-1.5 cm) or | |||
* Young patients with full-thickness tears who have a significant risk for the development of irreparable rotator cuff changes | |||
* Complete tear with significant pain and dysfunction after 6 months of treatment | |||
* Repeated dislocations | |||
=== | ==== Rotator cuff repair ==== | ||
Most repairs are done arthroscopically<ref name=":3">Millar NL, Wu X, Tantau R, Silverstone E, Murrell GA. Open versus two forms of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 2009;467(4):966-78.</ref>. Severity (partial vs full-thickness) will determine the approach. | |||
* | * Partial repair: The tendon and surrounding bone will be smoothed to avoid further damage and therefore allowing the tendon to heal mostly on its own<ref>American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/rotator-cuff-tears-surgical-treatment-options/ (accessed 30/08/2018).</ref> | ||
</ref> | |||
* Complete tear: Tear in middle of tendon: Suture the two parts of the tendon back together. Tear close or on its point of attachment on the head of the humerus: Attach the tendon back to its original place by an anchor (sometimes two). This anchor actually consists of a small screw that is bored into the head of the humerus with on the back surgical wires which hold the tendon in place<ref>Akpınar S, Uysal M, Pourbagher MA, Ozalay M, Cesur N, Hersekli MA. [https://europepmc.org/abstract/med/21908964 Prospective evaluation of the functional and anatomical results of arthroscopic repair in small and medium-sized full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus tendon.] Acta orthopaedica et traumatologica turcica 2011;45(4):248-53.</ref>. | |||
== Physiotherapy Management == | |||
Physiotherapy management depends on the extent of the tear, and plays in important role in both conservative management as well as post-surgical rehabilitation. More details can also be obtained from the [[Rotator Cuff Tears|rotator cuff]] page. | |||
=== Conservative Management === | |||
'''Physiotherapy goals''': | |||
* Improve pain together with NSAID’s (2-6 weeks) | |||
* [[Cryotherapy]] (only in first 48 hours) | |||
* [[Massage]] | |||
* Improve circulation (to control inflammation and speed up the healing process) | |||
* Improve range of motion: | |||
** [[Stretching]] (careful with timing, as stretching of acute injury may aggravate the tear):<ref name=":8">Kuhn JE. [http://kinesiologiarcb.com.ar/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Exercise-in-the-treatment-of-rotator-cuff-impingement-A-systematic-review-and-a-synthesized-evidence-based-rehabilitation-protocol.pdf Exercise in the treatment of rotator cuff impingement: a systematic review and a synthesized evidence-based rehabilitation protocol.] Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery 2009;18(1):138-60. | |||
</ref> | |||
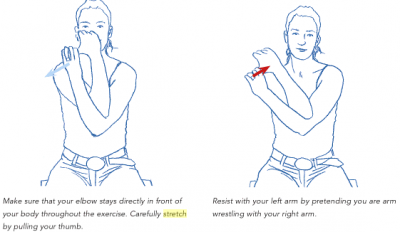
*** Crossover arm stretch: 12 seconds, 5 times a day; 5-6days/week | |||
[[Image:4.png|400x400px]] | |||
''Kristian Berg. Prescriptive stretching; Human Kinetics'' <ref name=":7">Kristian Berg, Human Kinetics:. Prescriptive stretching. 2011.</ref> | |||
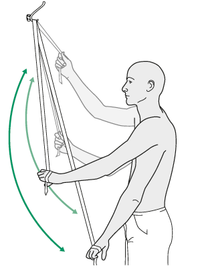
* Door stretch: 5 x 30 seconds (5 second rest in between) | |||
* | |||
* | * Passive/Active range of motion:<ref>Joseph Berman MD. Supraspinatus tear, http://www.josephbermanmd.com/diagnosis-treatament-of-the-shoulder/rotator-cuff-tear/ (accessed 29/04/2015).</ref> | ||
** Pendulum exercises: Forward and back, side-to-side, circular motion. 2 sets of 10 a day, 5-6days/week | |||
** Symptom limited active-assisted range of motion exercises | |||
[[Image:5.png|270x270px]] | |||
= | ''Kristian Berg. Prescriptive stretching; Human Kinetics <ref name=":7" />'' | ||
* | * Increase strength:<ref name=":9">Physioroom. Exercises to Strengthen the Rotator Cuff Muscles in the Shoulder.http://www.physioroom.com/experts/asktheexperts/answers/qa_mb_20050225.php (accessed 31/08/2018).</ref><ref>Heers G, Anders S, Werther M, Lerch K, Hedtmann A, Grifka J. [https://europepmc.org/abstract/med/15776325 Efficacy of home exercises for symptomatic rotator cuff tears in correlation to the size of the defect.] Sportverletzung Sportschaden: Organ der Gesellschaft fur Orthopadisch-Traumatologische Sportmedizin 2005;19(1):22-7. | ||
</ref> | |||
** Rotator cuff (especially supraspinatus) strengthening to improve muscle control and strength | |||
** Prone Horizontal Abduction progress by using resistance bands | |||
** Prone Row with External Rotation | |||
* Regain function of affected upper limb (up to 3 months) | |||
* Home exercise programme | |||
'''<u></u>'''<sup></sup> | |||
== Clinical Bottom Line == | |||
A supraspinatus tear can occur due to trauma or repeated micro-trauma and present as a partial or full-thickness tear.<ref name=":0" /> Most of the time, the tear occurs in the tendon or as an avulsion from the greater tuberosity<ref name=":6" />. The tear can be partial or full-thickness. Pain, loss of range of motion and weakness is the 3 most common symptoms.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":11" /><ref name=":13" /> Supraspinatus tears can be managed conservatively, with NSAID's and physiotherapy, as well as surgically to repair the tear. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Shoulder]] | [[Category:Shoulder]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Shoulder - Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Sports_Injuries]] | [[Category:Sports_Injuries]] | ||
[[Category:Sports Medicine]] | [[Category:Sports Medicine]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:32, 22 May 2023
Original Editor - Brecht Haex
Top Contributors - Leana Louw, Kim Jackson, Mats Vandervelde, Brecht Haex, Fasuba Ayobami, Vidya Acharya, Saimat Lachinova, Habibu Salisu Badamasi, Wendy Walker, Naomi O'Reilly, Wout Van Hees, Joao Costa, Shreya Pavaskar, Simisola Ajeyalemi, Anthony Mertens, Wanda van Niekerk and Rachael Lowe
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
A supraspinatus tear is a tear or rupture of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle. The supraspinatus is part of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Most of the time, it is accompanied by another rotator cuff muscle tear. This can occur due to trauma or repeated micro-trauma and present as a partial or full-thickness tear.[1] Quite often, the tear occurs in the tendon or as an avulsion from the greater tuberosity.[2]
Image: Supraspinatus muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view[3]
Clinical Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The shoulder joint is made up of three bones: the humerus, scapula and clavicle. The head of the humerus and the glenoid of the scapula form a ball-and-socket joint[1]. The supraspinatus muscle is located on the back of the shoulder, forming part of the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff consists of Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Subscapularis and teres minor. The rotator cuff covers the head of the humerus and keeps it in place. These muscles help to lift and rotate the arm. Visit the shoulder for more detailed information.
Supraspinatus[edit | edit source]
- Origin: Supraspinous fossa of the scapula
- Insertion: Greater tubercle of the humerus
- Innervation: Supraspinatus nerve (C5-C6)
- Function: Abduction of the glenohumeral joint; assists the rotator cuff in stabilizing, control and movement the shoulder; assists in preventing subluxation at the shoulder
Epidemiology/Aetiology[edit | edit source]
The aetiology of supraspinatus tears is multifactorial, consisting of age-related degeneration, microtrauma, and macrotrauma. It mostly affects the dominant arm with about 50% of people in their 80s experiencing this condition. [6][7] Injury and degeneration are the two main causes of rotator cuff tears. Rotator cuff tears are associated with older patients, those with a history of trauma and mostly affect the dominant arm.
Mechanism of Injury[edit | edit source]
Acute tear: Can occur with other shoulder injuries (e.g. clavicle fracture of shoulder dislocation)
- Fall on an outstretched arm
- Lifting something too heavy
Degenerative: Wear and tear of the tendon slowly over time
- Increases with the age
- More common in the dominant arm
- When you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, you have a greater risk for a tear in the opposite shoulder, even if you have no pain in the opposite shoulder.
Risk Factors[edit | edit source]
- > 40 years old
- Male > Female
- Smoking
- Genetics
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Body mass index
- Height
- Repetitive stress/lifting
- History of trauma
- Lack of blood supply
- Bony spurs
- Overhead activities and other people who do overhead work: Tennis players, Baseball pitchers, Painters, Carpenters, and Plumbers.
- Traumatic injury e.g. fall (more common cause in younger individuals)[1]
Characteristics/Clinical presentation[edit | edit source]
Supraspinatus tears are normally present as partial or full-thickness tears. It can be asymptomatic or symptomatic.
Partial thickness:
- Incomplete disruption of muscle fibres[1]
- Can progress to complete tear - Increasing pain is normally the first sign of the progression of a tear
Full thickness: Complete disruption of muscle fibres
- Large tears (1-1,5cm) have a high rate of progression
- If progression is suspected in conservatively managed cases - further investigation is warranted
- Smaller tears (<1cm) progress slower
Signs and Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Patients normally present with:[1][7][8]
- Pain/worsening pain (in cases where tears are progressing), the most common symptoms are:
- Pain when lifting and lowering your arm or with specific movement
- Pain at rest
- Pain at night, predominantly when you lie on the affected shoulder
- Traumatic tears: Sudden, intense pain often accompanied by a snapping sensation and immediate weakness in the upper arm
- Located anterolaterally and superiorly
- Referred to the level of the deltoid insertion with full-thickness tears
- Repetitive strain tear: Starts off mild and only when lifting your arm; over time the pain can become more noticeable at rest
- Aggravated in overhead or forward-flexed position
- Limited range of motion
- Reduced forward elevation, external rotation and abduction
- Struggle with activities like reaching behind back, combing hair and overhead activities
- Stiffness
- Weakness when rotating or lifting your arm
- Crepitus, Clicking, and Instability
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- Acromioclavicular joint injury
- Brachial plexus injury
- Bicipital tendinopathy
- Cervical radiculopathy
- Cervical spine sprain
- Cervical strain injuries
- Cervical disc injuries
- Cervical nerve root injury
- Cervical Spondylosis
- Cervical discogenic pain syndrome
- Clavicular fracture
- Sternoclavicular joint disorders
- Infraspinatus syndrome
- Contusions
- Rotator cuff tear
- Shoulder dislocation
- Myofascial pain
- Shoulder impingement syndrome
- Superior labrum lesions
- Shoulder subluxation
- Angina pectoris
- Myocardial infarction
- Subacromial impingement
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Subscapular nerve entrapment
- Shoulder instability
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
Physical Examination[edit | edit source]
Subjective interview:[edit | edit source]
- Onset: Spontaneous or after injury
- Duration of pain
- Pain provocation/aggravating factors
- Night rest
- Same problems in the past?
- Activity limitations
- Localize pain
- Past medical history
- Recreational or sport activities (possible overhead activities)
Observation:[edit | edit source]
- Any atrophy present
Range of motion:[edit | edit source]
- Expect reductions in flexion, abduction and external rotation
- If passive abduction range is more than active range, it is an indication of a rotator cuff tear
Muscle power:[edit | edit source]
- Test supraspinatus by resisting abduction at 90° and internal rotation
- Scapular movement may be affected
Palpation:[edit | edit source]
- Forearm behind back to palpate rotator cuff just anterior and below the acromion
- Muscle atrophy present
- Tenderness
Special tests:[edit | edit source]
- Drop-arm test: Active shoulder abduction to 90°, then return [11]
- Positive: Dropping the arm down with pain indicates a positive test
Drop Arm Test video provided by Clinically Relevant
- Jobe/supraspinatus/empty can test: Resist shoulder abduction and internal rotation[11]
- Positive: Pain/weakness
- Jobe/supraspinatus/empty can test: Resist shoulder abduction and internal rotation[11]
Empty Can Test video provided by Clinically Relevant
- Full can test: Resisted shoulder abduction in external rotation
- Positive: Pain/weakness
- Full can test: Resisted shoulder abduction in external rotation
Full Can Test video provided by Clinically Relevant
- Subacromial grind test: Patient standing and examiner standing facing the patient, the examiner grasps the patient's flexed elbow. The shoulder is passively abducted in the scapular plane to 90°. The examiner's other hand is placed over the patient's shoulder overlying the anterior acromion and greater tuberosity. The examiner passively internally and externally rotates the shoulder detecting the presence of palpable crepitus.
- Positive: Palpable crepitus.[12]
- Subacromial grind test: Patient standing and examiner standing facing the patient, the examiner grasps the patient's flexed elbow. The shoulder is passively abducted in the scapular plane to 90°. The examiner's other hand is placed over the patient's shoulder overlying the anterior acromion and greater tuberosity. The examiner passively internally and externally rotates the shoulder detecting the presence of palpable crepitus.
Special Investigations[edit | edit source]
X-rays[edit | edit source]
- Excluding sclerosis and osteophyte formation on the acromion
- X-rays measure the size of the subacromial space
- Unable to see the tendon
MRI[edit | edit source]
- MRI Scan shows partial or full tears in the tendons of the rotator cuff, inflammation to weak structures and cracks in the capsule
CT Scan[edit | edit source]
- CT scan is able to localize tendon when patient positioned with forearm behind the back
Ultrasound[edit | edit source]
- Ultrasound helps in localising tendon
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
- Short Form-36 (SF-36)
- Rotator Cuff Quality of Life (RC-QOL) scale
- Western Ontario Rotator Cuff (WORC) index
- Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH)[1]
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
Conservative Management[edit | edit source]
- Older (>70 years) patients with a chronic tear
- Patients with irreparable tears with irreversible changes
- Patients of any age with small (<1 cm) full-thickness tears
- As a result of the slow rate of progression of these tears
- Patients without a full-thickness tear
Management includes:[15]
NSAID's:
- Ibuprofen
Corticosteroid injections:
- Eliminate pain for a period of time, making physiotherapy management easier
- Tendon tissue can be weakened by these injections (which would have an adverse effect on the outcome of a possible surgery)
- Limited to 2 injections
- Physiotherapy (see Physiotherapy management below)
Surgical Management[edit | edit source]
- Failed conservative management
- Larger symptomatic full-thickness tears (1-1,5cm) as a result of the high rate of progression. Should be considered for earlier surgical repair in younger patients if the tear is repairable and the muscle degeneration is limited
- Acute large tears (>1 cm-1.5 cm) or
- Young patients with full-thickness tears who have a significant risk for the development of irreparable rotator cuff changes
- Complete tear with significant pain and dysfunction after 6 months of treatment
- Repeated dislocations
Rotator cuff repair[edit | edit source]
Most repairs are done arthroscopically[16]. Severity (partial vs full-thickness) will determine the approach.
- Partial repair: The tendon and surrounding bone will be smoothed to avoid further damage and therefore allowing the tendon to heal mostly on its own[17]
- Complete tear: Tear in middle of tendon: Suture the two parts of the tendon back together. Tear close or on its point of attachment on the head of the humerus: Attach the tendon back to its original place by an anchor (sometimes two). This anchor actually consists of a small screw that is bored into the head of the humerus with on the back surgical wires which hold the tendon in place[18].
Physiotherapy Management[edit | edit source]
Physiotherapy management depends on the extent of the tear, and plays in important role in both conservative management as well as post-surgical rehabilitation. More details can also be obtained from the rotator cuff page.
Conservative Management[edit | edit source]
Physiotherapy goals:
- Improve pain together with NSAID’s (2-6 weeks)
- Cryotherapy (only in first 48 hours)
- Massage
- Improve circulation (to control inflammation and speed up the healing process)
- Improve range of motion:
- Stretching (careful with timing, as stretching of acute injury may aggravate the tear):[19]
- Crossover arm stretch: 12 seconds, 5 times a day; 5-6days/week
- Stretching (careful with timing, as stretching of acute injury may aggravate the tear):[19]
Kristian Berg. Prescriptive stretching; Human Kinetics [20]
- Door stretch: 5 x 30 seconds (5 second rest in between)
- Passive/Active range of motion:[21]
- Pendulum exercises: Forward and back, side-to-side, circular motion. 2 sets of 10 a day, 5-6days/week
- Symptom limited active-assisted range of motion exercises
Kristian Berg. Prescriptive stretching; Human Kinetics [20]
- Increase strength:[22][23]
- Rotator cuff (especially supraspinatus) strengthening to improve muscle control and strength
- Prone Horizontal Abduction progress by using resistance bands
- Prone Row with External Rotation
- Regain function of affected upper limb (up to 3 months)
- Home exercise programme
Clinical Bottom Line[edit | edit source]
A supraspinatus tear can occur due to trauma or repeated micro-trauma and present as a partial or full-thickness tear.[1] Most of the time, the tear occurs in the tendon or as an avulsion from the greater tuberosity[2]. The tear can be partial or full-thickness. Pain, loss of range of motion and weakness is the 3 most common symptoms.[1][7][8] Supraspinatus tears can be managed conservatively, with NSAID's and physiotherapy, as well as surgically to repair the tear.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons, Ortho Info. Rotator cuff tears, http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=a00064 (accessed 29/08/2018).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Benazzo F, Marullo M, Pietrobono L. Supraspinatus rupture at the musculotendinous junction in a young woman. Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology 2014;15(3):231-4.
- ↑ Supraspinatus muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view image - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/supraspinatus-muscle
- ↑ Schünke M, Schulte E, Schumacher U, Voll M, Wesker K. Prometheus: Algemene anatomie en bewegingsapparaat, 2010. p600.
- ↑ Physioworks, Rotator Cuff Tear.http://physioworks.com.au/injuries-conditions-1/rotator-cuff-tears (accessed 29/08/2018).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Tashjian RZ. Epidemiology, natural history and indications for treatment of rotator cuff tears. Clinics in Sports Medicine 2012:31(4):589-604.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 Yamamoto A, Takagishi K, Osawa T, Yanagawa T, Nakajima D, Shitara H, Kobayashi T. Prevalence and risk factors of a rotator cuff tear in the general population. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery 2010:19(1):116-20.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Mayo Clinic Rotator cuff injury. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rotator-cuff-injury/symptoms-causes/dxc-20126923 (accessed 30/08/2018).
- ↑ Medscape. Supraspinatus tendonitis: Differential diagnoses, http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/93095-differential (Accessed 20/03/2015).
- ↑ Medscape. Rotator cuff injury: Differential diagnoses, http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/92814-differential, (Accessed 25/03/2015).
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Hughers PC, Taylor NF, Green RA. Most clinical tests cannot accurately diagnose rotator cuff pathology: a systematic review. Aust J Physiother 2008;54(3):159-70.
- ↑ Sawalha S, Fischer J. The accuracy of “subacromial grind test” in diagnosis of supraspinatus rotator cuff tears. International journal of shoulder surgery 2015;9(2):43-46.
- ↑ Walters J, editor. Orthopaedics - A guide for practitioners. 4th Edition. Cape Town: University of Cape Town, 2010.
- ↑ Orthop J. Rotator cuff tear: physical examination and conservative treatment. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tohoku University, 2013:197–204.
- ↑ Björkenheim JM, Paavolainen P, Ahovuo J, Slätis P. Surgical repair of the rotator cuff and surrounding tissues. Factors influencing the results. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 1988;(236):148-53.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Millar NL, Wu X, Tantau R, Silverstone E, Murrell GA. Open versus two forms of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 2009;467(4):966-78.
- ↑ American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/rotator-cuff-tears-surgical-treatment-options/ (accessed 30/08/2018).
- ↑ Akpınar S, Uysal M, Pourbagher MA, Ozalay M, Cesur N, Hersekli MA. Prospective evaluation of the functional and anatomical results of arthroscopic repair in small and medium-sized full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus tendon. Acta orthopaedica et traumatologica turcica 2011;45(4):248-53.
- ↑ Kuhn JE. Exercise in the treatment of rotator cuff impingement: a systematic review and a synthesized evidence-based rehabilitation protocol. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery 2009;18(1):138-60.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Kristian Berg, Human Kinetics:. Prescriptive stretching. 2011.
- ↑ Joseph Berman MD. Supraspinatus tear, http://www.josephbermanmd.com/diagnosis-treatament-of-the-shoulder/rotator-cuff-tear/ (accessed 29/04/2015).
- ↑ Physioroom. Exercises to Strengthen the Rotator Cuff Muscles in the Shoulder.http://www.physioroom.com/experts/asktheexperts/answers/qa_mb_20050225.php (accessed 31/08/2018).
- ↑ Heers G, Anders S, Werther M, Lerch K, Hedtmann A, Grifka J. Efficacy of home exercises for symptomatic rotator cuff tears in correlation to the size of the defect. Sportverletzung Sportschaden: Organ der Gesellschaft fur Orthopadisch-Traumatologische Sportmedizin 2005;19(1):22-7.