Peroneus (Fibularis) Longus Muscle: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
* Head and proximal two-thirds of the lateral surface of [[fibula]] | * Head and proximal two-thirds of the lateral surface of [[fibula]] | ||
* Intermuscular septa | * Intermuscular septa | ||
* Adjacent deep fascia<ref name=":0" /><ref>Peroneus Longus and Brevis. In: Kendall FP, McCreary EK, Provance PG. Muscle Testing and Function, 4th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1993. p.203.</ref> | * Adjacent deep fascia<ref name=":0">Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.</ref><ref>Peroneus Longus and Brevis. In: Kendall FP, McCreary EK, Provance PG. Muscle Testing and Function, 4th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1993. p.203.</ref> | ||
[[File:Peroneo_largo.jpg|thumb|281x281px]] | [[File:Peroneo_largo.jpg|thumb|281x281px]] | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
* In weight-bearing position depresses head of first metatarsal due to the strong pull on its insertion | * In weight-bearing position depresses head of first metatarsal due to the strong pull on its insertion | ||
* Maintains the transverse arch of the foot as a result of how it crosses the sole of the [[Foot Anatomy|foot]]. | * Maintains the transverse arch of the foot as a result of how it crosses the sole of the [[Foot Anatomy|foot]]. | ||
* Steadies the leg on the foot in single leg stance by drawing on the lateral leg, and stops it from collapsing medially.<ref name=":0" / | * Steadies the leg on the foot in single leg stance by drawing on the lateral leg, and stops it from collapsing medially.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
{{#ev:youtube|v_0TSoPzd3A|500}} <ref>Ebraheim N. Anatomy Of The Peroneus Longus Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v_0TSoPzd3A (accessed 17/06/2018). </ref> | {{#ev:youtube|v_0TSoPzd3A|500}} <ref>Ebraheim N. Anatomy Of The Peroneus Longus Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v_0TSoPzd3A (accessed 17/06/2018). </ref> | ||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
Peroneal tendon injuries are most commonly present in patients that are young, active, and in those who participate in sports such as football, soccer, and running. Injury to the peroneus longus tendon can cause lateral ankle pain and may lead to ankle instability.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
The peroneus longus muscle is susceptible to several pathologies, including: | |||
* [[Peroneal Tendinopathy|Peroneal tendinopathy]] | * [[Peroneal Tendinopathy|Peroneal tendinopathy]] | ||
* [[Peroneal tendon subluxation]] | * [[Peroneal tendon subluxation]] | ||
| Line 47: | Line 48: | ||
** Allows a varus position of the foot | ** Allows a varus position of the foot | ||
* Contracture/shortening: Results into an everted or valgus [[Foot Anatomy|foot]]. | * Contracture/shortening: Results into an everted or valgus [[Foot Anatomy|foot]]. | ||
* Peroneus longus muscles and tendon tears | * Peroneus longus muscles and tendon tears: Tears most commonly longitudinal due to subluxation over the fibula, however can also present as transverse.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
* Fibular avulsion fractures as a result of peroneus longus tendon tearing | * Fibular avulsion fractures as a result of peroneus longus tendon tearing | ||
* Painful os peroneum syndrome<ref>Hallinan JT, Wang W, Pathria MN, Smitaman E, Huang BK. [https://escholarship.org/content/qt6h93r9j0/qt6h93r9j0.pdf The peroneus longus muscle and tendon: a review of its anatomy and pathology.] Skeletal radiology. 2019 Sep;48(9):1329-44.</ref> | * Painful os peroneum syndrome<ref>Hallinan JT, Wang W, Pathria MN, Smitaman E, Huang BK. [https://escholarship.org/content/qt6h93r9j0/qt6h93r9j0.pdf The peroneus longus muscle and tendon: a review of its anatomy and pathology.] Skeletal radiology. 2019 Sep;48(9):1329-44.</ref> | ||
* [[Compartment Syndrome of the Lower Leg|Compartment Syndrome]]<ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Assessment == | == Assessment == | ||
Revision as of 17:33, 30 October 2020
Original Editor - Jenny Lim
Top Contributors - Jenny Lim, Beverly Klinger, Vidya Acharya, Patti Cavaleri, Kim Jackson, Leana Louw and Oyemi SilloDescription[edit | edit source]
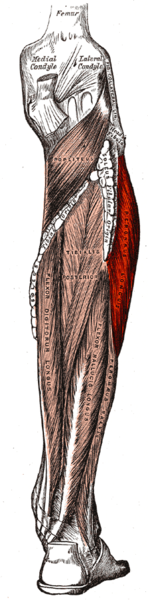
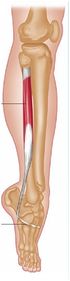
The Peroneus (Fibularis) Longus muscle, along with the Peroneus Brevis muscle make up the lateral compartment of the lower leg. The Peroneus Longus lies superficial to the Peroneus Brevis and is the largest of the Peroneal muscles.[1] The Peroneal Longus extends down the lateral compartment of the lower limb where at the midpoint it tapers in to a long tendon that descends in to the foot.[1][2]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
- Lateral condyle of tibia
- Head and proximal two-thirds of the lateral surface of fibula
- Intermuscular septa
- Adjacent deep fascia[3][4]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
- Lateral base of first metatarsal
- Medial cuneiform bone[3]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Superficial Peroneal (Fibular) nerve - L5, S1, S2.[1]
Artery[edit | edit source]
Anterior Tibial and Peroneal (Fibular) arteries.[1][3]
Function[edit | edit source]
- Eversion the ankle and foot
- Assists in ankle plantar flexion
- In weight-bearing position depresses head of first metatarsal due to the strong pull on its insertion
- Maintains the transverse arch of the foot as a result of how it crosses the sole of the foot.
- Steadies the leg on the foot in single leg stance by drawing on the lateral leg, and stops it from collapsing medially.[3]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Peroneal tendon injuries are most commonly present in patients that are young, active, and in those who participate in sports such as football, soccer, and running. Injury to the peroneus longus tendon can cause lateral ankle pain and may lead to ankle instability.[1]
The peroneus longus muscle is susceptible to several pathologies, including:
- Peroneal tendinopathy
- Peroneal tendon subluxation
- Weakness:
- Lessens the ability to stand on the toes
- Decreases the lateral stability of the ankle
- Allows a varus position of the foot
- Contracture/shortening: Results into an everted or valgus foot.
- Peroneus longus muscles and tendon tears: Tears most commonly longitudinal due to subluxation over the fibula, however can also present as transverse.[1]
- Fibular avulsion fractures as a result of peroneus longus tendon tearing
- Painful os peroneum syndrome[6]
- Compartment Syndrome[1]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
- Palpable proximal and posterior to the lateral malleolus.
- Peroneus longus and brevis tests
Treatment[edit | edit source]
- Strengthening
- Stretching
- Manual techniques such as massage, specific soft tissue mobilisations and myofascial release
- Dry needling
| [7] | [8] |
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Lezak B, Summers S. Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Extensor Hallucis Longus Muscle. August 2020
- ↑ Hallinan JT, Wang W, Pathria MN, Smitaman E, Huang BK. The peroneus longus muscle and tendon: a review of its anatomy and pathology. Skeletal radiology. 2019 Sep;48(9):1329-44.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.
- ↑ Peroneus Longus and Brevis. In: Kendall FP, McCreary EK, Provance PG. Muscle Testing and Function, 4th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1993. p.203.
- ↑ Ebraheim N. Anatomy Of The Peroneus Longus Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v_0TSoPzd3A (accessed 17/06/2018).
- ↑ Hallinan JT, Wang W, Pathria MN, Smitaman E, Huang BK. The peroneus longus muscle and tendon: a review of its anatomy and pathology. Skeletal radiology. 2019 Sep;48(9):1329-44.
- ↑ ReBalance Physiotherapy. Day -69: Peroneal Strengthening. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Xpwd5gTzXw (accessed 17/06/2018).
- ↑ Trevail T. Dry Needling: Peroneus Longus & Brevis. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ON0s8OFXfOs (accessed 17/06/2018).