Flail Chest: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
If the patient is mechanically ventilated or on Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) it may be difficult to diagnose and may only become obvious after extubation. | If the patient is mechanically ventilated or on Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) it may be difficult to diagnose and may only become obvious after extubation. | ||
[[File:300px-Fracturedribsmarked.jpg|thumb|282x282px]] | |||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
An abnormal chest movement during breathing may be a sign of flail chest. | |||
Radiologists use Chest X-Rays to look for the following: | Radiologists use Chest X-Rays to look for the following: | ||
“Three or more adjacent ribs are fractured in two or more places. Clinically this can be a segment of only one or two ribs can act as a flail segment” | “Three or more adjacent ribs are fractured in two or more places. Clinically this can be a segment of only one or two ribs can act as a flail segment”<br>CT is more accurate modality in sever blunt trauma. | ||
== Outcome Measures == | == Outcome Measures == | ||
| Line 54: | Line 56: | ||
[https://pulmonaryrehab.com.au/~resources/02_Patient_assessment/04_modified_borg_dyspnoea_scale.pdf Modified BORG Scale] | [https://pulmonaryrehab.com.au/~resources/02_Patient_assessment/04_modified_borg_dyspnoea_scale.pdf Modified BORG Scale] | ||
[https://www.physio-pedia.com/Visual_Analogue_Scale VAS Scale for Pain] | [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Visual_Analogue_Scale VAS Scale for Pain] | ||
== Physiotherapy Management / Interventions == | == Management == | ||
The management of flail chest or blunt chest trauma depend mainly on adequate pain control, respiratory management | |||
=== Medical Management<ref name=":0" /> === | |||
==== '''Medications''': ==== | |||
# Simple Analgesics | |||
# Opioids like morphin when pain didn't controlled with analgesic | |||
# Patient Controlled Analgesia | |||
# Operative fixation and Regional Anaesthetic | |||
==== '''Surgery''': ==== | |||
'''''Conservative''''' | |||
* Regional anesthesia | |||
* Serratus anterior block | |||
* Paravertebral block | |||
* Thoracic epidural | |||
'''''Internal fixation''''' | |||
* It's difficult and challenging procedure due to the nature of rib . | |||
* Decreases stay in ICU and MV duration.. | |||
* Incision site is Similar to thoracotomy and the latissmus dorsi muscle wasn't incised. | |||
* Anterior fracture- plates and locking screws | |||
* Posterior fracture - intramedullary splints | |||
=== Physiotherapy Management / Interventions === | |||
Chest physiotherapy management consists of the following: | Chest physiotherapy management consists of the following: | ||
| Line 65: | Line 91: | ||
2. Pain Management and Education (May, Hillermann & Patil, 2016) | 2. Pain Management and Education (May, Hillermann & Patil, 2016) | ||
* Education on fracture healing | * Education on fracture healing | ||
3. Early mobilization if possible | 3. Early mobilization if possible<ref name=":0" /> | ||
* Transfers to sitting out of bed | * Transfers to sitting out of bed | ||
* Mobilization 2-3x daily and SOOB 3-4x/day | * Mobilization 2-3x daily and SOOB 3-4x/day | ||
| Line 77: | Line 103: | ||
* Positioning in side lying and high sitting | * Positioning in side lying and high sitting | ||
== | == Resources == | ||
[http://cochranelibrary-wiley.com/store/10.1002/14651858.CD009919.pub2/asset/CD009919.pdf?v=1&t=jifoudyr&s=e7896e4d8456ad584d26733382cd346002f2a11e cochranelibrary wiley.com] | |||
[https://www.rch.org.au/trauma-service/manual/chest-injury/ www.rch.org.au/trauma service/manual/chest-injury] | |||
[https://www.wcpt.org/wcpt2017/FS-01 www.wcpt.org] | |||
https:// | [https://radiopaedia.org/articles/flail-chest radiopaedia.org articles, flail-chest] | ||
== References == | |||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 117: | Line 127: | ||
7. Solomon L. Apley's concise system of orthopaedics and fractures. 3rd ed.. ed. Warwick D, Nayagam S, Apley AG, editors. London : New York: London : Hodder Arnold New York : Distributed in the United States by Oxford University Press; 2005. | 7. Solomon L. Apley's concise system of orthopaedics and fractures. 3rd ed.. ed. Warwick D, Nayagam S, Apley AG, editors. London : New York: London : Hodder Arnold New York : Distributed in the United States by Oxford University Press; 2005. | ||
[[Category:Acute Care]] | [[Category:Acute Care]] | ||
[[Category:Respiratory]] | [[Category:Respiratory]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiopulmonary]] | [[Category:Cardiopulmonary]] | ||
[[Category:Acute Respiratory Disorders - Conditions]] | [[Category:Acute Respiratory Disorders - Conditions]] | ||
Revision as of 20:31, 4 April 2020
This article is currently under review and may not be up to date. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (Template:4/Template:4/Template:2020)
Introduction[edit | edit source]
A flail segment is a portion of the rib cage that breaks due to blunt thoracic trauma, high speed motor vehicle crash and becomes unattached from the chest wall.[1]It can occur when 3 or more ribs are broken in at least two places, although not everyone with type of injury will develop a flail chest. However, if these injuries cause a segment of the chest to move independently, Generation of negative intrapleural pressure indicates a true paradoxical flail segment[2]. This condition is of clinical significance in elderly patients or patients who have chronic lung disease, associated with morbidity and mortality.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
This pathology of rib fracture associated with decrease chest movement due to pain that reduces the tidal volume and may predispose to significant atelectasis, impaired gas exchange in the in affected lung beneath the fractured rib, altered in breathing mechanism. All these contributing factors may predispose later to pneumonia and pulmonary secretions retention, paradoxical chest movement.[2]
Types:
- Complete
- Incomplete
- Physeal
Classification according to the nature of the fracture:
- Spiral
- Transverse
- Comminuted
- Compression
Associated conditions:[edit | edit source]
Pulmonary complications 48-72 hours after admission[4]:
- Haemothorax
- Pneumothorax
- Atelectasis
- Pneumonia
- Pleural effusion
- Subcutaneous emphysema
- ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome)
- Pulmonary emboli
- Aspiration
- Lobar collapse
Risk factors for developing associated conditions[4]:
- Patient >65 years old
- rib fractures >3 ribs
- History of chronic lung conditions or CVD
- Pre-injury anti-coagulant use
- SpO2 <90%
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
The patient may complain of severe chest wall pain and may have tachypnea. On close observation there may be paradoxical chest wall movement. On inspiration the flail segment will move inwards whilst the rest of the chest expands and on expiration the flail segment will move outwards whilst the rest of the chest contracts.
If the patient is mechanically ventilated or on Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) it may be difficult to diagnose and may only become obvious after extubation.
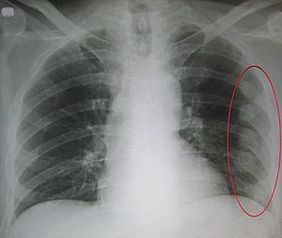
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
An abnormal chest movement during breathing may be a sign of flail chest.
Radiologists use Chest X-Rays to look for the following:
“Three or more adjacent ribs are fractured in two or more places. Clinically this can be a segment of only one or two ribs can act as a flail segment”
CT is more accurate modality in sever blunt trauma.
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Management[edit | edit source]
The management of flail chest or blunt chest trauma depend mainly on adequate pain control, respiratory management
Medical Management[2][edit | edit source]
Medications:[edit | edit source]
- Simple Analgesics
- Opioids like morphin when pain didn't controlled with analgesic
- Patient Controlled Analgesia
- Operative fixation and Regional Anaesthetic
Surgery:[edit | edit source]
Conservative
- Regional anesthesia
- Serratus anterior block
- Paravertebral block
- Thoracic epidural
Internal fixation
- It's difficult and challenging procedure due to the nature of rib .
- Decreases stay in ICU and MV duration..
- Incision site is Similar to thoracotomy and the latissmus dorsi muscle wasn't incised.
- Anterior fracture- plates and locking screws
- Posterior fracture - intramedullary splints
Physiotherapy Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
Chest physiotherapy management consists of the following:
1. Ventilatory Management - supplemental oxygen therapy, continuous positive airway pressure or intubation if necessary (May, Hillermann & Patil, 2016)
- CPAP - for negative intrapleural pressure and paradoxical movement, increases TV (May, Hillermann & Patil, 2015)
- Open/closed suction if patient intubated (Berney, Haines & Denehy, 2012)
2. Pain Management and Education (May, Hillermann & Patil, 2016)
- Education on fracture healing
3. Early mobilization if possible[2]
- Transfers to sitting out of bed
- Mobilization 2-3x daily and SOOB 3-4x/day
4. Chest and airway clearance techniques (if inadequate) (May, Hillermann & Patil, 2016)
- ACT: nebulizer with ACBT and education
- Bubble PEP or Flutter
5. Deep breathing exercises and supported coughing technique (May, Hillermann & Patil, 2016)
- Supported Cough: Wrap around technique or rolled up towel
- DBE/TEE’s with SMIs (2-4 secs hold)
6. Positioning (Berney, Haines & Denehy, 2012)
- Positioning in side lying and high sitting
Resources[edit | edit source]
www.rch.org.au/trauma service/manual/chest-injury
radiopaedia.org articles, flail-chest
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Pettiford BL, Luketich JD, Landreneau RJ. The management of flail chest. Thoracic surgery clinics. 2007 Feb 1;17(1):25-33.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 May L, Hillermann C, Patil S. Rib fracture management. Bja Education. 2016 Jan 1;16(1):26-32.
- ↑ The First Aid Show. Flail Chest. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aeOzrwf6y5M[last accessed 4/4/2020]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Battle C, Hutchings H, Evans PA. Blunt chest wall trauma: a review. Trauma. 2013 Apr;15(2):156-75.
References[edit | edit source]
- Battle C, Hutchings H, Evans PA. Blunt chest wall trauma: A review. Trauma. 2013;15(2):156-75.
2. Berney S, Haines K, Denehy L. Physiotherapy in Critical Care in Australia. Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy. 2012;23(1):19-25.
3. Jena R, Agrawal A, Sandeep Y, Shrikhande N. Understanding of flail chest injuries and concepts in management. International Journal of Studentsí Research. 2016;6(1):3-5.
4. Leinicke AJ, Elmore DL, Freeman AB, Colditz AG. Operative Management of Rib Fractures in the Setting of Flail Chest: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Annals of Surgery. 2013;258(6):914-21.
5. May L, Hillermann C, Patil S. Rib fracture management. BJA Education. 2016;16(1):26-32.
6. Pettiford BL, Luketich JD, Landreneau RJ. The Management of Flail Chest. Thoracic Surgery Clinics. 2007;17(1):25-33.
7. Solomon L. Apley's concise system of orthopaedics and fractures. 3rd ed.. ed. Warwick D, Nayagam S, Apley AG, editors. London : New York: London : Hodder Arnold New York : Distributed in the United States by Oxford University Press; 2005.