Ilioinguinal Nerve: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<div class="noeditbox">This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! ({{11}}/{{12}}/{{2023}})</div> | <div class="noeditbox">This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! ({{11}}/{{12}}/{{2023}})</div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[File:Lumbar Plexus Gray.png|thumb|265x265px]] | |||
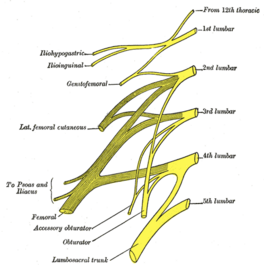
The ilioinguinal nerve is a mixed nerve that originates from the lumbar plexus. It emerges near the outer edge of the psoas major muscle and travels downward through the front of the abdominal wall. It stays beneath the peritoneum and passes in front of the quadratus lumborum muscle, continues downwards and obliquely across its surface, then it passes over the anterior surface of the iliacus muscle until it reaches the iliac crest. From there, it traverses through the [[Transversus Abdominis|transversus abdominis]] and the [[Internal Abdominal Oblique|internal oblique]] muscles. As it continues, it becomes visible near the [[Femoral Triangle|groin]] area, passing through the superficial [[Inguinal Canal|inguinal ring]] just in front of the spermatic cord in males. | The ilioinguinal nerve is a mixed nerve that originates from the lumbar plexus. It emerges near the outer edge of the psoas major muscle and travels downward through the front of the abdominal wall. It stays beneath the peritoneum and passes in front of the quadratus lumborum muscle, continues downwards and obliquely across its surface, then it passes over the anterior surface of the iliacus muscle until it reaches the iliac crest. From there, it traverses through the [[Transversus Abdominis|transversus abdominis]] and the [[Internal Abdominal Oblique|internal oblique]] muscles. As it continues, it becomes visible near the [[Femoral Triangle|groin]] area, passing through the superficial [[Inguinal Canal|inguinal ring]] just in front of the spermatic cord in males. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 32: | ||
Ilioinguinal nerve injuries frequently occur following abdominal surgery, abdominal wall trauma, accidently during surgery because of traumatic trochar from laparoscopic surgeries, or during inguinal hernia repairs. However, when the motor branches of the nerve are affected, it can result in weakened transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscles, potentially leading to the development of inguinal hernias. | Ilioinguinal nerve injuries frequently occur following abdominal surgery, abdominal wall trauma, accidently during surgery because of traumatic trochar from laparoscopic surgeries, or during inguinal hernia repairs. However, when the motor branches of the nerve are affected, it can result in weakened transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscles, potentially leading to the development of inguinal hernias. | ||
Furthermore, ilioinguinal nerve entrapment may also occur due to the presence of sutures in close proximity, leading to sensory disturbances along the nerve's path, a condition known as nerve entrapment. | Furthermore, ilioinguinal nerve entrapment may also occur due to the presence of sutures in close proximity, leading to sensory disturbances along the nerve's path, a condition known as nerve entrapment<ref>Whiteside JL, Barber MD, Walters MD, Falcone T. Anatomy of ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves in relation to trocar placement and low transverse incisions. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. 2003 Dec 1;189(6):1574-8.</ref>. | ||
Ilioinguinal neuralgia one of the common causes for chronic lower abdominal and anterior [[Chronic Pelvic Pain|pelvic pain]]. | Ilioinguinal neuralgia one of the common causes for chronic lower abdominal and anterior [[Chronic Pelvic Pain|pelvic pain]]. | ||
== Assessment == | == Assessment == | ||
[[Ultrasound Scans|Diagnostic ultrasound]] we can track the nerve when it becomes superficial down to the superficial inguinal ring<ref>Gofeld M, Christakis M. Sonographically guided ilioinguinal nerve block. Journal of ultrasound in medicine. 2006 Dec;25(12):1571-5.</ref>. | |||
[[Electrodiagnosis|Electrodiagnostic stud]]<nowiki/>y to exclude other causes like; radiculopathy from lumbar or [[Lumbar Plexus|lumbar plexus]] injury<ref>Cho HM, Park DS, Kim DH, Nam HS. Diagnosis of ilioinguinal nerve injury based on electromyography and ultrasonography: a case report. Annals of rehabilitation medicine. 2017 Aug 31;41(4):705-8.</ref>. | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Nerve block: nerve block guided b imaging ultrasound proved to be effective for treatment of ilioinguinal neuralgia and approximately 55–70% showed a beneficial analgesic post-inguinal hernia surgery<ref>Wong AK, Ng AT. [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11916-020-00913-4#Sec6 Review of ilioinguinal nerve blocks for ilioinguinal neuralgia post hernia surger]y. Current Pain and Headache Reports. 2020 Dec;24:1-5.</ref>. | |||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
Revision as of 00:47, 17 December 2023
Original Editor - Khloud Shreif
Top Contributors - Khloud Shreif, Candace Goh and Ines Musabyemariya
Description[edit | edit source]
The ilioinguinal nerve is a mixed nerve that originates from the lumbar plexus. It emerges near the outer edge of the psoas major muscle and travels downward through the front of the abdominal wall. It stays beneath the peritoneum and passes in front of the quadratus lumborum muscle, continues downwards and obliquely across its surface, then it passes over the anterior surface of the iliacus muscle until it reaches the iliac crest. From there, it traverses through the transversus abdominis and the internal oblique muscles. As it continues, it becomes visible near the groin area, passing through the superficial inguinal ring just in front of the spermatic cord in males.
Root[edit | edit source]
Originate from the anterior rami from L1 nerve roots in the lower back, in some cases it receives contribution from T12 or l2 in other cases upon its origin.
Branches[edit | edit source]
Ilioinguinal nerve gives motor branches to the transversus abdominis and the internal oblique muscles when it passes through the posterior abdominal wall.
After existing though superficial inguinal ring it gives sensor branches; anterior labial nerve in females and anterior scrotal nerve in male
Function[edit | edit source]
Motor[edit | edit source]
The motor innervation to transversus abdominis and the internal oblique muscles
Sensory[edit | edit source]
Anterior labial nerve in females gives cutaneous innervation to anterior one-third of the labium majora, mons pubis, and root of clitoris.
Anterior scrotal nerve in males gives sensory innervation to skin of the anterior 1/3 of the scrotum and the root of the penis
In addition cutaneous innervation to the superior medial thigh.
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Ilioinguinal nerve injuries frequently occur following abdominal surgery, abdominal wall trauma, accidently during surgery because of traumatic trochar from laparoscopic surgeries, or during inguinal hernia repairs. However, when the motor branches of the nerve are affected, it can result in weakened transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscles, potentially leading to the development of inguinal hernias.
Furthermore, ilioinguinal nerve entrapment may also occur due to the presence of sutures in close proximity, leading to sensory disturbances along the nerve's path, a condition known as nerve entrapment[1].
Ilioinguinal neuralgia one of the common causes for chronic lower abdominal and anterior pelvic pain.
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Diagnostic ultrasound we can track the nerve when it becomes superficial down to the superficial inguinal ring[2].
Electrodiagnostic study to exclude other causes like; radiculopathy from lumbar or lumbar plexus injury[3].
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Nerve block: nerve block guided b imaging ultrasound proved to be effective for treatment of ilioinguinal neuralgia and approximately 55–70% showed a beneficial analgesic post-inguinal hernia surgery[4].
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Whiteside JL, Barber MD, Walters MD, Falcone T. Anatomy of ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves in relation to trocar placement and low transverse incisions. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. 2003 Dec 1;189(6):1574-8.
- ↑ Gofeld M, Christakis M. Sonographically guided ilioinguinal nerve block. Journal of ultrasound in medicine. 2006 Dec;25(12):1571-5.
- ↑ Cho HM, Park DS, Kim DH, Nam HS. Diagnosis of ilioinguinal nerve injury based on electromyography and ultrasonography: a case report. Annals of rehabilitation medicine. 2017 Aug 31;41(4):705-8.
- ↑ Wong AK, Ng AT. Review of ilioinguinal nerve blocks for ilioinguinal neuralgia post hernia surgery. Current Pain and Headache Reports. 2020 Dec;24:1-5.