Partial Hip Replacement: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Partial Hip Replacement/Hip hemiarthroplasty is an orthopaedic procedure for the treatment of certain femoral neck fractures where the femoral head is removed and replaced. The prefix hemi (meaning half) refers to the fact that the prosthetic femoral head articulates with the native acetabulum. | Partial Hip Replacement/Hip hemiarthroplasty is an orthopaedic procedure for the treatment of certain femoral neck fractures where the femoral head is removed and replaced. The prefix hemi (meaning half) refers to the fact that the prosthetic femoral head articulates with the native acetabulum. | ||
In partial hip replacement, where there is a fracture in the femoral neck and the fracture cannot be pinned, the ball must be replaced but the socket is still strong<ref name=":0" />. | |||
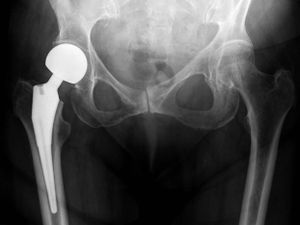
Image 1: X-ray of the hips, with a right-sided hip replacement of the hemiarthroplasty type. | Image 1: X-ray of the hips, with a right-sided hip replacement of the hemiarthroplasty type. | ||
== Indication | == Indication == | ||
Hemiarthroplasty is indicated for the surgical treatment of [[Hip Fracture|subcapital neck fractures]] that are displaced and at high risk of femoral head [[Avascular Necrosis|avascular necrosis]] (Garden III and IV fractures). As the procedure is quicker and far less morbid than internal fixation, hemiarthroplasty is also routinely used in older, less active and co-morbid patients that would not be good surgical candidates for total arthroplasty. In younger or more active patients, outcomes are better with total hip arthroplast<ref name=":0">Radiopedia [https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hip-hemiarthroplasty Hemiarthroplasty] Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hip-hemiarthroplasty<nowiki/>(accessed 15.2.2021)</ref>.<ref name="Description">Partial hip replacement, https://advancedortho.me/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/Partial-Hip-Replacement.pdf (accessed 6 April 2017)</ref> | |||
== Technique == | == Technique == | ||
The femoral stem is inserted similar to that of a total hip arthroplasty and can be cemented or non-cemented. | [[File:Ligaments of the hip joint anterior aspect Primal.png|right|frameless]] | ||
Hemiarthroplasty simply involves removing the broken femoral head, trimming the fractured end of the neck and inserting a femoral stem (one piece prosthesis of stem and ball). The femoral stem is inserted similar to that of a total hip arthroplasty and can be cemented or non-cemented. The acetabulum is never interfered with as it is still in very good condition<ref>Bone smart Partial Hip Replacement Surgery | |||
Available from: https://bonesmart.org/hip/partial-hip-replacement-surgery/ (accessed 16.2.2021) | |||
</ref>. | |||
Most partial hip replacement surgeries can be performed in less than one hour in a hospital or surgical center. The surgeon can choose to conduct open surgery, where a long incision is made diagonal to the joint, or a less-invasive computer-assisted procedure that requires only one or two small cuts. Computer-assisted surgery is usually preferred whenever the amount of bone that needs to be resurfaced or realigned is minimal<ref>Wise geek [https://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-partial-hip-replacement.htm PHR] Available from:https://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-partial-hip-replacement.htm (accessed 16.2.2021)</ref>. | |||
== Complications == | |||
* infection | |||
* haematoma | |||
* non-union or malunion | |||
* implant failure | |||
* periprosthetic fracture | |||
* loosening | |||
* dislocation | |||
* osteolysis (in bipolar hemiarthroplasty)<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== | == Physiotherapy == | ||
The below is a brief outline. For a comprehensive guide see [[Total Hip Replacement]] as protocol are very similar. | |||
== Post Surgery == | |||
'''Moving around''' | |||
As soon as possible teach client how to move without dislocating the hip ie "hip precautions" that must be followed. Most often, this means that client: | |||
* Avoids twisting at the hips (keep shoulders, hips, knees, and feet facing forward). | |||
* Do not let affected leg cross the center of your body toward the other leg eg in following situations | |||
** Do not cross your legs or feet. | |||
** Be very careful getting in or out of bed or a car. Make sure leg does not cross that imaginary line down the middle of the body. | |||
** Keep a pillow between your knees when you are lying down. When client on back, the pillow rests under the affected leg and on top of the other leg. This helps with turning onto side without twisting at the hips. | |||
'''On the day of surgery or the day after''' | |||
Educate and teach client | |||
* Procedure for in out bed ( help initially) | |||
* Use of walker or crutches. | |||
* Safe: sit down and stand up, dressing, use the toilet, shower and stairs. | |||
After surgery client will probably be walking with crutches or a walker. You may be able to climb a few stairs and get in and out of bed and chairs. | |||
'''Discharge''' | |||
Client will need someone to help you at home for the next few weeks. If client needs more extensive rehab, they may go to a specialized rehab centre for more treatment. | |||
Client will go home with a bandage and stitches, staples, tissue glue, or tape strips (removed when doctor allows). Stitches or staples, doctor removes 10 days to 3 weeks after surgery (Glue or tape strips will fall off on their own over time). Client may still have some mild pain and the area may be swollen for 3 to 4 months after surgery. | |||
Client continues the rehabilitation program (rehab) started in the hospital. The better rehab exercises performed, the sooner client will get strength and movement back. Most people are able to go back to work 4 weeks to 4 months after surgery<ref>Michigan Medicine [https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/abr6036 PHR] Available from: https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/abr6036 (accessed 16.2.2021)</ref>. | |||
<br> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 07:47, 16 February 2021
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Asma Alshehri, Kim Jackson, Lauren Lopez, George Prudden, WikiSysop and Ahmed Nassef
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Partial Hip Replacement/Hip hemiarthroplasty is an orthopaedic procedure for the treatment of certain femoral neck fractures where the femoral head is removed and replaced. The prefix hemi (meaning half) refers to the fact that the prosthetic femoral head articulates with the native acetabulum.
In partial hip replacement, where there is a fracture in the femoral neck and the fracture cannot be pinned, the ball must be replaced but the socket is still strong[1].
Image 1: X-ray of the hips, with a right-sided hip replacement of the hemiarthroplasty type.
Indication[edit | edit source]
Hemiarthroplasty is indicated for the surgical treatment of subcapital neck fractures that are displaced and at high risk of femoral head avascular necrosis (Garden III and IV fractures). As the procedure is quicker and far less morbid than internal fixation, hemiarthroplasty is also routinely used in older, less active and co-morbid patients that would not be good surgical candidates for total arthroplasty. In younger or more active patients, outcomes are better with total hip arthroplast[1].[2]
Technique[edit | edit source]
Hemiarthroplasty simply involves removing the broken femoral head, trimming the fractured end of the neck and inserting a femoral stem (one piece prosthesis of stem and ball). The femoral stem is inserted similar to that of a total hip arthroplasty and can be cemented or non-cemented. The acetabulum is never interfered with as it is still in very good condition[3].
Most partial hip replacement surgeries can be performed in less than one hour in a hospital or surgical center. The surgeon can choose to conduct open surgery, where a long incision is made diagonal to the joint, or a less-invasive computer-assisted procedure that requires only one or two small cuts. Computer-assisted surgery is usually preferred whenever the amount of bone that needs to be resurfaced or realigned is minimal[4].
Complications[edit | edit source]
- infection
- haematoma
- non-union or malunion
- implant failure
- periprosthetic fracture
- loosening
- dislocation
- osteolysis (in bipolar hemiarthroplasty)[1]
Physiotherapy[edit | edit source]
The below is a brief outline. For a comprehensive guide see Total Hip Replacement as protocol are very similar.
Post Surgery[edit | edit source]
Moving around
As soon as possible teach client how to move without dislocating the hip ie "hip precautions" that must be followed. Most often, this means that client:
- Avoids twisting at the hips (keep shoulders, hips, knees, and feet facing forward).
- Do not let affected leg cross the center of your body toward the other leg eg in following situations
- Do not cross your legs or feet.
- Be very careful getting in or out of bed or a car. Make sure leg does not cross that imaginary line down the middle of the body.
- Keep a pillow between your knees when you are lying down. When client on back, the pillow rests under the affected leg and on top of the other leg. This helps with turning onto side without twisting at the hips.
On the day of surgery or the day after
Educate and teach client
- Procedure for in out bed ( help initially)
- Use of walker or crutches.
- Safe: sit down and stand up, dressing, use the toilet, shower and stairs.
After surgery client will probably be walking with crutches or a walker. You may be able to climb a few stairs and get in and out of bed and chairs.
Discharge
Client will need someone to help you at home for the next few weeks. If client needs more extensive rehab, they may go to a specialized rehab centre for more treatment.
Client will go home with a bandage and stitches, staples, tissue glue, or tape strips (removed when doctor allows). Stitches or staples, doctor removes 10 days to 3 weeks after surgery (Glue or tape strips will fall off on their own over time). Client may still have some mild pain and the area may be swollen for 3 to 4 months after surgery.
Client continues the rehabilitation program (rehab) started in the hospital. The better rehab exercises performed, the sooner client will get strength and movement back. Most people are able to go back to work 4 weeks to 4 months after surgery[5].
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Radiopedia Hemiarthroplasty Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hip-hemiarthroplasty(accessed 15.2.2021)
- ↑ Partial hip replacement, https://advancedortho.me/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/Partial-Hip-Replacement.pdf (accessed 6 April 2017)
- ↑ Bone smart Partial Hip Replacement Surgery Available from: https://bonesmart.org/hip/partial-hip-replacement-surgery/ (accessed 16.2.2021)
- ↑ Wise geek PHR Available from:https://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-partial-hip-replacement.htm (accessed 16.2.2021)
- ↑ Michigan Medicine PHR Available from: https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/abr6036 (accessed 16.2.2021)