Pleural Effusion: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- [ | '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Chelsea_Mclene|Chelsea McLene]] | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Pleural effusion is collection of unusual amount of fluid in pleural cavity. <ref name=":1">Light RW | Pleural effusion is a collection of an unusual amount of fluid in the pleural cavity. <ref name=":1">Light RW. [https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMcp010731 Pleural effusion]. New England Journal of Medicine. 2002 Jun 20;346(25):1971-7.</ref> | ||
The [[Lung Anatomy|pleura]] are two continuous membranes, the parietal and visceral pleura, which form a sac to enclose each lung. The normal parietal Plura produces fluid which is reabsorbed by the visceral pleura. Normally, for smooth movement of lungs, only teaspoons of watery fluid are in the pleural space.<ref>Rajgaria A. [https://www.pharmatutor.org/articles/plueral-effusion-disease-of-lungs PLUERAL EFFUSION-DISEASE OF LUNGS.] [last accessed 24/03/2021]</ref> When fluid builds up in the space between the layers of pleura, a pleural effusion has occurred. Either excessive fluid production (for example as a result of inflammation) or impaired absorption leads to an accumulation of fluid. | |||
{{#ev:youtube|f6bngHjMLA0|300}}<ref name=":0">Armando Hasudungan. Pleural Effusion (DETAILED) - (pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, treatment). Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f6bngHjMLA0 [last accessed 24/3/2021]</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|f6bngHjMLA0|300}}<ref name=":0">Armando Hasudungan. Pleural Effusion (DETAILED) - (pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, treatment). Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f6bngHjMLA0 [last accessed 24/3/2021]</ref> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 20: | ||
Most common cause of this type is [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Introduction_to_Congestive_Heart_Failure congestive heart failure]. | Most common cause of this type is [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Introduction_to_Congestive_Heart_Failure congestive heart failure]. | ||
* Less protein | * Less protein | ||
* Few cells<ref name=":2">Light RW, Macgregor MI, Luchsinger PC, Ball WC | * Few cells<ref name=":2">Light RW, Macgregor MI, Luchsinger PC, Ball WC. [https://semanticscholar.org/paper/a19f8e462b613741559ec919dcbd3837786a175e Pleural effusions: the diagnostic separation of transudates and exudates"]. 1972. Ann Intern Med. 77 (4): 507–13.</ref> | ||
==== Exudative ==== | ==== Exudative ==== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 31: | ||
=== By the underlying cause === | === By the underlying cause === | ||
=== By the origin of the fluid === | === By the origin of the fluid === | ||
* Serous fluid ( | * Serous fluid (hydrothorax) | ||
* Blood ([https://www.physio-pedia.com/Hemothorax haemothorax]) | * Blood ([https://www.physio-pedia.com/Hemothorax haemothorax]) | ||
* Chyle (chylothorax) | * Chyle (chylothorax) | ||
* Pus ( | * Pus (pyothorax) | ||
* Urine (urinothorax) | * Urine (urinothorax) | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
* | *[[Dyspnoea|Breathlessness]] | ||
* Chest pain | |||
* May have cough | * May have cough | ||
* Weakness | * Weakness | ||
* May or may not have fever | |||
== Clinical signs == | |||
* Auscultation: [[Pleural Friction Rub|Pleural rub]], reduced breath sounds, reduced vocal resonance | |||
* Reduced chest expansion | |||
* Percussion note: stony dull | |||
*[https://www.physio-pedia.com/Auscultation Heart Sounds]: Third heart sound can be heard. | |||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
There are many causes, some of them are: | There are many causes, some of them are: | ||
* Congestive heart failure | |||
* Leak from other organs | * Leak from other organs | ||
* Autoimmune conditions: [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Rheumatoid_Arthritis RA], [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Systemic_Lupus_Erythematosus Lupus] | * Autoimmune conditions: [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Rheumatoid_Arthritis RA], [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Systemic_Lupus_Erythematosus Lupus] | ||
| Line 60: | Line 63: | ||
* [[Blood Tests|Blood Test]]: Neutrophilia | * [[Blood Tests|Blood Test]]: Neutrophilia | ||
* [[CT Scans|CT Scan]] | * [[CT Scans|CT Scan]] | ||
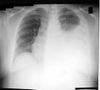
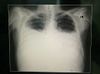
* [https://www.physio-pedia.com/X-Rays X-ray]: Presence of fluid in the pleural cavity which appears white on X-rays, while air space looks black.<ref>Corne; et al. (2002). | * [https://www.physio-pedia.com/X-Rays X-ray]: Presence of fluid in the pleural cavity which appears white on X-rays, while air space looks black.<ref>Corne; et al. (2002). [https://scholar.google.com/scholar_url?url=https://epos.myesr.org/esr/viewing/index.php%3Fmodule%3Dviewing_poster%26task%3D%26pi%3D138426&hl=en&sa=T&oi=gsb&ct=res&cd=0&d=3713063537200917663&ei=2V9bYNGpBJ-R6rQPps2BmAE&scisig=AAGBfm1CoKxrqXCaKSl7OWE_6KWkFgPmAQ Chest X-Ray Made Easy]. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN .</ref><ref>Sahn SA, Heffner JE. [https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=WiPSBQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA209&ots=BH4yCZANrx&sig=BTCeZBy8UPmhNHNYmKaKa_0Q67I Pleural fluid analysis]. Textbook of pleural diseases. 2008 Apr 25;2:209-6.</ref>Blunting of the costophrenic angle occurs in small collections, where more extensive change on x-ray is seen in larger collections. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
The principle treatment approach with pleural effusion is to treat the underlying cause. | The principle treatment approach with pleural effusion is to treat the underlying cause. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 69: | ||
* Pleural Decortication: Surgeons can operate inside the pleural space, removing inflammation and unhealthy tissue by thoracoscopy or [[thoracotomy]]. | * Pleural Decortication: Surgeons can operate inside the pleural space, removing inflammation and unhealthy tissue by thoracoscopy or [[thoracotomy]]. | ||
* Chemotherapy | * Chemotherapy | ||
* [[Thoracentesis]] <ref>de Menezes Lyra R | * [[Thoracentesis]] <ref>de Menezes Lyra R. [https://scholar.google.com/scholar_url?url=https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(15)47196-X/abstract&hl=en&sa=T&oi=gsb&ct=res&cd=0&d=4801023564618924139&ei=d19bYJP0A4nSyQT5jLPoCQ&scisig=AAGBfm0tVOHRr6CWuXd5Ek4MG83Raihwew A modified outer cannula can help thoracentesis after pleural biopsy] (PDF). Chest. 1997. 112(1):296</ref> | ||
* Pleural Biopsy | * Pleural Biopsy | ||
* [https://physio-pedia.com/Chest_Drains?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=related_articles&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Drainage] by intercostal tubes | * [https://physio-pedia.com/Chest_Drains?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=related_articles&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Drainage] by intercostal tubes | ||
| Line 73: | Line 76: | ||
== Role of Physiotherapy == | == Role of Physiotherapy == | ||
Physiotherapy has an important role in stabilizing and controlling breathing. It aids in chest fluid drainage and in clearing chest secretions. People who receive respiratory physiotherapy as part of their treatment will tend to achieve a quicker recovery with fewer complications. | Physiotherapy has an important role in stabilizing and controlling breathing. It aids in chest fluid drainage and in clearing chest secretions. People who receive respiratory physiotherapy as part of their treatment will tend to achieve a quicker recovery with fewer complications. | ||
==== Secretion clearance: ==== | |||
* Effective / productive [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Assisted_Coughing#:~:text=Manual%20assisted%20cough%20is%20the,rapid%20change%20to%20negative%20pressure. coughing techniques] | |||
* Postural drainage in sitting and lying | |||
* Manual assistance, including [[percussion]], vibrations and shaking | |||
==== Breathing technique retraining: ==== | |||
* Controlling respiratory rate | |||
* [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Diaphragmatic_Breathing_Exercises Diaphragmatic breathing] | |||
* Controlling / reducing breath volume | |||
* Relaxation breathing exercises | |||
==== Education and Advice: ==== | |||
* Illness cause and progression | |||
* Effects of environmental and allergen factors. | |||
* Medication management | |||
(Read about [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Chest_Physiotherapy chest physiotherapy]) | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 20:55, 9 January 2024
Original Editor - Chelsea McLene
Top Contributors - Chelsea Mclene, Rosie Swift, Kim Jackson and Khloud Shreif
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Pleural effusion is a collection of an unusual amount of fluid in the pleural cavity. [1]
The pleura are two continuous membranes, the parietal and visceral pleura, which form a sac to enclose each lung. The normal parietal Plura produces fluid which is reabsorbed by the visceral pleura. Normally, for smooth movement of lungs, only teaspoons of watery fluid are in the pleural space.[2] When fluid builds up in the space between the layers of pleura, a pleural effusion has occurred. Either excessive fluid production (for example as a result of inflammation) or impaired absorption leads to an accumulation of fluid.
Classification[edit | edit source]
By Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
Transudative[edit | edit source]
Transudative type of pleural effusion rarely needs to be drained. It is formed from the liquid which leaks around the pleura.
Most common cause of this type is congestive heart failure.
- Less protein
- Few cells[4]
Exudative[edit | edit source]
Exudative type of pleural effusion requires to be drained. It is formed from extra liquid, protein, blood, inflammatory cells or sometimes bacteria that leak across damaged blood vessels into the pleura.
The causes of this type include pneumonia and lung cancer.
- More protein
- Large amount of cells[4]
By the underlying cause[edit | edit source]
By the origin of the fluid[edit | edit source]
- Serous fluid (hydrothorax)
- Blood (haemothorax)
- Chyle (chylothorax)
- Pus (pyothorax)
- Urine (urinothorax)
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
- Breathlessness
- Chest pain
- May have cough
- Weakness
- May or may not have fever
Clinical signs[edit | edit source]
- Auscultation: Pleural rub, reduced breath sounds, reduced vocal resonance
- Reduced chest expansion
- Percussion note: stony dull
- Heart Sounds: Third heart sound can be heard.
Causes[edit | edit source]
There are many causes, some of them are:
- Congestive heart failure
- Leak from other organs
- Autoimmune conditions: RA, Lupus
- Cancer
- Pulmonary embolism[5][1]
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- Blood Test: Neutrophilia
- CT Scan
- X-ray: Presence of fluid in the pleural cavity which appears white on X-rays, while air space looks black.[6][7]Blunting of the costophrenic angle occurs in small collections, where more extensive change on x-ray is seen in larger collections.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The principle treatment approach with pleural effusion is to treat the underlying cause.
- Medication: Antibiotics, Diuretics
- Pleural Decortication: Surgeons can operate inside the pleural space, removing inflammation and unhealthy tissue by thoracoscopy or thoracotomy.
- Chemotherapy
- Thoracentesis [8]
- Pleural Biopsy
- Drainage by intercostal tubes
- Pleurodesis
Role of Physiotherapy[edit | edit source]
Physiotherapy has an important role in stabilizing and controlling breathing. It aids in chest fluid drainage and in clearing chest secretions. People who receive respiratory physiotherapy as part of their treatment will tend to achieve a quicker recovery with fewer complications.
Secretion clearance:[edit | edit source]
- Effective / productive coughing techniques
- Postural drainage in sitting and lying
- Manual assistance, including percussion, vibrations and shaking
Breathing technique retraining:[edit | edit source]
- Controlling respiratory rate
- Diaphragmatic breathing
- Controlling / reducing breath volume
- Relaxation breathing exercises
Education and Advice:[edit | edit source]
- Illness cause and progression
- Effects of environmental and allergen factors.
- Medication management
(Read about chest physiotherapy)
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Light RW. Pleural effusion. New England Journal of Medicine. 2002 Jun 20;346(25):1971-7.
- ↑ Rajgaria A. PLUERAL EFFUSION-DISEASE OF LUNGS. [last accessed 24/03/2021]
- ↑ Armando Hasudungan. Pleural Effusion (DETAILED) - (pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, treatment). Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f6bngHjMLA0 [last accessed 24/3/2021]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Light RW, Macgregor MI, Luchsinger PC, Ball WC. Pleural effusions: the diagnostic separation of transudates and exudates". 1972. Ann Intern Med. 77 (4): 507–13.
- ↑ Light RW. Pleural effusions. Medical Clinics. 2011 Nov 1;95(6):1055-70.
- ↑ Corne; et al. (2002). Chest X-Ray Made Easy. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN .
- ↑ Sahn SA, Heffner JE. Pleural fluid analysis. Textbook of pleural diseases. 2008 Apr 25;2:209-6.
- ↑ de Menezes Lyra R. A modified outer cannula can help thoracentesis after pleural biopsy (PDF). Chest. 1997. 112(1):296