Arterial Blood Gases: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Image:ABG.jpg|thumb|right|241x241px|Blood Gas Analyser]]Arterial blood gases (ABG's) is a blood test which is used to give an indication of ventilation, gas exchange and acid-base status and is taken from an arterial blood supply<ref name="Hough">Hough A. Physiotherapy in Respiratory Care. An evidence based-approach to respiratory and cardiac managemenmt. 3rd ed. Cheltenham: Nelson Thomas Ltd. 2001</ref>. The arterial blood gas test is one of the most common tests performed on patients in intensive care units. At other levels of care, [[Pulse Oximeter|pulse oximetry]] plus transcutaneous carbon dioxide measurement is a less invasive alternative method of obtaining similar information.<ref name=":0">Scope health Arterial Gasometry: What is it? Why is it Necessary? Procedure, Compensation, Metabolic Disorders and Results Available: https://scopeheal.com/arterial-blood-gas/ (accessed 9.5.2022)</ref> | [[Image:ABG.jpg|thumb|right|241x241px|Blood Gas Analyser]]Arterial blood gases (ABG's) is a blood test which is used to give an indication of ventilation, gas exchange and acid-base status and is taken from an arterial blood supply<ref name="Hough">Hough A. Physiotherapy in Respiratory Care. An evidence based-approach to respiratory and cardiac managemenmt. 3rd ed. Cheltenham: Nelson Thomas Ltd. 2001</ref>. The arterial blood gas test is one of the most common tests performed on patients in intensive care units. At other levels of care, [[Pulse Oximeter|pulse oximetry]] plus transcutaneous carbon dioxide measurement is a less invasive alternative method of obtaining similar information.<ref name=":0">Scope health Arterial Gasometry: What is it? Why is it Necessary? Procedure, Compensation, Metabolic Disorders and Results Available: https://scopeheal.com/arterial-blood-gas/ (accessed 9.5.2022)</ref> | ||
To perform this test, blood is collected from a specific artery, usually the radial artery of the wrist. This blood sample allows an accurate determination of the amount of oxygen that passes from the lungs to the blood. This test is the one most commonly performed to diagnose cases of [[Respiratory Failure|respiratory failure]]<ref name=":4">Well being pole Gasometry Available:https://wellbeingpole.com/gasometry/ (accessed 9.5.2022)</ref>. | To perform this test, blood is collected from a specific artery, usually the radial artery of the wrist. This blood sample allows an accurate determination of the amount of oxygen that passes from the lungs to the blood. This test is the one most commonly performed to diagnose cases of [[Respiratory Failure|respiratory failure]]<ref name=":4">Well being pole Gasometry Available:https://wellbeingpole.com/gasometry/ (accessed 9.5.2022)</ref>.<br>Arterial blood gas test results can show if: | ||
<br>Arterial blood gas test results can show if: | |||
* Lungs are getting enough oxygen. | * Lungs are getting enough oxygen. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 35: | ||
* Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2): 35-45 mmHg | * Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2): 35-45 mmHg | ||
* Bicarbonate (HCO3): 22-26 mEq/L | * Bicarbonate (HCO3): 22-26 mEq/L | ||
* Oxygen saturation (O2 Sat): 94-100% | * Oxygen saturation (O2 Sat): 94-100%<ref>Nurse org. ABG test Available:https://nurse.org/articles/arterial-blood-gas-test/ (accessed 9.5.2022)</ref> | ||
== Interpretation of ABGs == | == Interpretation of ABGs == | ||
Revision as of 02:18, 9 May 2022
Original Editor - Scott Buxton
Top Contributors - Adam Vallely Farrell, Kim Jackson, Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka, Scott Buxton, Lucinda hampton, Rachael Lowe, Admin, Joao Costa, 127.0.0.1, Laura Ritchie, Naomi O'Reilly, Abbey Wright and Angeliki Chorti
Arterial Blood Gases[edit | edit source]
Arterial blood gases (ABG's) is a blood test which is used to give an indication of ventilation, gas exchange and acid-base status and is taken from an arterial blood supply[1]. The arterial blood gas test is one of the most common tests performed on patients in intensive care units. At other levels of care, pulse oximetry plus transcutaneous carbon dioxide measurement is a less invasive alternative method of obtaining similar information.[2]
To perform this test, blood is collected from a specific artery, usually the radial artery of the wrist. This blood sample allows an accurate determination of the amount of oxygen that passes from the lungs to the blood. This test is the one most commonly performed to diagnose cases of respiratory failure[3].
Arterial blood gas test results can show if:
- Lungs are getting enough oxygen.
- Lungs are removing enough carbon dioxide.
- Kidneys are working properly.[2]
Uses[edit | edit source]
ABGs are very useful for detecting conditions that cause respiratory failure. Including: Asthma; Pulmonary fibrosis; Pulmonary edema; Hypoventilation; Hyperventilation; Sepsis; Renal metabolism disorder.[3]
Measurements[edit | edit source]
The key components to an ABG are:
- pH - This measures the balance of acids and bases in your blood.
- Partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) - This measures the pressure of oxygen dissolved in your blood.
- Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) - This measures the amount of carbon dioxide in your blood and how well carbon dioxide can move out of your body.
- Bicarbonate (HCO3) - This is calculated using the measured values of pH and PaCO2 to determine the amount of the basic compound made from carbon dioxide (CO2.)
- Oxygen saturation (O2 Sat) - This measures how much hemoglobin in your blood is carrying oxygen.
- Oxygen content (O2CT) - This measures the amount of oxygen in your blood.
- Hemoglobin - This measures the amount of hemoglobin in your blood.
Normative Values[edit | edit source]
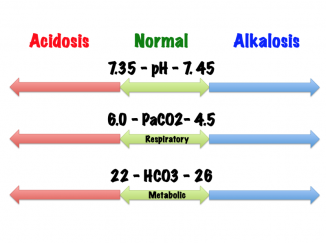
According to the National Institute of Health, typical normal values are:
- pH: 7.35-7.45
- Partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2): 75 to 100 mmHg
- Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2): 35-45 mmHg
- Bicarbonate (HCO3): 22-26 mEq/L
- Oxygen saturation (O2 Sat): 94-100%[4]
Interpretation of ABGs[edit | edit source]
- Look at the pH
- Increased = Alkalosis
- Decreased = Acidosis
- Look at the PaCO2
- Increased = Respiratory Acidosis
- Decreased = Respiratory Alkalosis
- Look at the HCO3
- Increased = Metabolic Alkalosis
- Decreased = Metabolic Acidosis
- Look at the O2
The results should always be read and compared in reference to the patients previous ABG (if available) as you will then be able to assess a trend and make a more accurate assessment on whether you should treat or if your treatment has be successful or not.
Tutorials[edit | edit source]
Useful Resources[edit | edit source]
Associated Topics[edit | edit source]
- Respiratory Failure
- Hypoxaemia
- Oxygen Therapy
- Oxygen Dissociation Cure
- Anaemia
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Hough A. Physiotherapy in Respiratory Care. An evidence based-approach to respiratory and cardiac managemenmt. 3rd ed. Cheltenham: Nelson Thomas Ltd. 2001
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Scope health Arterial Gasometry: What is it? Why is it Necessary? Procedure, Compensation, Metabolic Disorders and Results Available: https://scopeheal.com/arterial-blood-gas/ (accessed 9.5.2022)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Well being pole Gasometry Available:https://wellbeingpole.com/gasometry/ (accessed 9.5.2022)
- ↑ Nurse org. ABG test Available:https://nurse.org/articles/arterial-blood-gas-test/ (accessed 9.5.2022)
- ↑ https://ed.ted.com/on/9q9pS35Z
- ↑ Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Tic-Tac-Toe Examples. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_OpvyEIlFj8[last accessed 27/03/18]
- ↑ 6 Easy Steps to ABG Analysis. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WUf-cPpnrXw[last accessed 27/03/18]
- ↑ ABGs (Arterial Blood Gas). Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kfJws8NQW1k[last accessed 27/03/18]