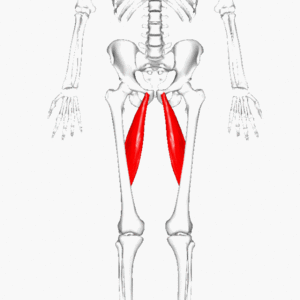
Adductor Longus
Original Editor - Leana Louw
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Leana Louw, Memoona Awan, Kim Jackson, Vidya Acharya and Ines Musabyemariya
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Adductor longus is one of the adductor muscles of the medial thigh.[1] Together with adductor brevis, adductor magnus, gracilis and obturator externus, it makes up the hip adductors.[1]
This large fan-shaped muscle is situated most anteriorly of this group and covers the middle part of adductor magnus and the anterior part of adductor brevis.[1]
The muscle forms the medial border of the femoral triangle.
Origin[edit | edit source]
Strong tendon from anterior aspect of pubic body inferior to pubic crest.[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Expands into a fan shape, attaching broadly to the linea aspera on the middle third of femur.[1]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Anterior devision of obturator nerve (L2, L3, L4).[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
Adduction of femur.[1]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
- Manual muscle testing:[2]
- Patient positioned in side-lying with side being tested resting at the bottom on the bed. The top leg is supported by the examiner in 25 degrees of abduction. The examiner applies manual resistance to the distal femur proximal to the knee joint in the direction of the bed while the patient actively adducts against the examiner's hand.
- Determine strength by using Oxford grades 0-5.
- Adductor squeeze test
- Hip adductor length test:[3]
- Patient is positioned in crook-lying with a posterior pelvic tilt. The patient abducts the hips by moving the knees outwards towards the sides of the bed.
- Adductor stiffness: Patient not able to maintain position, (+) anterior pelvic tilt
- Inhibition of gluteus medius and external rotators of hip can be noted,, causing muscle imbalances and compensatory movement patterns.
- Tests for abdominal weakness as well.
- Patient is positioned in crook-lying with a posterior pelvic tilt. The patient abducts the hips by moving the knees outwards towards the sides of the bed.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.
- ↑ Hislop H, Avers D, Brown M. Daniels and Worthingham's Muscle Testing: Techniques of manual examination. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013.
- ↑ Norris CM. Spinal stabilisation: 4. Muscle imbalance and the low back. Physiotherapy 1995;81(3):127-38.