Grey and White Matter: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
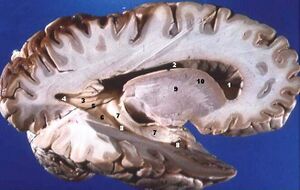
[[File:Human brain right.jpeg|thumb|Grey and white matter Human brain]] | |||
The central nervous system is made up of grey matter and white matter. | The central nervous system is made up of grey matter and white matter. | ||
# Gray matter: named for its pinkish-gray color, is home to neural cell bodies, axon terminals, and dendrites, as well as all nerve synapses. This brain tissue is abundant in the cerebellum, cerebrum, and brain stem. It also forms a butterfly-shaped portion of the central spinal cord. | # Gray matter: named for its pinkish-gray color, is home to neural cell bodies, axon terminals, and dendrites, as well as all nerve synapses. This brain tissue is abundant in the [[cerebellum]], [[cerebrum]], and [[Brainstem|brain stem]]. It also forms a butterfly-shaped portion of the central [[Spinal cord anatomy|spinal cord]]. | ||
# White matter: composed of bundles of axons. These axons are coated with myelin, a mixture of proteins and lipids, that helps conduct nerve signals and protect the axons. White matter conducts, processes, and send nerve signals up and down the spinal cord<ref>Spinalcord Gray vs white matter Available:https://www.spinalcord.com/blog/gray-matter-vs-white-matter-in-the-brain (accessed 1.5.2022)</ref>. | # White matter: composed of bundles of [[axons]]. These axons are coated with myelin, a mixture of proteins and lipids, that helps conduct [[Neurone|nerve]] signals and protect the axons. White matter conducts, processes, and send nerve signals up and down the spinal cord<ref>Spinalcord Gray vs white matter Available:https://www.spinalcord.com/blog/gray-matter-vs-white-matter-in-the-brain (accessed 1.5.2022)</ref>. | ||
== Gray Matter == | == Gray Matter == | ||
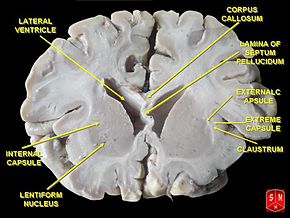
[[File:PD Basal ganglia .jpg|thumb|Basal ganglia]] | |||
Grey matter makes up the outer most layer of the brain. | Grey matter makes up the outer most layer of the brain. | ||
# The grey matter surrounding the cerebrum is known as the cortex of the brain. There are two major cortexes in the brain, the cerebral cortex and the cerebellar cortex. Interestingly the highest concentration of neuronal cells is in the cerebellum, which has more than the rest of the brain combined. | # The grey matter surrounding the cerebrum is known as the [[Cerebral Cortex|cortex]] of the brain. There are two major cortexes in the brain, the cerebral cortex and the cerebellar cortex. Interestingly the highest concentration of neuronal cells is in the cerebellum, which has more than the rest of the brain combined. | ||
# There are also areas of grey matter that are in the inner sections of the brain known as or nuclei. | # There are also areas of grey matter that are in the inner sections of the brain known as or nuclei. eg [[Basal Ganglia]] | ||
The grey matter has a large number of neurons present, which allows it to process information and release new information through axon signaling found in the white matter. The grey matter throughout the central nervous system allows enables individuals to control movement, memory, and emotions. Different areas of the brain are responsible for various functions, and grey matter plays a significant role in all aspects of human life. | The grey matter has a large number of neurons present, which allows it to process information and release new information through axon signaling found in the white matter. The grey matter throughout the central nervous system allows enables individuals to control movement, memory, and emotions. Different areas of the brain are responsible for various functions, and grey matter plays a significant role in all aspects of human life. | ||
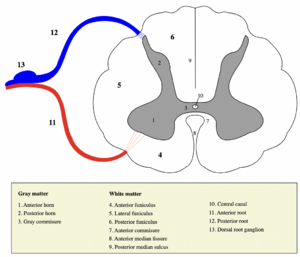
[[File:Gray matter spinal cord.png|thumb|Spinal cord – section]] | |||
In the spinal cord the gray matter forms a “butterfly” structure. The three sections are the anterior grey column, the posterior grey column, and the lateral grey column<ref>Mercadante AA, Tadi P. Neuroanatomy, Gray Matter.2020 Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553239/ (accessed 1.5.2022)</ref>. | In the spinal cord the gray matter forms a “butterfly” structure. The three sections are the anterior grey column, the posterior grey column, and the lateral grey column<ref>Mercadante AA, Tadi P. Neuroanatomy, Gray Matter.2020 Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553239/ (accessed 1.5.2022)</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 02:20, 1 May 2022
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton and Ahmed M Diab
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The central nervous system is made up of grey matter and white matter.
- Gray matter: named for its pinkish-gray color, is home to neural cell bodies, axon terminals, and dendrites, as well as all nerve synapses. This brain tissue is abundant in the cerebellum, cerebrum, and brain stem. It also forms a butterfly-shaped portion of the central spinal cord.
- White matter: composed of bundles of axons. These axons are coated with myelin, a mixture of proteins and lipids, that helps conduct nerve signals and protect the axons. White matter conducts, processes, and send nerve signals up and down the spinal cord[1].
Gray Matter[edit | edit source]
Grey matter makes up the outer most layer of the brain.
- The grey matter surrounding the cerebrum is known as the cortex of the brain. There are two major cortexes in the brain, the cerebral cortex and the cerebellar cortex. Interestingly the highest concentration of neuronal cells is in the cerebellum, which has more than the rest of the brain combined.
- There are also areas of grey matter that are in the inner sections of the brain known as or nuclei. eg Basal Ganglia
The grey matter has a large number of neurons present, which allows it to process information and release new information through axon signaling found in the white matter. The grey matter throughout the central nervous system allows enables individuals to control movement, memory, and emotions. Different areas of the brain are responsible for various functions, and grey matter plays a significant role in all aspects of human life.
In the spinal cord the gray matter forms a “butterfly” structure. The three sections are the anterior grey column, the posterior grey column, and the lateral grey column[2].
- Anterior grey column: important for all motor movements. The anterior portion of the grey matter connects to the brain through the pyramidal tract, which originates in the cerebral cortex. Signal pass along the axons found in the white matter. As the signals meet at the spinal cord, the signals are translated allow for voluntary motion.
- Posterior grey column: the section of the spinal cord that receives sensory signals allowing for constant interaction between the environment and the body.
- Lateral grey column: found in the middle of the grey matter of the spinal cord and extends out to the sides from the base of the spine. The lateral grey column is responsible for regulating the autonomic nervous system through its role in activating the sympathetic nervous system.
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Spinalcord Gray vs white matter Available:https://www.spinalcord.com/blog/gray-matter-vs-white-matter-in-the-brain (accessed 1.5.2022)
- ↑ Mercadante AA, Tadi P. Neuroanatomy, Gray Matter.2020 Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553239/ (accessed 1.5.2022)