Frontotemporal Dementia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Frontotemporal Dementia age of onset can be as early as the age of 40, with 54 being the average age of onset, and is often misdiagnosed in younger adults as a psychiatric issue and in older adults as [[Alzheimer's Disease|Alzheimer’s]]. Older adults can start to see symptoms all the way into their 80s <ref>Stages of Frontotemporal Dementia: Symptoms, Age of Onset, Risk Factors, Life Expectancy. Available from://www.griswoldhomecare.com/blog/2018/june/stages-of-frontotemporal-dementia-symptoms-age-o/ ( Accessed, 09/08/2021).</ref> . | Frontotemporal Dementia age of onset can be as early as the age of 40, with 54 being the average age of onset, and is often misdiagnosed in younger adults as a psychiatric issue and in older adults as [[Alzheimer's Disease|Alzheimer’s]]. Older adults can start to see symptoms all the way into their 80s <ref>Stages of Frontotemporal Dementia: Symptoms, Age of Onset, Risk Factors, Life Expectancy. Available from://www.griswoldhomecare.com/blog/2018/june/stages-of-frontotemporal-dementia-symptoms-age-o/ ( Accessed, 09/08/2021).</ref> . | ||
{{#ev:youtube|v=QuJFLr5Ib9k|width}} | |||
== Viewing == | |||
This 3 minute video is a good introduction. | |||
{{#ev:youtube|v=QuJFLr5Ib9k|width}}<ref>Alzheimer's Society What is FTD Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QuJFLr5Ib9k<nowiki/>(accessed 15.3.2022)</ref> | |||
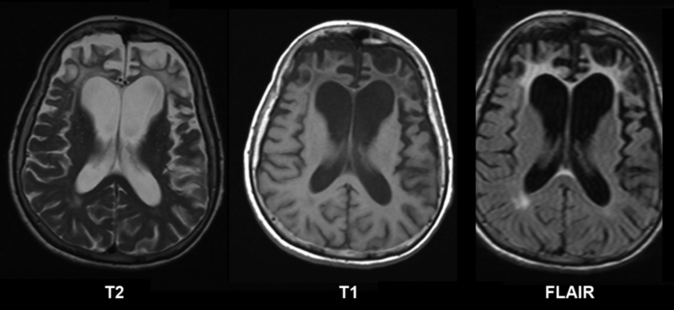
Below: [[Brain Anatomy|Brain]] MRI of a female of 65 years with frontotemporal dementia. [[Cerebral Cortex|Cortical]] and white matter atrophy of the frontal lobes is clear in all images.[[File:Pick's disease.png|center|674x674px]] | Below: [[Brain Anatomy|Brain]] MRI of a female of 65 years with frontotemporal dementia. [[Cerebral Cortex|Cortical]] and white matter atrophy of the frontal lobes is clear in all images.[[File:Pick's disease.png|center|674x674px]] | ||
Revision as of 02:40, 15 March 2022
Description[edit | edit source]
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) is the pathological description of a group of neurodegenerative disorders characterised by focal atrophy of the frontal and/or temporal cortices. These results in variable clinical manifestations collectively known as frontotemporal dementia (FTD) syndromes.
There are three types of frontotemporal disorders (FTD):
- Behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD)
- Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) aka language variant frontotemporal dementia (lvFTD); non-fluent variant primary progressive aphasia (nfvPPA); semantic variant primary progressive aphasia (svPPA); logopaenic variant primary progressive aphasia (lvPPA)
- Motor disorders: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); Corticobasal degeneration; Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP)[1]
Note: The motor disorders are generally considered separate entities but, however, frequently have overlapping features of FTD
Frontotemporal Dementia age of onset can be as early as the age of 40, with 54 being the average age of onset, and is often misdiagnosed in younger adults as a psychiatric issue and in older adults as Alzheimer’s. Older adults can start to see symptoms all the way into their 80s [2] .
Viewing[edit | edit source]
This 3 minute video is a good introduction.
Below: Brain MRI of a female of 65 years with frontotemporal dementia. Cortical and white matter atrophy of the frontal lobes is clear in all images.
Etiology[edit | edit source]
Scientists are beginning to understand the biological and genetic basis for the changes observed in brain cells that lead to FTD. FTLD is an umbrella term for a heterogeneous group of diseases that can be characterised based on the type of glial and neuronal proteinaceous inclusions or underlying genetic mutation. Three major types of FTLD based on of the type of proteinaceous inclusions:
- FTLD-tau: misfolded tau protein (see tauopathies)
- FTLD-TDP: transactive response DNA binding protein 43 (TDP-43)
- FTLD-FUS: fused in sarcoma protein (rare)
In most cases, the cause of a FTD is unknown. Individuals with a family history of FTD are more likely to develop such a disorder. About 10 to 30% of bvFTD is due to specific genetic mutations including:
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of FTD are often misunderstood. Family members and friends may think that a person is misbehaving, leading to anger and conflict. It is important to understand that people with these disorders cannot control their behaviors and other symptoms and lack any awareness of their illness.
The three types of frontotemporal disorders (FTD present differently
1.Behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia: The most common FTD, bvFTD, involves changes in personality, behavior, and judgment. People with this disorder may have problems with cognition, but their memory may stay relatively intact. Symptoms can include:
- Problems planning and sequencing (thinking through which steps come first, second, and so on)
- Difficulty prioritizing tasks or activities
- Repeating the same activity or saying the same word over and over
- Acting impulsively or saying or doing inappropriate things without considering how others perceive the behavior
- Becoming disinterested in family or activities they used to care about
- Over time, language and/or movement problems may occur, and the person living with bvFTD will need more care and supervision.
2. Primary progressive aphasia PPA: involves changes in the ability to communicate (use of language to speak, read, write, and understand what others are saying). This includes difficulty using or understanding words (aphasia) and difficulty speaking properly (e.g., slurred speech). People with PPA may have one or both of these symptoms. They may become mute or unable to speak. Many people with PPA develop symptoms of dementia. Problems with memory, reasoning, and judgment are not apparent at first but can develop over time. In addition, some people with PPA may experience significant behavioral changes, similar to those seen in bvFTD, as the disease progresses.
3. Motor disorders: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); Corticobasal degeneration; Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), rare neurological movement disorders associated with FTD, may affect thinking and language abilities.[1][4]
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
FTD can be hard to diagnose because the symptoms are similar to those of other conditions.
Many different tools are used to diagnose FTD. The medical history of the patient as well as special imaging tests and lab tests are some of the tools to help make a diagnosis. The diagnosis is made on a clinical basis, although genetic testing can confirm some specific subtypes [5].
The below may help with diagnosis
- Subjective and objective examination
- Personal and family medical history
- Laboratory tests to help rule out other conditions
- Genetic testing
- Conduct tests to assess memory, thinking, language skills, and physical functioning
- Order imaging of the brain[4]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
So far, there is no cure for FTD and no way to slow down or prevent these diseases. However, there are ways to manage symptoms. A team of specialists eg doctors, physical, speech, and occupational therapists, familiar with these disorders can help guide treatment.
1. Non Drug Treatment [6]
- Interventions for helping or adjusting behaviors.
- Speech Therapy to improve communication abilities.
- Antidepressant and antipsychotic medications for emotional and behavioral changes.
- Cholinesterase inhibitors for memory and attention.
- Antioxidant tocopherol (vitamin E) to counteract the damage in brain cells that causes PiD/ FTD and slow the worsening of the disease.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs and hormone replacement therapy are also being used by some specialists who treat PiD/ FTD as experimental treatments and are therefore not widely accepted.
Life with FTD - Home Care Program[edit | edit source]
It is recommended for People with FTD to remain physically, mentally and socially active as long as they can. In order to this, they need to:
- Daily physical activity such as walking for at least 20 minutes.
- Mental activity and stimulation such as puzzles, games, reading to slow the progression of the disease.
- Social interaction is recommended as a stimulating and enjoyable activity.
- Have balanced diet to maintain a healthy weight and prevent malnutrition and constipation.
- Smoking is prohibited for health and safety reasons.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Radiopedia Frontotemporal lobar degeneration Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/frontotemporal-lobar-degeneration-1(accessed 15.3.2022)
- ↑ Stages of Frontotemporal Dementia: Symptoms, Age of Onset, Risk Factors, Life Expectancy. Available from://www.griswoldhomecare.com/blog/2018/june/stages-of-frontotemporal-dementia-symptoms-age-o/ ( Accessed, 09/08/2021).
- ↑ Alzheimer's Society What is FTD Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QuJFLr5Ib9k(accessed 15.3.2022)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 NIH What Are Frontotemporal Disorders? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Available:https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-are-frontotemporal-disorders (accessed 15.3.22)
- ↑ What is Pick’s Disease? Available from: https://www.brightfocus.org/alzheimers-disease/article/what-picks-disease (Accessed, 01/08/2021).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Pick Disease. Available from: https://www.emedicinehealth.com/pick_disease/article_em.htm (Accessed, 05/08/2021).
- ↑ Pick Disease of the Brain: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/health/picks-disease#symptoms (Accessed, 01/08/2021).
- ↑ The Audiopedia. What is Pick’s DISEASE? What does PICK’S DISEASE mean? PICK’S DISEASE meaning & explanation. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ILn2LNzevdc [Accessed, 06/08/2021]
- ↑ Brain and Beyond. What is Frontotemporal Dementia and Pick's Disease? Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fbLeQXi4RW8[Accessed, 06/08/2021]