Partial Hip Replacement: Difference between revisions
Lauren Lopez (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:User Name|Asma Alshehri]] | ||
'''Original Editor '''- | |||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== | == Introduction == | ||
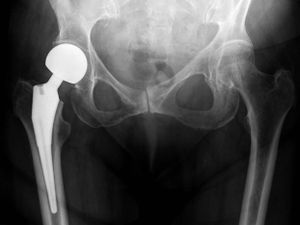
[[File:Hemiarthroplasty hip.jpg|alt=|thumb|R hip hemiarthroplasty ]] | |||
Partial Hip Replacement/Hip hemiarthroplasty is an orthopaedic procedure for the treatment of certain [[Femoral Neck Fractures|femoral neck fractures]] where the [[Femur|femoral]] head is removed and replaced. "Hemi" refers to the fact that the prosthetic femoral head articulates with the original acetabulum.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
Hemiarthroplasty is desirable for the: | |||
== | # Surgical treatment of [[Femoral Neck Hip Fracture|subcapital neck fractures]] that are displaced and at high risk of femoral head [[Avascular Necrosis|avascular necrosis]] ([[Femoral Neck Fractures, Garden Classification|Garden III and IV fractures]]). | ||
# [[Multimorbidity|Co-morbid]], less active, older patients (not good surgical candidates for [[Total Hip Replacement|THR]]) as long procedure with high morbidity in this group (younger or more active patients, THR has a better outcome).<ref name=":0">Radiopedia [https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hip-hemiarthroplasty Hemiarthroplasty] Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hip-hemiarthroplasty<nowiki/>(accessed 15.2.2021)</ref><ref name="Description">Partial hip replacement, https://advancedortho.me/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/Partial-Hip-Replacement.pdf (accessed 6 April 2017)</ref> | |||
== Technique == | |||
[[File:Walking frame.jpg|right|frameless]] | |||
The femoral stem is inserted similar to that of a total hip arthroplasty and can be cemented or non-cemented. The acetabulum is not interfered with as it is still in good condition.<ref>Bone smart Partial Hip Replacement Surgery | |||
Available from: https://bonesmart.org/hip/partial-hip-replacement-surgery/ (accessed 16.2.2021) | |||
</ref><ref name=":0" /> Most partial hip replacement surgeries can be performed in less than one hour in a hospital or surgical centre. The surgeon can choose to conduct open surgery, where a long incision is made diagonal to the joint, or a less-invasive computer-assisted procedure that requires only one or two small cuts. Computer-assisted surgery is usually preferred whenever the amount of bone that needs to be resurfaced or realigned is minimal<ref>Wise geek [https://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-partial-hip-replacement.htm PHR] Available from:https://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-partial-hip-replacement.htm (accessed 16.2.2021)</ref>. | |||
== Complications == | |||
Complications following THR can be loosely divided into systemic and procedure specific complications. Incidence of complications have improved over time, due to [[Surgery and General Anaesthetic|surgical]] and anaesthetic techniques improvements, along with the better diagnosis and management of these complications.<ref>Park C, Merchant I. Complications of total hip replacement. InTotal Hip Replacement-An Overview 2018 Nov 5. IntechOpen. Available:https:https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/61241 (accessed 14.12.2022) </ref> | |||
[ | * In a study it was found that the complication rate for hemiarthroplasty was notably higher when compared to THR. This may be explained by a poorer physiological condition of the hemiarthroplasty group upon admission. There were also a larger proportion of patients in this group with a [[Barthel Index|Barthel score]]5 <19. This score reflects mobility, and lower mobility makes the group slower to rehabilitate and mobilise post-operatively, (making them more vulnerable to chest and urinary infection). This may have contributed to the high rate of chest and urosepsis in this group | ||
* It is well documented that the rate of dislocation in THR performed following a fractured neck of the femur is significantly higher.<ref>Dawson D, Milligan D, Callachand F, Cusick L. Hip hemi-arthroplasty vs total hip replacement for displaced intra-capsular hip fractures: retrospective age and sex matched cohort study. The Ulster Medical Journal. 2018 Jan;87(1):17.Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5849947/ (accessed 16.12.2022)</ref> | |||
* Hemiarthroplasty is frequently less painful and requires fewer hospital stays than a full hip replacement.<ref>brandonorthopaedics Hemiarthroplasty Vs Total Hip Replacement: Key Differences Available:https://www.brandonorthopedics.com/hemiarthroplasty-vs-total-hip-replacement-key-differences/ (accessed 16.12.2022)</ref> | |||
See [[Total Hip Replacement Complications|Hip Replacement Complications]] | |||
== Physiotherapy == | |||
For a comprehensive guide see [[Total Hip Replacement]], protocol the same. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Orthopaedic_Surgical_Procedures]] | [[Category:Orthopaedic_Surgical_Procedures]] | ||
[[Category:Older People/Geriatrics]] | [[Category:Older People/Geriatrics]] | ||
[[Category:Older People/Geriatrics - Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Older People/Geriatrics - Interventions]] | |||
[[Category:Osteoarthritis]] | |||
[[Category:Arthroplasty]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:56, 11 January 2024
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Asma Alshehri, Kim Jackson, Lauren Lopez, George Prudden, WikiSysop and Ahmed Nassef
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Partial Hip Replacement/Hip hemiarthroplasty is an orthopaedic procedure for the treatment of certain femoral neck fractures where the femoral head is removed and replaced. "Hemi" refers to the fact that the prosthetic femoral head articulates with the original acetabulum.[1]
Hemiarthroplasty is desirable for the:
- Surgical treatment of subcapital neck fractures that are displaced and at high risk of femoral head avascular necrosis (Garden III and IV fractures).
- Co-morbid, less active, older patients (not good surgical candidates for THR) as long procedure with high morbidity in this group (younger or more active patients, THR has a better outcome).[1][2]
Technique[edit | edit source]
The femoral stem is inserted similar to that of a total hip arthroplasty and can be cemented or non-cemented. The acetabulum is not interfered with as it is still in good condition.[3][1] Most partial hip replacement surgeries can be performed in less than one hour in a hospital or surgical centre. The surgeon can choose to conduct open surgery, where a long incision is made diagonal to the joint, or a less-invasive computer-assisted procedure that requires only one or two small cuts. Computer-assisted surgery is usually preferred whenever the amount of bone that needs to be resurfaced or realigned is minimal[4].
Complications[edit | edit source]
Complications following THR can be loosely divided into systemic and procedure specific complications. Incidence of complications have improved over time, due to surgical and anaesthetic techniques improvements, along with the better diagnosis and management of these complications.[5]
- In a study it was found that the complication rate for hemiarthroplasty was notably higher when compared to THR. This may be explained by a poorer physiological condition of the hemiarthroplasty group upon admission. There were also a larger proportion of patients in this group with a Barthel score5 <19. This score reflects mobility, and lower mobility makes the group slower to rehabilitate and mobilise post-operatively, (making them more vulnerable to chest and urinary infection). This may have contributed to the high rate of chest and urosepsis in this group
- It is well documented that the rate of dislocation in THR performed following a fractured neck of the femur is significantly higher.[6]
- Hemiarthroplasty is frequently less painful and requires fewer hospital stays than a full hip replacement.[7]
See Hip Replacement Complications
Physiotherapy[edit | edit source]
For a comprehensive guide see Total Hip Replacement, protocol the same.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Radiopedia Hemiarthroplasty Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hip-hemiarthroplasty(accessed 15.2.2021)
- ↑ Partial hip replacement, https://advancedortho.me/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/Partial-Hip-Replacement.pdf (accessed 6 April 2017)
- ↑ Bone smart Partial Hip Replacement Surgery Available from: https://bonesmart.org/hip/partial-hip-replacement-surgery/ (accessed 16.2.2021)
- ↑ Wise geek PHR Available from:https://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-partial-hip-replacement.htm (accessed 16.2.2021)
- ↑ Park C, Merchant I. Complications of total hip replacement. InTotal Hip Replacement-An Overview 2018 Nov 5. IntechOpen. Available:https:https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/61241 (accessed 14.12.2022)
- ↑ Dawson D, Milligan D, Callachand F, Cusick L. Hip hemi-arthroplasty vs total hip replacement for displaced intra-capsular hip fractures: retrospective age and sex matched cohort study. The Ulster Medical Journal. 2018 Jan;87(1):17.Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5849947/ (accessed 16.12.2022)
- ↑ brandonorthopaedics Hemiarthroplasty Vs Total Hip Replacement: Key Differences Available:https://www.brandonorthopedics.com/hemiarthroplasty-vs-total-hip-replacement-key-differences/ (accessed 16.12.2022)