Amputations: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Undo revision 96111 by Cornelia Barth (talk)) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- The | '''Original Editor '''- The [[Open Physio|Open Physio]] project. | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
= Introduction = | = Introduction = | ||
Amputation is the removal of a body extremity by trauma, prolonged constriction, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as malignancy or gangrene. In some cases, it is carried out on individuals as a preventative surgery for such problems. A special case is that of congenital amputation, a congenital disorder, wherefetal limbs have been cut off by constrictive bands. In some countries, amputation of the hands, feet or other body parts is or was used as a form of punishment for people who committed crimes. Amputation has also been used as a tactic in war and acts of terrorism; it may also occur as a war injury.<ref>Wikipedia. Amputation. http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Amputation (accessed 29 May 2014).</ref> | Amputation is the removal of a body extremity by trauma, prolonged constriction, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as malignancy or gangrene. In some cases, it is carried out on individuals as a preventative surgery for such problems. A special case is that of congenital amputation, a congenital disorder, wherefetal limbs have been cut off by constrictive bands. In some countries, amputation of the hands, feet or other body parts is or was used as a form of punishment for people who committed crimes. Amputation has also been used as a tactic in war and acts of terrorism; it may also occur as a war injury.<ref name="wiki">Wikipedia. Amputation. http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Amputation (accessed 29 May 2014).</ref> | ||
== Causes of amputations == | == Causes of amputations == | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
*''Congenical limb deficiency'' <ref>Day HJB. The ISO/ISPO classification of congenital limb deficiency. Prosthetics and Orthotics International 1991; 15: 67-69.</ref> | *''Congenical limb deficiency'' <ref>Day HJB. The ISO/ISPO classification of congenital limb deficiency. Prosthetics and Orthotics International 1991; 15: 67-69.</ref> | ||
*''Phocomelia'': "a congenital deformity in which the limbs are extremely shortened so that the feet and hands arise close to the trunk"<ref> | *''Phocomelia'': "a congenital deformity in which the limbs are extremely shortened so that the feet and hands arise close to the trunk"<ref>MedlinePlus. Medical Dictionary, phocomelia. http://www.merriam-webster.com/medlineplus/phocomelia (accessed 29 May 2014).</ref> | ||
=== Acquired === | === Acquired === | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
*Vascular | *Vascular | ||
**Ischaemia | **Ischaemia | ||
** | **[[Diabetes]] | ||
**Frostbite | **Frostbite | ||
**Arterial insufficiency leading to death or decay of body tissue (gangrene) | **Arterial insufficiency leading to death or decay of body tissue (gangrene) | ||
**Chronic leg ulcer leading to | **Chronic leg ulcer leading to [[Septicaemia]] | ||
*Malignant tumours e.g. sarcoma (cancer of the connective tissue) | *Malignant tumours e.g. sarcoma (cancer of the connective tissue) | ||
*Trauma | *Trauma e.g. stabbing and gun shoot, car accident, animal bite; in some cases leading to | ||
**''Traumatic amputation: ''a physical | **''Traumatic amputation: ''a physical separation of the limb in the course of the traumatic event | ||
== | == Types of amputations == | ||
#[[Image:Amputation.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Transfemoral Amputation]]Professional - emergency life saving procedure, mainly used when primary healing is delayed e.g infection, ischaemia, .. etc | |||
#Definitive - used after professional amputation | |||
#Anatomical amputations: | |||
* | #*disarticulation e.g. through the ankle joint (Syme's) amputation | ||
* | #*mid shaft amputations e.g. Below the knee, Above the knee ..etc. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Surgical procedures | == Surgical procedures == | ||
Two surgical procedures | |||
1-myodesis: the muscles and fascia are sutered directly to the distal residual bone for better prosthetic control | |||
2-myoplastic: suture to opposite muscle in the residual limb to to each other and to the periosteum or to the distal end of the cut bone for weight bearing purposes | |||
== Ideal stump == | == Ideal stump == | ||
| Line 66: | Line 55: | ||
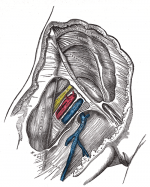
== Location of pulses == | == Location of pulses == | ||
[[Image:Femoral triangle.png|thumb|right|150px|Femoral Triangle]] | |||
*Foot pulse ( | *Foot pulse ([[Tibia#Medial_Malleolus|Medial malleolus]] or dorsum of the foot) | ||
*Popliteal (behind the knee) | *Popliteal (behind the knee) | ||
*Femoral (within the femoral triangle) | *Femoral (within the femoral triangle) | ||
| Line 75: | Line 64: | ||
== Special investigations == | == Special investigations == | ||
[[Image:Doppler ultrasound.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Doppler Ultrasound]] <br> | |||
* | *[[X-Rays|X-rays]] | ||
*CT scan | *CT scan | ||
*Angiogram (outlines blood vessels) | *Angiogram (outlines blood vessels) | ||
| Line 97: | Line 86: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="right" | | | align="right" | | ||
| | | {{#ev:youtube|jQUFmOmX35o|300}} <ref>ladybessviernes, UDM PT Students. Buerger Allen's Exercise. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQUFmOmX35o [last accessed 01/12/12]</ref> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 111: | Line 100: | ||
=== Balance and gait retraining === | === Balance and gait retraining === | ||
*Improve | *Improve [[Balance|static]] and [[Balance|dynamic]] balance | ||
*Use | *Use [[Parallel bars]], [[Zimmer frame|walking frame]] then [[Crutches]] (in that order) | ||
*Therapist stands on the amp side, using a belt around the patient’s waist to support | *Therapist stands on the amp side, using a belt around the patient’s waist to support | ||
*Rest if the patient feels tired | *Rest if the patient feels tired | ||
| Line 118: | Line 107: | ||
{| width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | {| width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{#ev:youtube|Xh4rPJFgRx8|300}} <ref>Clegstories. Gait Training with C-Leg®: Stance Phase Training. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xh4rPJFgRx8 [last accessed 08/12/12]</ref> | ||
| | | {{#ev:youtube|E11gQs0oIt0|300}} <ref>Clegstories. Gait Training with C-Leg®: Swing Phase Training. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E11gQs0oIt0 [last accessed 08/12/12]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{#ev:youtube|1C_C5N9reB8|300}}<ref>Clegstories. Clegstories. Gait Training with C-Leg®: Sitting Down and Standing Up. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_lBkrLZ4PGo [last accessed 08/12/12]</ref> | ||
| | | {{#ev:youtube|Z6bvgDaOkcI|300}}<ref> Clegstories. Gait Training with C-Leg®: Stairs. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z6bvgDaOkcI [last accessed 08/12/12]</ref> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 139: | Line 128: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="right" | | | align="right" | | ||
{{#ev:youtube|T1SA_6hzTxQ|300}} <ref>Richard Major. Physiotherapy Stump or Residual Limb Wrapping. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T1SA_6hzTxQ[last accessed 08/12/12]</ref> | |||
|} | |} | ||
*For hygiene and skin care see handout on amputations | *For hygiene and skin care see handout on amputations | ||
*A hip flexion | *A hip flexion [[Contracture]] may develop because of elevation to reduce swelling | ||
*Stump bandaging is done to ‘cone’ the stump, thereby preventing oedema, which occurs because there is no muscle pump and the stump hangs | *Stump bandaging is done to ‘cone’ the stump, thereby preventing oedema, which occurs because there is no muscle pump and the stump hangs | ||
*Swelling must be prevented to allow proper attachment of the | *Swelling must be prevented to allow proper attachment of the [[Prosthesis]], and the prevention of [[Pressure sores]] | ||
*The stump sock is put on first, then the prosthesis | *The stump sock is put on first, then the prosthesis | ||
*The prosthesis must be cleaned and maintained (Children who are still growing, grow out of their prostheses) | *The prosthesis must be cleaned and maintained (Children who are still growing, grow out of their prostheses) | ||
== | == Types of wheelchairs == | ||
* | |||
For double lower limb amputations, the wheels are set further back. | |||
== Complications == | == Complications == | ||
| Line 165: | Line 149: | ||
Phantom limb pain | Phantom limb pain | ||
== Recent Related Research (from | == Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | ||
<div class="researchbox"> | <div class="researchbox"> | ||
< | <rss>http://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=14QrMe-OFeMCUTROXREO2Goj4A_9ueFIW_SXkIUqFfh4iIHk-X|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10</rss> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Amputees]] [[Category:Open_Physio]] | |||
Revision as of 15:09, 30 May 2014
Original Editor - The Open Physio project.
Top Contributors - Niha Mulla, Cornelia Barth, Laura Ritchie, Admin, Rachael Lowe, Saeed Dokhnan, Adam Vallely Farrell, Tony Lowe, WikiSysop, Kim Jackson, Shaimaa Eldib, Lauren Lopez, Sai Kripa and Tarina van der Stockt
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Amputation is the removal of a body extremity by trauma, prolonged constriction, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as malignancy or gangrene. In some cases, it is carried out on individuals as a preventative surgery for such problems. A special case is that of congenital amputation, a congenital disorder, wherefetal limbs have been cut off by constrictive bands. In some countries, amputation of the hands, feet or other body parts is or was used as a form of punishment for people who committed crimes. Amputation has also been used as a tactic in war and acts of terrorism; it may also occur as a war injury.[1]
Causes of amputations [edit | edit source]
Congenital [edit | edit source]
- Congenical limb deficiency [2]
- Phocomelia: "a congenital deformity in which the limbs are extremely shortened so that the feet and hands arise close to the trunk"[3]
Acquired[edit | edit source]
- Vascular
- Ischaemia
- Diabetes
- Frostbite
- Arterial insufficiency leading to death or decay of body tissue (gangrene)
- Chronic leg ulcer leading to Septicaemia
- Malignant tumours e.g. sarcoma (cancer of the connective tissue)
- Trauma e.g. stabbing and gun shoot, car accident, animal bite; in some cases leading to
- Traumatic amputation: a physical separation of the limb in the course of the traumatic event
Types of amputations[edit | edit source]
- Professional - emergency life saving procedure, mainly used when primary healing is delayed e.g infection, ischaemia, .. etc
- Definitive - used after professional amputation
- Anatomical amputations:
- disarticulation e.g. through the ankle joint (Syme's) amputation
- mid shaft amputations e.g. Below the knee, Above the knee ..etc.
Surgical procedures [edit | edit source]
Two surgical procedures
1-myodesis: the muscles and fascia are sutered directly to the distal residual bone for better prosthetic control
2-myoplastic: suture to opposite muscle in the residual limb to to each other and to the periosteum or to the distal end of the cut bone for weight bearing purposes
Ideal stump[edit | edit source]
1-skin flaps: skinshould be mobile , sensation is intact , no scars
2-muscles are divided 3 to 5 cm distal to the level of bone resection
3-nerves are gently pulled and cut cleanly, so that they retract well proximal to the bone level to reduce the complication of neuroma
Location of pulses[edit | edit source]
- Foot pulse (Medial malleolus or dorsum of the foot)
- Popliteal (behind the knee)
- Femoral (within the femoral triangle)
- If a leg has been amputated because of gangrene, the remaining leg is examined for a pulse
Special investigations[edit | edit source]
- X-rays
- CT scan
- Angiogram (outlines blood vessels)
- Doppler ultrasound (occlusion of vessels)
- Venogram and arteriogram
- Radioactive dye injected into the blood
Arterial insufficiency[edit | edit source]
- Surgery to improve circulation
- Bypass grafts (autogenous graft uses a vein to bypass the obstructed area)
- Synthetic grafts
Management[edit | edit source]
Buerger’s exercises[edit | edit source]
| [4] |
- Stimulates collateral blood flow in the patient’s leg
- It is performed for 20 min.
- The leg is elevated until the toes go white, then lowered, then level
- Repeat 2-3 times to improve collateral circulation
Connective tissue massage[edit | edit source]
Dynamic stump exercises[edit | edit source]
Balance and gait retraining[edit | edit source]
- Improve static and dynamic balance
- Use Parallel bars, walking frame then Crutches (in that order)
- Therapist stands on the amp side, using a belt around the patient’s waist to support
- Rest if the patient feels tired
| [5] | [6] |
| [7] | [8] |
Short wave diathermy (SWD)[edit | edit source]
Through the pelvis to warm the arteries (contraindicated in patients with arterial insufficiency because the warmth leads to increased metabolism, causing a greater demand for nutrients, which are not available)
Post-operative care[edit | edit source]
- Maintain function in the remaining leg and stump to maintain peripheral circulation
- Maintain respiratory function (important with smokers and those patients under general anaesthesia)
Stump care[edit | edit source]
| [9] |
- For hygiene and skin care see handout on amputations
- A hip flexion Contracture may develop because of elevation to reduce swelling
- Stump bandaging is done to ‘cone’ the stump, thereby preventing oedema, which occurs because there is no muscle pump and the stump hangs
- Swelling must be prevented to allow proper attachment of the Prosthesis, and the prevention of Pressure sores
- The stump sock is put on first, then the prosthesis
- The prosthesis must be cleaned and maintained (Children who are still growing, grow out of their prostheses)
Types of wheelchairs[edit | edit source]
For double lower limb amputations, the wheels are set further back.
Complications[edit | edit source]
Phantom limb pain
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=14QrMe-OFeMCUTROXREO2Goj4A_9ueFIW_SXkIUqFfh4iIHk-X|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Wikipedia. Amputation. http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Amputation (accessed 29 May 2014).
- ↑ Day HJB. The ISO/ISPO classification of congenital limb deficiency. Prosthetics and Orthotics International 1991; 15: 67-69.
- ↑ MedlinePlus. Medical Dictionary, phocomelia. http://www.merriam-webster.com/medlineplus/phocomelia (accessed 29 May 2014).
- ↑ ladybessviernes, UDM PT Students. Buerger Allen's Exercise. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQUFmOmX35o [last accessed 01/12/12]
- ↑ Clegstories. Gait Training with C-Leg®: Stance Phase Training. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xh4rPJFgRx8 [last accessed 08/12/12]
- ↑ Clegstories. Gait Training with C-Leg®: Swing Phase Training. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E11gQs0oIt0 [last accessed 08/12/12]
- ↑ Clegstories. Clegstories. Gait Training with C-Leg®: Sitting Down and Standing Up. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_lBkrLZ4PGo [last accessed 08/12/12]
- ↑ Clegstories. Gait Training with C-Leg®: Stairs. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z6bvgDaOkcI [last accessed 08/12/12]
- ↑ Richard Major. Physiotherapy Stump or Residual Limb Wrapping. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T1SA_6hzTxQ[last accessed 08/12/12]