Flail Chest: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Sonal Joshi (talk | contribs) (Changes in Introduaction) |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:User Name|Jennifer Lohmus]] and [[User:User Name|Collin Lim]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
[[ | <div class="noeditbox"> This article is currently under review and may not be up to date. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (14/11/2022) </div> | ||
== Introduction == | |||
[[File:Rib Cage.jpg|right|frameless]] | |||
A flail chest is described when a segment of the rib cage breaks due to blunt thoracic trauma and becomes unattached from the chest wall.<ref>Pettiford BL, Luketich JD, Landreneau RJ. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1547412707000072 The management of flail chest]. Thoracic surgery clinics. 2007 Feb 1;17(1):25-33.</ref>It can occur when 3 or more [[ribs]] are broken in at least two places, although not everyone with this type of injury will develop a flail chest. However, when these injuries cause a segment of the chest to move independently, the generation of negative intrapleural pressure indicates a true paradoxical flail segment<ref name=":0">May L, Hillermann C, Patil S. [https://academic.oup.com/bjaed/article/16/1/26/2463139 Rib fracture management]. Bja Education. 2016 Jan 1;16(1):26-32.</ref>. This condition is of clinical significance in elderly patients or patients who have chronic [[COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)|lung disease]], associated with morbidity and mortality. | |||
== Pathophysiology == | == Pathophysiology == | ||
This pathology of rib fracture is associated with decreased chest movement due to pain. This further reduces the tidal volume and may predispose to significant [[atelectasis]], impaired gas exchange in the affected lung beneath the fractured rib, altered in breathing mechanism. All these contributing factors may lead to [[pneumonia]], pulmonary secretion retention and paradoxical chest movement.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|aeOzrwf6y5M|300}}<ref>The First Aid Show. Flail Chest. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aeOzrwf6y5M[last accessed 4/4/2020]</ref> | |||
=== Types === | |||
* Complete | * Complete | ||
* Incomplete | * Incomplete | ||
* Physeal | * Physeal | ||
'''Classification''' according to the nature of the fracture: | '''Classification''' according to the nature of the [[fracture]]: | ||
* Spiral | * Spiral | ||
* Transverse | * Transverse | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
* Compression | * Compression | ||
== Associated | == Associated Conditions == | ||
'''Pulmonary complications''' 48-72 hours after admission | '''Pulmonary complications''' 48-72 hours after admission<ref name=":1">Battle C, Hutchings H, Evans PA. [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1460408613488480?casa_token=W3lXPVP7tXQAAAAA%3AlKXGwqilcXiYb8Og87uF7VZ8ltsDSlWBnJeCj1JIoda6P0B-xPF1THbVOvoDxBvFZO8m38j_KVNnWg Blunt chest wall trauma: a review. Trauma.] 2013 Apr;15(2):156-75.</ref>: | ||
* Haemothorax | * Haemothorax | ||
* Pneumothorax | * [[Pneumothorax]] | ||
* Atelectasis | * [[Atelectasis]] | ||
* Pneumonia | * [[Pneumonia]] | ||
* Pleural effusion | * Pleural effusion | ||
* Subcutaneous emphysema | * Subcutaneous emphysema | ||
* ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) | * ARDS [[Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)|(Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome]]) | ||
* Pulmonary emboli | * [[Pulmonary Embolism|Pulmonary emboli]] | ||
* Aspiration | * Aspiration | ||
* Lobar collapse | * Lobar collapse | ||
'''Risk factors''' for developing associated conditions | '''Risk factors''' for developing associated conditions<ref name=":1" />: | ||
* >65 years old | * Patient >65 years old | ||
* >3 | * rib fractures >3 ribs | ||
* | * History of chronic lung conditions or CVD | ||
* Pre-injury anti-coagulant use | * Pre-injury anti-coagulant use | ||
* <90% | * SpO2 <90% | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
The clinical presentation depends on the severity of the impact, size of the flail segment and to what extent lung affected.<ref name=":2">Jena RK, Agrawal A, Sandeep Y, Shrikhande NN. [http://www.ijsronline.net/article.asp?issn=2321-6662;year=2016;volume=6;issue=1;spage=3;epage=5;aulast=Jena Understanding of flail chest injuries and concepts in management]. International Journal of Students’ Research. 2016 Jan 1;6(1):3.</ref>The patient may complain of severe chest wall pain and may have tachypnea. On close observation there may be paradoxical chest wall movement. On inspiration the flail segment will move inwards whilst the rest of the chest expands and on expiration the flail segment will move outwards whilst the rest of the chest contracts. | |||
If the patient is mechanically ventilated or on Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) it may be difficult to diagnose and may only become obvious after extubation. | |||
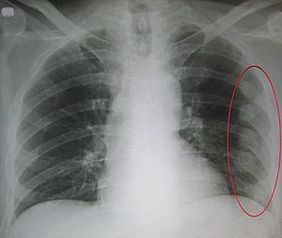
[[File:300px-Fracturedribsmarked.jpg|thumb|282x282px]] | |||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
An abnormal chest movement during breathing may be a sign of flail chest. Radiologists use Chest [[X-Rays]] to look for the following: “Three or more adjacent ribs are fractured in two or more places. Clinically this can be a segment of only one or two ribs can act as a flail segment”. HRCT is more accurate modality in severe blunt trauma. | |||
Radiologists use Chest X-Rays to look for the following: | |||
“Three or more adjacent ribs are fractured in two or more places. Clinically this can be a segment of only one or two ribs can act as a flail segment” | |||
== Outcome Measures == | == Outcome Measures == | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
[https://pulmonaryrehab.com.au/~resources/02_Patient_assessment/04_modified_borg_dyspnoea_scale.pdf Modified BORG Scale] | [https://pulmonaryrehab.com.au/~resources/02_Patient_assessment/04_modified_borg_dyspnoea_scale.pdf Modified BORG Scale] | ||
[https://www.physio-pedia.com/Visual_Analogue_Scale VAS Scale for Pain] | [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Visual_Analogue_Scale VAS Scale for Pain] | ||
== Medical Management == | == Medical Management == | ||
=== Medications === | |||
# Simple Analgesics | # Simple [[Pain Medications|Analgesics]]<ref name=":0" /> | ||
# Opioids | # Opioids like morphin when pain is not controlled with simple analgesics | ||
# Patient Controlled Analgesia | # Patient Controlled Analgesia | ||
# Operative fixation and Regional Anaesthetic | # Operative fixation and Regional Anaesthetic | ||
=== Surgery === | |||
* Regional anesthesia | |||
* Regional | |||
* Serratus anterior block | * Serratus anterior block | ||
* Paravertebral block | * Paravertebral block | ||
* Thoracic epidural | * [[Thoracic Anatomy|Thoracic]] epidural | ||
== | ==== Internal Fixation ==== | ||
* It is a difficult and challenging procedure due to the nature of the rib. | |||
* Decreases stay in ICU and MV duration. | |||
* Incision site is Similar to thoracotomy and the latissmus dorsi muscle wasn't incised. | |||
* Anterior fracture- plates and locking screws | |||
* Posterior fracture - intramedullary splints | |||
== Physiotherapy Management == | |||
Role of chest physiotherapy for inpatient care depend on secretion clearance to prevent respiratory infection, restore normal lung volume, pulmonary function. There's still little information about physical therapy role after discharge from the hospital. | |||
= | Management consists of the following: | ||
* Ventilatory Management - supplemental oxygen therapy, continuous positive airway pressure or intubation if necessary<ref name=":0" /> | |||
** CPAP - for negative intrapleural pressure and paradoxical movement, increases TV | |||
** Open/closed suction if patient intubated. | |||
* [[Pain Assessment|Pain Management]] and Education | |||
** Education on fracture healing | |||
** Early mobilization if possible<ref name=":0" /> to prevent contracture and loss of muscle mass | |||
** Transfers to sitting out of bed | |||
** Mobilization 2-3 times daily and sitting out of bed 3-4 time/day | |||
* Chest and airway clearance techniques (if inadequate) | |||
** ACBT: nebulizer with [[Active Cycle of Breathing Technique|ACBT]] and education | |||
** Bubble PEP or Flutter | |||
* Deep breathing exercises and supported coughing technique | |||
** Supported Cough: Wrap around technique or rolled up towel | |||
** DBE/TEE’s with SMIs (2-4 secs hold) | |||
* Positioning<ref>Berney S, Haines K, Denehy L. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3286496/ Physiotherapy in critical care in Australia]. Cardiopulmonary physical therapy journal. 2012 Mar;23(1):19.</ref> | |||
** Positioning in side lying and high sitting | |||
It was recommended to apply chest physiotherapy after adequate pain relief modalities<ref name=":2" /> | |||
A study<ref>Mohamed HG, Ragab EI, Bary MA, Elshazly M, Latif AF. [https://fnur.stafpu.bu.edu.eg/Medical%20and%20Surgical%20%20Nursing/1873/publications/Hanan%20Gaber%20Mohammed%20Mahmoud_0_ajnr-6-6-15%20(3).pdf The Impact of Chest Physiotherapy Technique (CPT) on Respiration, Pain and Quality of Life Post Thoracic Wall Fixation Surgery among Flail Chest Patients (FC)]. American Journal of Nursing. 2018 Oct 31;6(6):471-83.</ref> done in 2018 in Egypt in patients with flail chest referred for chest physiotherapy showed improved QOL on 1st, 3rd and 6th month follow up of starting the treatment. It included an exercise protocol of, | |||
# Diaphragmatic exercise | |||
# Coughing exercise | |||
# Intermittent pressure breathing | |||
# Secretion mobilization techniques(percussion, vibration & incentive spirometry) | |||
== Resources == | |||
[https://www.rch.org.au/trauma-service/manual/chest-injury/ www.rch.org.au/trauma service/manual/chest-injury] | |||
[https://radiopaedia.org/articles/flail-chest radiopaedia.org articles, flail-chest] | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Acute Care]] | [[Category:Acute Care]] | ||
[[Category:Respiratory]] | [[Category:Respiratory]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiopulmonary]] | |||
[[Category:Acute Respiratory Disorders - Conditions]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:41, 16 November 2023
Introduction[edit | edit source]
A flail chest is described when a segment of the rib cage breaks due to blunt thoracic trauma and becomes unattached from the chest wall.[1]It can occur when 3 or more ribs are broken in at least two places, although not everyone with this type of injury will develop a flail chest. However, when these injuries cause a segment of the chest to move independently, the generation of negative intrapleural pressure indicates a true paradoxical flail segment[2]. This condition is of clinical significance in elderly patients or patients who have chronic lung disease, associated with morbidity and mortality.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
This pathology of rib fracture is associated with decreased chest movement due to pain. This further reduces the tidal volume and may predispose to significant atelectasis, impaired gas exchange in the affected lung beneath the fractured rib, altered in breathing mechanism. All these contributing factors may lead to pneumonia, pulmonary secretion retention and paradoxical chest movement.[2]
Types[edit | edit source]
- Complete
- Incomplete
- Physeal
Classification according to the nature of the fracture:
- Spiral
- Transverse
- Comminuted
- Compression
Associated Conditions[edit | edit source]
Pulmonary complications 48-72 hours after admission[4]:
- Haemothorax
- Pneumothorax
- Atelectasis
- Pneumonia
- Pleural effusion
- Subcutaneous emphysema
- ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome)
- Pulmonary emboli
- Aspiration
- Lobar collapse
Risk factors for developing associated conditions[4]:
- Patient >65 years old
- rib fractures >3 ribs
- History of chronic lung conditions or CVD
- Pre-injury anti-coagulant use
- SpO2 <90%
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
The clinical presentation depends on the severity of the impact, size of the flail segment and to what extent lung affected.[5]The patient may complain of severe chest wall pain and may have tachypnea. On close observation there may be paradoxical chest wall movement. On inspiration the flail segment will move inwards whilst the rest of the chest expands and on expiration the flail segment will move outwards whilst the rest of the chest contracts.
If the patient is mechanically ventilated or on Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) it may be difficult to diagnose and may only become obvious after extubation.
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
An abnormal chest movement during breathing may be a sign of flail chest. Radiologists use Chest X-Rays to look for the following: “Three or more adjacent ribs are fractured in two or more places. Clinically this can be a segment of only one or two ribs can act as a flail segment”. HRCT is more accurate modality in severe blunt trauma.
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
Medications[edit | edit source]
- Simple Analgesics[2]
- Opioids like morphin when pain is not controlled with simple analgesics
- Patient Controlled Analgesia
- Operative fixation and Regional Anaesthetic
Surgery[edit | edit source]
- Regional anesthesia
- Serratus anterior block
- Paravertebral block
- Thoracic epidural
Internal Fixation[edit | edit source]
- It is a difficult and challenging procedure due to the nature of the rib.
- Decreases stay in ICU and MV duration.
- Incision site is Similar to thoracotomy and the latissmus dorsi muscle wasn't incised.
- Anterior fracture- plates and locking screws
- Posterior fracture - intramedullary splints
Physiotherapy Management[edit | edit source]
Role of chest physiotherapy for inpatient care depend on secretion clearance to prevent respiratory infection, restore normal lung volume, pulmonary function. There's still little information about physical therapy role after discharge from the hospital.
Management consists of the following:
- Ventilatory Management - supplemental oxygen therapy, continuous positive airway pressure or intubation if necessary[2]
- CPAP - for negative intrapleural pressure and paradoxical movement, increases TV
- Open/closed suction if patient intubated.
- Pain Management and Education
- Education on fracture healing
- Early mobilization if possible[2] to prevent contracture and loss of muscle mass
- Transfers to sitting out of bed
- Mobilization 2-3 times daily and sitting out of bed 3-4 time/day
- Chest and airway clearance techniques (if inadequate)
- ACBT: nebulizer with ACBT and education
- Bubble PEP or Flutter
- Deep breathing exercises and supported coughing technique
- Supported Cough: Wrap around technique or rolled up towel
- DBE/TEE’s with SMIs (2-4 secs hold)
- Positioning[6]
- Positioning in side lying and high sitting
It was recommended to apply chest physiotherapy after adequate pain relief modalities[5]
A study[7] done in 2018 in Egypt in patients with flail chest referred for chest physiotherapy showed improved QOL on 1st, 3rd and 6th month follow up of starting the treatment. It included an exercise protocol of,
- Diaphragmatic exercise
- Coughing exercise
- Intermittent pressure breathing
- Secretion mobilization techniques(percussion, vibration & incentive spirometry)
Resources[edit | edit source]
www.rch.org.au/trauma service/manual/chest-injury
radiopaedia.org articles, flail-chest
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Pettiford BL, Luketich JD, Landreneau RJ. The management of flail chest. Thoracic surgery clinics. 2007 Feb 1;17(1):25-33.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 May L, Hillermann C, Patil S. Rib fracture management. Bja Education. 2016 Jan 1;16(1):26-32.
- ↑ The First Aid Show. Flail Chest. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aeOzrwf6y5M[last accessed 4/4/2020]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Battle C, Hutchings H, Evans PA. Blunt chest wall trauma: a review. Trauma. 2013 Apr;15(2):156-75.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Jena RK, Agrawal A, Sandeep Y, Shrikhande NN. Understanding of flail chest injuries and concepts in management. International Journal of Students’ Research. 2016 Jan 1;6(1):3.
- ↑ Berney S, Haines K, Denehy L. Physiotherapy in critical care in Australia. Cardiopulmonary physical therapy journal. 2012 Mar;23(1):19.
- ↑ Mohamed HG, Ragab EI, Bary MA, Elshazly M, Latif AF. The Impact of Chest Physiotherapy Technique (CPT) on Respiration, Pain and Quality of Life Post Thoracic Wall Fixation Surgery among Flail Chest Patients (FC). American Journal of Nursing. 2018 Oct 31;6(6):471-83.