Myoglobin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Myoglobin (Hb) is an iron-containing heme protein that is present predominantly in the sarcoplasm of skeletal and cardiac | [[File:Myoglobin and heme.png|right|frameless]] | ||
Myoglobin (Hb) is an [[iron]]-containing heme [[Proteins|protein]] that is present predominantly in the sarcoplasm of [[Muscle Cells (Myocyte)|skeletal]] and [[Muscle: Cardiac|cardiac muscle]]<nowiki/>s. Due to the presence of heme moiety, myoglobin serves as a carrier and store for oxygen in muscle cells of the body. Myoglobin has more affinity for oxygen as compared to hemoglobin. As a result, it can acquire oxygen from hemoglobin, hence transferring it from the [[blood]] to the muscle tissues.<ref>Anwar MY, Gupta V. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557379/ Myoglobinuria]. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021 Feb 6.Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557379/ (accessed 23.11.2021)</ref> | |||
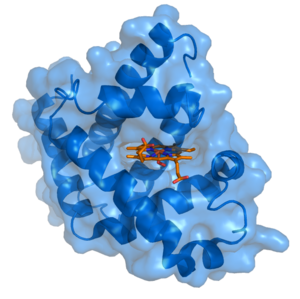
IMAGE 1: Cartoon representation of Myoglobin (blue) with heme group (orange) | |||
Here is the basic information Mb. | Here is the basic information Mb. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 14: | ||
* It is a low molecular weight oxygen-binding heme protein and is one of the most important proteins in the human body. | * It is a low molecular weight oxygen-binding heme protein and is one of the most important proteins in the human body. | ||
* It acts as an oxygen reservoir unit, suppling oxygen to working muscles. | * It acts as an oxygen reservoir unit, suppling oxygen to working muscles. | ||
* It is mainly found in the heart and skeletal muscle cells, occurring in the highest concentration in the striated muscles of vertebrates. | * It is mainly found in the [[Anatomy of the Human Heart|heart]] and [[Muscle|skeletal muscle]] cells, occurring in the highest concentration in the striated muscles of vertebrates. | ||
* In skeletal muscle it serves to transport oxygen from the cell membrane to the mitochondria. | * In skeletal muscle it serves to transport oxygen from the cell membrane to the [[mitochondria]]. | ||
* Diving mammals such as seals and whales are able to remain submerged for long periods because they have greater amounts of myoglobin in their muscles than other animals do<ref>Biochem [https://biochemden.com/myoglobin/ Myoglobin] Available:https://biochemden.com/myoglobin/ (accessed 23.11.2021)</ref>. | * Diving mammals such as seals and whales are able to remain submerged for long periods because they have greater amounts of myoglobin in their muscles than other animals do<ref>Biochem [https://biochemden.com/myoglobin/ Myoglobin] Available:https://biochemden.com/myoglobin/ (accessed 23.11.2021)</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 05:39, 23 November 2021
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Myoglobin (Hb) is an iron-containing heme protein that is present predominantly in the sarcoplasm of skeletal and cardiac muscles. Due to the presence of heme moiety, myoglobin serves as a carrier and store for oxygen in muscle cells of the body. Myoglobin has more affinity for oxygen as compared to hemoglobin. As a result, it can acquire oxygen from hemoglobin, hence transferring it from the blood to the muscle tissues.[1]
IMAGE 1: Cartoon representation of Myoglobin (blue) with heme group (orange)
Here is the basic information Mb.
- It is a low molecular weight oxygen-binding heme protein and is one of the most important proteins in the human body.
- It acts as an oxygen reservoir unit, suppling oxygen to working muscles.
- It is mainly found in the heart and skeletal muscle cells, occurring in the highest concentration in the striated muscles of vertebrates.
- In skeletal muscle it serves to transport oxygen from the cell membrane to the mitochondria.
- Diving mammals such as seals and whales are able to remain submerged for long periods because they have greater amounts of myoglobin in their muscles than other animals do[2].
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Anwar MY, Gupta V. Myoglobinuria. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021 Feb 6.Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557379/ (accessed 23.11.2021)
- ↑ Biochem Myoglobin Available:https://biochemden.com/myoglobin/ (accessed 23.11.2021)