Adductor Longus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(added information to the Adductor Longus Muscle Image for people who can't see the item) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
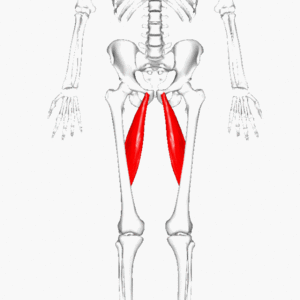
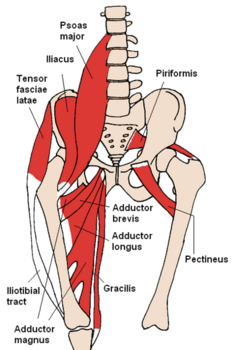
[[File:Adductor longus.gif|thumb|alt=|Adductor longus]]Adductor longus is one of the adductor muscles of the medial thigh.<ref name=":0">Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.</ref> Together with [[Adductor Brevis|adductor brevis]], [[Adductor Magnus|adductor magnus]], [[gracilis]] and [[Obturator Externus|obturator externus]], it makes up the [[Hip Adductors|hip adductors]].<ref name=":0" /> | [[File:Adductor longus.gif|thumb|alt=This is the image of Adductor Longus muscle which originates from anterior aspect of pubic body inferior to pubic crest and expands into a fan shape, attaching broadly to the linea aspera on the middle third of femur. |Adductor longus]]Adductor longus is one of the adductor muscles of the medial thigh.<ref name=":0">Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.</ref> Together with [[Adductor Brevis|adductor brevis]], [[Adductor Magnus|adductor magnus]], [[gracilis]] and [[Obturator Externus|obturator externus]], it makes up the [[Hip Adductors|hip adductors]].<ref name=":0" /> | ||
This large fan-shaped muscle is situated most anteriorly of this group and covers the middle part of [[Adductor Magnus|adductor magnus]] and the anterior part of [[Adductor Brevis|adductor brevis]].<ref name=":0" /> | This large fan-shaped muscle is situated most anteriorly of this group and covers the middle part of [[Adductor Magnus|adductor magnus]] and the anterior part of [[Adductor Brevis|adductor brevis]].<ref name=":0" /> | ||
Revision as of 16:49, 1 June 2023
Original Editor - Leana Louw
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Leana Louw, Memoona Awan, Kim Jackson, Ines Musabyemariya and Vidya Acharya
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Adductor longus is one of the adductor muscles of the medial thigh.[1] Together with adductor brevis, adductor magnus, gracilis and obturator externus, it makes up the hip adductors.[1]
This large fan-shaped muscle is situated most anteriorly of this group and covers the middle part of adductor magnus and the anterior part of adductor brevis.[1]
The muscle forms the medial border of the femoral triangle.
The muscles in this compartment are believed to be evolved from both hip extensor and flexor columns[2].
Origin[edit | edit source]
Strong tendon from anterior aspect of pubic body inferior to pubic crest.[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Expands into a fan shape, attaching broadly to the linea aspera on the middle third of femur.[1]
This insertion point is between the insertion of the adductor magnus and the origin of vastus medialis muscle, and inferior to the adductor brevis insertion.[2]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Anterior devision of obturator nerve (L2, L3, L4).[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
The main action of the adductor group of muscles is to adduct the thigh at the hip joint.
- The adductor longus muscle also plays a role in external/lateral rotation and flexion of the thigh.
- Along with the other hip adductors it helps to stabilize the pelvis in standing and aiding in balancing the body on the lower limb during walking.[1][2]
Physiotherapy Relevance[edit | edit source]
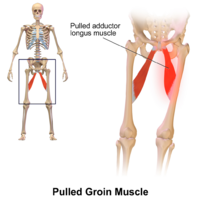
Adductor Tendinopathy is a common cause of medial leg and groin pain, especially among athletes. It is a common among injury in such sports as eg ice skating, horse riding, soccer, football, karate, running. Sudden changes in direction cause a quick adduction against a large abduction force thereby stressing the tendon, most commonly at its origin. It is caused by a disproportional strain of the muscles, often in combination with a poor warm-up and a lack of stretching.[3]
Assessment and Treatment[edit | edit source]
Adductor injuries are often overlooked. An early assessment is essential to prevent it becoming a career threatening injury for an athlete.
For a guide to Physiotherapy treatment and assessment see Groin Strain Adductor Tendinopathy
- It is essential to do a thorough assessment of the pelvis and core as well as the thigh muscles. Designing a strengthening program to address which muscles are weak and which muscles are tight is vital. Treatment should include strengthening of the muscles around pelvis and core, along side with stretches to be completed following all training sessions.[3]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Ken Hub Adductor Longus Available: https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/adductor-longus-muscle(accessed 20.1.2022)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Adductor Brevis
- ↑ Hislop H, Avers D, Brown M. Daniels and Worthingham's Muscle Testing: Techniques of manual examination. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013.