Anterior Scalene: Difference between revisions
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Category:Anatomy - Cervical Spine" to "") |
(Reordered the page, added references, corrected grammar and punctual errors) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
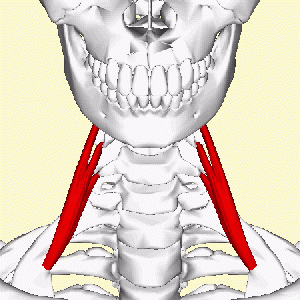
The anterior scalene, AKA scalenus anterior (scalenus anticus; Latin: musculus scalenus anterior) muscle is one of the lateral muscles of the neck, belonging to the scalene group. It is deeply placed, lying behind the [[Sternocleidomastoid|Sternocleidomastoid]]. | |||
It is located between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery | It is located between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery. The roots of the [[Brachial plexus|brachial plexus]] pass posterior to it. The phrenic nerve crosses its anterior surface.<ref>Harry WG, Bennett JD, Guha SC. Scalene muscles and the brachial plexus: anatomical variations and their clinical significance. Clinical Anatomy: The Official Journal of the American Association of Clinical Anatomists and the British Association of Clinical Anatomists. 1997;10(4):250-2.</ref><br> [[Image:Scalenus anterior - animation04.gif|center|300x300px]]<br> | ||
[[Image:Scalenus anterior - animation04.gif|center|300x300px]]<br> | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
Anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of [[Cervical Vertebrae|cervical vertebrae]] C3-C6 <ref>https://teachmeanatomy.info/neck/muscles/scalene/</ref> | |||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
By a narrow, flat tendon attaches into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first rib, and into the ridge on the upper surface of the rib in front of the subclavian groove | |||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Anterior branches of the cervical nerves C5-C7 | |||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
Ascending cervical branch of the inferior thyroid artery | |||
== Action and Function == | |||
== Action == | |||
Anterior scalene can perform individually or in synergistic group with other two scalenes ([[Middle Scalene|Middle]] and [[Posterior Scalene|Posterior]]): | |||
* Individually, bends the neck laterally on the same side - '''side flexor''' | |||
* In synergistic group: | |||
- Bilateral contraction causes anterior flexion of the neck - '''flexors''' | |||
- Ipsilateral contraction produces rotation of the cervical spine to the same side<ref>J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2002 Oct;32(10):488-96. Actions of the scalene muscles for rotation of the cervical spine in macaque and human. Buford JA, Yoder SM, Heiss DG, Chidley JV.</ref> - '''rotators''' | |||
- Elevate the 1st rib and are '''accessory muscles of respiration''' | |||
<div class="researchbox"> </div> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 21:37, 5 February 2020
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors - Kim Jackson, Wendy Walker, Chrysolite Jyothi Kommu, Admin, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop and Milijana Delevic
Description[edit | edit source]
The anterior scalene, AKA scalenus anterior (scalenus anticus; Latin: musculus scalenus anterior) muscle is one of the lateral muscles of the neck, belonging to the scalene group. It is deeply placed, lying behind the Sternocleidomastoid.
It is located between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery. The roots of the brachial plexus pass posterior to it. The phrenic nerve crosses its anterior surface.[1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of cervical vertebrae C3-C6 [2]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
By a narrow, flat tendon attaches into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first rib, and into the ridge on the upper surface of the rib in front of the subclavian groove
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Anterior branches of the cervical nerves C5-C7
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Ascending cervical branch of the inferior thyroid artery
Action and Function[edit | edit source]
Anterior scalene can perform individually or in synergistic group with other two scalenes (Middle and Posterior):
- Individually, bends the neck laterally on the same side - side flexor
- In synergistic group:
- Bilateral contraction causes anterior flexion of the neck - flexors
- Ipsilateral contraction produces rotation of the cervical spine to the same side[3] - rotators
- Elevate the 1st rib and are accessory muscles of respiration
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Harry WG, Bennett JD, Guha SC. Scalene muscles and the brachial plexus: anatomical variations and their clinical significance. Clinical Anatomy: The Official Journal of the American Association of Clinical Anatomists and the British Association of Clinical Anatomists. 1997;10(4):250-2.
- ↑ https://teachmeanatomy.info/neck/muscles/scalene/
- ↑ J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2002 Oct;32(10):488-96. Actions of the scalene muscles for rotation of the cervical spine in macaque and human. Buford JA, Yoder SM, Heiss DG, Chidley JV.