Overview of Patellofemoral Joint Instability: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Jess Bell|Jess Bell]] based on the course by [https://members.physio-pedia.com/course_tutor/claire-robertson/ Claire Robertson]<br> | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Jess Bell|Jess Bell]] based on the course by [https://members.physio-pedia.com/course_tutor/claire-robertson/ Claire Robertson]<br> | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Patellofemoral instability is a complex orthopaedic condition that frequently affects children and adolescents.<ref>Bailey MEA, Metcalfe A, Hing CB, Eldridge J; BASK Patellofemoral Working Group. [https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0968-0160(21)00065-X Consensus guidelines for | Patellofemoral instability is a complex orthopaedic condition that frequently affects children and adolescents.<ref>Bailey MEA, Metcalfe A, Hing CB, Eldridge J; BASK Patellofemoral Working Group. [https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0968-0160(21)00065-X Consensus guidelines for managing patellofemoral instability]. Knee. 2021;29:305-12. </ref><ref name=":0">Vellios EE, Trivellas M, Arshi A, Beck JJ. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7083998/ Recurrent Patellofemoral Instability in the Pediatric Patient: Management and Pitfalls]. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(1):58-68. </ref> It is estimated that the incidence of patellofemoral instability in paediatric patients ranges from 23 to 43 per 100,000 person-years. The highest rates are in teenagers aged between 14 and 18 years<ref name=":0" />, with the first episode of dislocation typically occurring at the age of 15.<ref>Kim HK, Parikh S. Patellofemoral Instability in Children: [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9174504/pdf/kjr-23-674.pdf Imaging Findings and Therapeutic Approaches.] Korean J Radiol. 2022 Jun;23(6):674-687.</ref> | ||
The management of patellofemoral instability is complex.<ref name=":3">Jaquith BP, Parikh SN. [https://journals.lww.com/pedorthopaedics/Abstract/2017/10000/Predictors_of_Recurrent_Patellar_Instability_in.13.aspx Predictors of recurrent patellar instability in children and adolescents after first-time dislocation]. J Pediatr Orthop. 2017;37(7):484-90. </ref> Vellios et al.<ref name=":0" /> note that first-time dislocation may be managed conservatively (i.e. through rehabilitation, bracing, activity modification), but as many as 36 percent of patients will have recurrent instability on the same leg. | The management of patellofemoral instability is complex.<ref name=":3">Jaquith BP, Parikh SN. [https://journals.lww.com/pedorthopaedics/Abstract/2017/10000/Predictors_of_Recurrent_Patellar_Instability_in.13.aspx Predictors of recurrent patellar instability in children and adolescents after first-time dislocation]. J Pediatr Orthop. 2017;37(7):484-90. </ref> Vellios et al.<ref name=":0" /> note that first-time dislocation may be managed conservatively (i.e. through rehabilitation, bracing, and activity modification), but as many as 36 percent of patients will have recurrent instability on the same leg. | ||
== Definitions == | == Definitions == | ||
'''Patellofemoral stability''' is defined as “constraint by passive soft tissue tethers and chondral/bony geometry that, with muscular forces, guide the patella into the trochlear groove and keep it engaged within the trochlear groove as the knee flexes and extends.” <ref name=":1">Post WR, Fithian DC. [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2325967117750352 Patellofemoral instability: a consensus statement from the AOSSM/PFF Patellofemoral Instability Workshop]. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(1):2325967117750352. </ref> | <blockquote>'''Patellofemoral stability''' is defined as “constraint by passive soft tissue tethers and chondral/bony geometry that, with muscular forces, guide the patella into the trochlear groove and keep it engaged within the trochlear groove as the knee flexes and extends.” <ref name=":1">Post WR, Fithian DC. [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2325967117750352 Patellofemoral instability: a consensus statement from the AOSSM/PFF Patellofemoral Instability Workshop]. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(1):2325967117750352. </ref></blockquote><blockquote>'''Patellofemoral instability''' is defined as “symptomatic deficiency of the aforementioned passive constraint (patholaxity) such that the patella may escape partially or completely from its asymptomatic position with respect to the femoral trochlea under the influence of displacing force.”<ref name=":1" /></blockquote> | ||
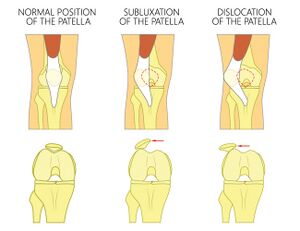
[[File:Patella Dislocation and Subluxation - Shutterstock Image - ID 637362388.jpg|thumb|Comparison of a patella in situ, subluxed and dislocated.]] | |||
'''Dislocation''' - the [[patella]] comes completely out of the trochlea (see image). Dislocation might be caused by a:<ref name=":2">Robertson C. Patellofemoral Joint Instability Course. Plus. 2022.</ref> | |||
'''Dislocation''' - patella comes completely out of the trochlea. Dislocation might be caused by a:<ref name=":2">Robertson C. Patellofemoral Joint Instability Course. | |||
* | * Traumatic event (e.g. rugby tackle) | ||
** In these cases, the knee has been structurally intact prior to injury<ref>Duthon VB. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877056814003302 Acute traumatic patellar dislocation]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(1 Suppl):S59-67. </ref> | ** In these cases, the knee has been structurally intact prior to injury<ref>Duthon VB. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877056814003302 Acute traumatic patellar dislocation]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(1 Suppl):S59-67. </ref> | ||
** These individuals tend to have a better prognosis as there are no underlying structural morphological elements to predispose them to instability | ** These individuals tend to have a better prognosis as there are no underlying structural morphological elements to predispose them to instability | ||
| Line 22: | Line 18: | ||
** These individuals tend to have a structural element which predisposes them to instability | ** These individuals tend to have a structural element which predisposes them to instability | ||
'''Subluxation''' - a “halfway" point between | '''Subluxation''' - a “halfway" point between a patella in situ and dislocation (see image).<ref name=":2" /> Patients with a subluxing patella may complain of a painful knee / anterior knee pain.<ref name=":2" /><ref>Monk AP, Doll HA, Gibbons CL, Ostlere S, Beard DJ, Gill HS, Murray DW. [https://online.boneandjoint.org.uk/doi/full/10.1302/0301-620X.93B10.27205 The patho-anatomy of patellofemoral subluxation]. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(10):1341-7.</ref> | ||
== Recurrent Patellofemoral Instability == | == Recurrent Patellofemoral Instability == | ||
Recurrent patellofemoral instability is relatively common.<ref name=":4">Migliorini F, Oliva F, Maffulli GD, Eschweiler J, Knobe M, Tingart M, Maffulli N. [https://josr-online.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13018-021-02383-9 Isolated medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for recurrent patellofemoral instability: analysis of outcomes and risk factors]. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):239. </ref> Individuals who experience recurrent patellofemoral instability often have specific pathoanatomical features which predispose them to patellar dislocation. Migliorini<ref name=":4" /> note the following risk factors: | Recurrent patellofemoral instability is relatively common.<ref name=":4">Migliorini F, Oliva F, Maffulli GD, Eschweiler J, Knobe M, Tingart M, Maffulli N. [https://josr-online.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13018-021-02383-9 Isolated medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for recurrent patellofemoral instability: analysis of outcomes and risk factors]. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):239. </ref> Individuals who experience recurrent patellofemoral instability often have specific pathoanatomical features which predispose them to patellar dislocation. Migliorini et al.<ref name=":4" /> note the following risk factors: | ||
* Bony conformation abnormalities (e.g. trochlear dysplasia) | * Bony conformation abnormalities (e.g. trochlear dysplasia) | ||
* Lower limb mal-alignment syndromes | * Lower limb mal-alignment syndromes | ||
* Soft tissue abnormalities (e.g. patella alta) | * Soft tissue abnormalities (e.g. [[patella alta]]) | ||
Jaquith and Parikh<ref name=":3" /> found that the following are risk factors for multiple dislocations in children and adolescents: | Jaquith and Parikh<ref name=":3" /> found that the following are risk factors for multiple dislocations in children and adolescents: | ||
# Aged under 14 years at first dislocation | |||
# History of contralateral dislocation | |||
# Any type of trochlear dysplasia | |||
# Skeletal immaturity (i.e. the physis in the distal [[femur]] or proximal [[tibia]] are still partially / fully open) | |||
# Long patellar tendon | |||
The number of risk factors a child / adolescent has | The number of risk factors a child / adolescent has impacts their risk of recurrent dislocations:<ref name=":3" /> | ||
* Children who have | * Children who have '''risk factors 2-5''' are 88 percent likely to have recurrent dislocations | ||
* Having any three risk factors is associated with a 75 percent risk of recurrent dislocations | * Having any '''three''' risk factors is associated with a 75 percent risk of recurrent dislocations | ||
* Having any two risk factors is associated with a predicted risk of around 55 percent | * Having any '''two''' risk factors is associated with a predicted risk of around 55 percent | ||
* 97 percent of recurrences occur within three years<ref name=":2" /> | * 97 percent of recurrences occur within three years<ref name=":2" /> | ||
Jaquith and Parikh<ref name=":3" /> found that the mean age of first dislocation for children who experienced re-dislocation was 12.9 years and for those who did not re-dislocate, the mean age of first dislocation was 13.8 years. Thus, '''13 years''' is an important milestone when considering patellofemoral dislocation.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
== Morphology and Instability == | == Morphology and Instability == | ||
| Line 59: | Line 55: | ||
The following are important features to consider when assessing individuals with potential / confirmed patellofemoral instability:<ref name=":2" /> | The following are important features to consider when assessing individuals with potential / confirmed patellofemoral instability:<ref name=":2" /> | ||
* Morphology of the | * Morphology of the trochlea | ||
* Position of the tibial tubercle | * Position of the tibial tubercle | ||
* Length of the | * Length of the patellar tendon | ||
== Morphology of the Trochlea == | == Morphology of the Trochlea == | ||
The patella is essentially a floating bone which needs to stay in the trochlea (i.e. the groove of the distal femur). It is well recognised that trochlear dysplasia is associated with | The patella is essentially a floating bone which needs to stay in the trochlea (i.e. the groove of the distal femur). It is well recognised that trochlear dysplasia is associated with patellofemoral instability.<ref name=":5">Batailler C, Neyret P. [https://eor.bioscientifica.com/configurable/content/journals$002feor$002f3$002f5$002f2058-5241.3.170058.xml?t:ac=journals%24002feor%24002f3%24002f5%24002f2058-5241.3.170058.xml Trochlear dysplasia: imaging and treatment options]. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3(5):240-47.</ref> | ||
=== | === Trochlear Depth === | ||
Ideally, the trochlea will be deep, with a sharp inclination on the lateral side. It is important to look out for a “shallow trochlea” on an MRI report. Patients may also have a long lateral facet and / or shallow inclination.<ref name=":2" /> | Ideally, the trochlea will be deep, with a sharp inclination on the lateral side. It is important to look out for a “shallow trochlea” on an MRI report. Patients may also have a long lateral facet and / or shallow inclination.<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| Line 81: | Line 75: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
There is a spectrum of | There is a spectrum of trochlear dysplasia. Ideally, a trochlea will be shaped liked a soup bowl. Individuals who have a saucer-shaped trochlea (i.e. shallow) are more likely to experience subluxation or dislocation. They may report that it feels like their patella is “skidding around” or “slipping”. At the more extreme end of the spectrum, patients can have a domed trochlea. These persons are most likely to dislocate and are unlikely to stabilise without surgery (e.g. trochleoplasty).<ref name=":2" /><blockquote>“High-grade trochlear dysplasia is characterized by the combination of a flat and/or prominent trochlea proud of the anterior femoral cortex, which offers inadequate tracking during flexion and leads to patellar subluxation.”<ref name=":5" /></blockquote> | ||
=== Trochleoplasty - Prevention of Rapid Wear === | === Trochleoplasty - Prevention of Rapid Wear === | ||
* Addresses | * Addresses trochlear morphology, [[Q Angle|Q angle]] and TT-TG distance (see below) | ||
* Addresses | * Addresses a long patellar tendon (see below) | ||
* Addresses the over-stretching of medial structures | * Addresses the over-stretching of medial structures (see below) | ||
Please note that | Please note that trochleoplasty is major surgery and outcomes are better when this procedure is performed on pristine chondral surfaces (i.e. on individuals in their late teens).<ref name=":2" /> | ||
=== Non-Operative Rehabilitation === | === Non-Operative Rehabilitation === | ||
| Line 95: | Line 89: | ||
* Look out for patients using descriptors such as ‘slipping’ | * Look out for patients using descriptors such as ‘slipping’ | ||
* Robertson<ref name=":2" /> notes that patellofemoral instability is often associated with small patellae and hypermobility | * Robertson<ref name=":2" /> notes that patellofemoral instability is often associated with small patellae and [[Benign Joint Hypermobility Syndrome|hypermobility]] | ||
* It is important to try to establish if the individual is subluxing, | * It is important to try to establish if the individual is subluxing, dislocating or has general excess mobility | ||
* If the problem is with engagement, look at rehabilitating in the early range of motion, avoiding pain | * If the problem is with engagement, look at rehabilitating in the early range of motion, avoiding pain | ||
* Isometrics are very useful | * Isometrics are very useful | ||
* Robertson<ref name=":2" /> also notes that individuals with multi-directional instability are often very puffy in their parapatellar soft tissues | * Robertson<ref name=":2" /> also notes that individuals with multi-directional instability are often very puffy in their parapatellar soft tissues | ||
* They often have medial and lateral fat pad oedema | * They often have medial and lateral [[Fat Pad Syndrome|fat pad]] oedema | ||
* Can consider bracing (see below) | * Can consider bracing (see below) | ||
* Not always isolated to terminal extension instability | * Not always isolated to terminal extension instability | ||
| Line 109: | Line 103: | ||
* Is there any chondral damage or bone oedema? If yes where? | * Is there any chondral damage or bone oedema? If yes where? | ||
** Lateral facet / lateral trochlea, then consider Q brace<ref name=":6">Callaghan MJ, Parkes MJ, Hutchinson CE, Gait AD, Forsythe LM, Marjanovic EJ, et al. [https://ard.bmj.com/content/74/6/1164.long A randomised trial of a brace for patellofemoral osteoarthritis targeting knee pain and bone marrow lesions]. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(6):1164-70. </ref> | ** Lateral facet / lateral trochlea, then consider Q brace<ref name=":6">Callaghan MJ, Parkes MJ, Hutchinson CE, Gait AD, Forsythe LM, Marjanovic EJ, et al. [https://ard.bmj.com/content/74/6/1164.long A randomised trial of a brace for patellofemoral osteoarthritis targeting knee pain and bone marrow lesions]. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(6):1164-70. </ref> | ||
** If no damage then consider a | ** If no damage, then consider a patellar stabilising brace | ||
===== Q Brace ===== | ===== Q Brace ===== | ||
Callaghan et al.<ref name=":6" /> explored the use of a Bioskin Patellar Tracking Q Brace on patients with painful patellofemoral osteoarthritis (PFJOA):<ref name=":6" /> | Callaghan et al.<ref name=":6" /> explored the use of a Bioskin Patellar Tracking Q Brace on patients with painful patellofemoral joint osteoarthritis (PFJOA):<ref name=":6" /> | ||
* MRI was used to monitor bone marrow | * MRI was used to monitor bone marrow lesions in lateral PFJOA | ||
* Participants either wore a brace or had no brace (control) | * Participants either wore a brace or had no brace (control) | ||
* Participants in the brace group wore their braces for a mean of 7.4 hours per day | * Participants in the brace group wore their braces for a mean of 7.4 hours per day | ||
* At the six-week follow-up, Callaghan et al.<ref name=":6" /> found that subjects using the Q brace | * At the six-week follow-up, Callaghan et al.<ref name=":6" /> found that subjects using the Q brace had decreased pain, as well as a reduction in the volume of patellofemoral bone marrow lesions | ||
==== Taping ==== | ==== Taping ==== | ||
* McConnell taping can be useful for lateral pathology (see video below) | * McConnell taping can be useful for lateral pathology (see video below) | ||
* K tape can be used to stabilise the knee | * K tape can be used to stabilise the knee<ref name=":2" /> | ||
{{#ev:youtube|WbHXYnwUwws}}<ref> McConnell Physiotherapy Group. MCCONNELL KNEE TAPING (OFFICIAL). Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WbHXYnwUwws [last accessed 14/6/2022]</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|WbHXYnwUwws}}<ref> McConnell Physiotherapy Group. MCCONNELL KNEE TAPING (OFFICIAL). Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WbHXYnwUwws [last accessed 14/6/2022]</ref> | ||
== Position of the Tibial Tubercle == | == Position of the Tibial Tubercle == | ||
Ideally, the tibial tubercle will be positioned directly under the trochlea. However, some people present with a lateralised tibial tuberosity. When the quadriceps | Ideally, the tibial tubercle will be positioned directly under the trochlea. However, some people present with a lateralised tibial tuberosity. When the quadriceps works, the position of the tibial tubercle creates an overall lateralising force, which can have an impact on stability.<ref name=":2" /> | ||
TT-TG distance (tibial tuberosity-trochlear groove) is measured on MRI to accurately determine the position of the tibial tubercle in relation to the trochlea.<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":7">Heidenreich MJ, Camp CL, Dahm DL, Stuart MJ, Levy BA, Krych AJ. [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00167-015-3715-4 The contribution of the tibial tubercle to patellar instability: analysis of tibial tubercle-trochlear groove (TT-TG) and tibial tubercle-posterior cruciate ligament (TT-PCL) distances]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(8):2347-51. </ref> The greater | TT-TG distance (tibial tuberosity-trochlear groove) is measured on MRI to accurately determine the position of the tibial tubercle in relation to the trochlea.<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":7">Heidenreich MJ, Camp CL, Dahm DL, Stuart MJ, Levy BA, Krych AJ. [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00167-015-3715-4 The contribution of the tibial tubercle to patellar instability: analysis of tibial tubercle-trochlear groove (TT-TG) and tibial tubercle-posterior cruciate ligament (TT-PCL) distances]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(8):2347-51. </ref> The greater the distance, the more lateralised the tibial tuberosity.<ref name=":7" /> | ||
To measure TT-TG distance:<ref name=":2" /> | To measure TT-TG distance:<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| Line 135: | Line 129: | ||
* A line is made through the trochlea and tibial tuberosity | * A line is made through the trochlea and tibial tuberosity | ||
* The distance between these two lines is measured<ref name=":2" /> | * The distance between these two lines is measured<ref name=":2" /> | ||
** Up to | ** Up to 15 mm is considered normal | ||
** 15-20 mm may start to affect stability and potentially create pain | ** 15-20 mm may start to affect stability and potentially create pain | ||
** ≥20 mm indicates individuals at risk for future instability<ref name=":7" /> | ** ≥20 mm indicates individuals at risk for future instability<ref name=":7" /> | ||
When MRI is not available, it is possible to conduct a visual examination. You can then ask patient to perform a static quadriceps hold and look to see if the patella moves laterally. While this is not an accurate measure, it can be useful when | When MRI is not available, it is possible to conduct a visual examination. You can then ask the patient to perform a static quadriceps hold and look to see if the patella moves laterally. While this is not an accurate measure, it can be useful when considered alongside the overall clinical picture.<ref name=":2" /> | ||
=== Non-Operative Management of a Large TT-TG === | === Non-Operative Management of a Large TT-TG === | ||
A lateralised tibial tuberosity causes a lateral valgus movement, which overloads the lateral facet and provides a lateral force. Thus, it is important for patients to avoid:<ref name=":2" /> | A lateralised tibial tuberosity causes a lateral valgus movement, which overloads the lateral facet and provides a lateral force. Thus, it is important for patients to avoid the following femoral positions:<ref name=":2" /> | ||
* Adduction | * Adduction | ||
* Internal rotation | * Internal rotation | ||
* Adduction with | * Adduction with internal rotation | ||
Check also if the patient is anteverted (using [[Craig's Test|Craig's test]] - see video below). Other points to consider include:<ref name=":2" /> | Check also if the patient is anteverted (using [[Craig's Test|Craig's test]] - see video below). Other points to consider include:<ref name=":2" /> | ||
* Are patients aware of any issues with dynamic control (i.e. do they knock their knees when running) | * Are patients aware of any issues with dynamic control (i.e. do they knock their knees when running?) | ||
* Do they have weakness or poor NMS control? | * Do they have weakness or poor neuromusculoskeletal (NMS) control? | ||
* Can they correct this? What cues work best? | * Can they correct this? What cues work best? | ||
* Consider at what angle of hip flexion the rotation problem occurs | * Consider at what angle of hip flexion the rotation problem occurs | ||
| Line 161: | Line 155: | ||
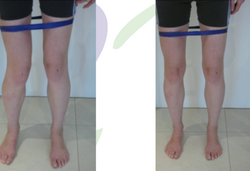
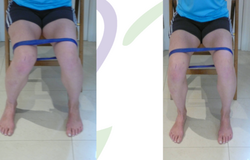
The following exercises can be useful in the rehabilitation of individuals with a large TT-TG:<ref name=":2" /> | The following exercises can be useful in the rehabilitation of individuals with a large TT-TG:<ref name=":2" /> | ||
<gallery widths="250" heights="350"> | |||
File:Standing.png|Rotational control in standing. | |||
File:Rotational Control for PJI in sitting.png|Eccentric control in sitting. | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Length of the Patellar Tendon == | |||
A patella alta is essentially a “high-riding” patella.<ref name=":2" /> It can occur when individuals are born with long patellar tendons<ref name=":2" /> and it is known to be associated with patellofemoral instability.<ref name=":8">Patel RM, Gombosh M, Polster J, Andrish J. Patellar [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2325967120959318 Tendon imbrication is a safe and efficacious technique to shorten the patellar tendon in patients with patella alta]. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020;8(10):2325967120959318. </ref> | |||
The Insall-Salvati ratio is most often used to measure the height of the patella.<ref name=":9">Gaillard F, Weerakkody Y. Insall-Salvati ratio. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org. Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/insall-salvati-ratio?lang=us (accessed 14 June 2022).</ref> It compares patellar tendon length with patellar length.<ref name=":9" /> An ideal ratio is 1:1. This can also be informally assessed in the clinic.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
=== Non-Operative Management of Patella Alta === | |||
In individuals with patella alta, the patella takes longer to enter the trochlea. Typically, the patella will engage in the trochlea at around 15 degrees of knee flexion. But this is delayed in individuals with patella alta.<ref name=":8" /> Thus, their knee is relatively more unstable for the first 30 degrees of knee flexion.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
It is, therefore, important to target 0-30 degrees of knee flexion with dynamic stability. Conservative management should focus on making the [[Vastus Medialis Oblique]] (VMO) architecturally favourable - i.e. increase the fibre angle and the insertion ratio.<ref name=":2" /><ref>Khoshkhoo M, Killingback A, Robertson CJ, Adds PJ. The effect of exercise on vastus medialis oblique muscle architecture: An ultrasound investigation. Clin Anat. 2016;29(6):752-8. </ref> | |||
== Medial Patellofemoral Ligament == | |||
The [[Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL)|medial patellofemoral ligament]] (MPFL) is the primary restraint to the patella, so it can have a significant impact on stability. While people do not tend to have a congenital problem with this ligament, it is disrupted after dislocation (either very stretched or ruptured).<ref name=":2" /> | |||
If a patient presents after a confirmed or potential dislocating event, look for:<ref name=":2" /> | |||
* Bruising | |||
* Swelling | |||
* Medial tenderness (just medial to the patella) | |||
These will increase your suspicion of a MPFL injury.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
== Outcome Measures == | |||
The following outcome measures can be useful in this client group:<ref name=":2" /> | |||
* [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0968016015002343 Norwich Instability Score]: highlights degree of instability and impact on life | |||
* [[Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia|Tampa Score of Kinesiophobia]]: highlights level of [[kinesiophobia]] (i.e. the fear of movement) | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
[[Category:Knee]] | [[Category:Knee]] | ||
[[Category:Course Pages]] | [[Category:Course Pages]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Plus Content]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:41, 24 October 2023
Top Contributors - Jess Bell, Kim Jackson, Wanda van Niekerk and Ewa Jaraczewska
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Patellofemoral instability is a complex orthopaedic condition that frequently affects children and adolescents.[1][2] It is estimated that the incidence of patellofemoral instability in paediatric patients ranges from 23 to 43 per 100,000 person-years. The highest rates are in teenagers aged between 14 and 18 years[2], with the first episode of dislocation typically occurring at the age of 15.[3]
The management of patellofemoral instability is complex.[4] Vellios et al.[2] note that first-time dislocation may be managed conservatively (i.e. through rehabilitation, bracing, and activity modification), but as many as 36 percent of patients will have recurrent instability on the same leg.
Definitions[edit | edit source]
Patellofemoral stability is defined as “constraint by passive soft tissue tethers and chondral/bony geometry that, with muscular forces, guide the patella into the trochlear groove and keep it engaged within the trochlear groove as the knee flexes and extends.” [5]
Patellofemoral instability is defined as “symptomatic deficiency of the aforementioned passive constraint (patholaxity) such that the patella may escape partially or completely from its asymptomatic position with respect to the femoral trochlea under the influence of displacing force.”[5]
Dislocation - the patella comes completely out of the trochlea (see image). Dislocation might be caused by a:[6]
- Traumatic event (e.g. rugby tackle)
- In these cases, the knee has been structurally intact prior to injury[7]
- These individuals tend to have a better prognosis as there are no underlying structural morphological elements to predispose them to instability
- Minor trauma - a slight tap / knock to the knee causes dislocation
- These individuals tend to have a structural element which predisposes them to instability
Subluxation - a “halfway" point between a patella in situ and dislocation (see image).[6] Patients with a subluxing patella may complain of a painful knee / anterior knee pain.[6][8]
Recurrent Patellofemoral Instability[edit | edit source]
Recurrent patellofemoral instability is relatively common.[9] Individuals who experience recurrent patellofemoral instability often have specific pathoanatomical features which predispose them to patellar dislocation. Migliorini et al.[9] note the following risk factors:
- Bony conformation abnormalities (e.g. trochlear dysplasia)
- Lower limb mal-alignment syndromes
- Soft tissue abnormalities (e.g. patella alta)
Jaquith and Parikh[4] found that the following are risk factors for multiple dislocations in children and adolescents:
- Aged under 14 years at first dislocation
- History of contralateral dislocation
- Any type of trochlear dysplasia
- Skeletal immaturity (i.e. the physis in the distal femur or proximal tibia are still partially / fully open)
- Long patellar tendon
The number of risk factors a child / adolescent has impacts their risk of recurrent dislocations:[4]
- Children who have risk factors 2-5 are 88 percent likely to have recurrent dislocations
- Having any three risk factors is associated with a 75 percent risk of recurrent dislocations
- Having any two risk factors is associated with a predicted risk of around 55 percent
- 97 percent of recurrences occur within three years[6]
Jaquith and Parikh[4] found that the mean age of first dislocation for children who experienced re-dislocation was 12.9 years and for those who did not re-dislocate, the mean age of first dislocation was 13.8 years. Thus, 13 years is an important milestone when considering patellofemoral dislocation.[6]
Morphology and Instability[edit | edit source]
This is an area of growth:[6]
- Imaging is improving
- More sophisticated surgeries are available
- Our understanding of the subtleties associated with this condition is improving
- There is an awareness that individuals with patellofemoral instability are more likely to have accelerated wear leading to premature patellofemoral arthritis
Dysplasia Assessment[edit | edit source]
The following are important features to consider when assessing individuals with potential / confirmed patellofemoral instability:[6]
- Morphology of the trochlea
- Position of the tibial tubercle
- Length of the patellar tendon
Morphology of the Trochlea[edit | edit source]
The patella is essentially a floating bone which needs to stay in the trochlea (i.e. the groove of the distal femur). It is well recognised that trochlear dysplasia is associated with patellofemoral instability.[10]
Trochlear Depth[edit | edit source]
Ideally, the trochlea will be deep, with a sharp inclination on the lateral side. It is important to look out for a “shallow trochlea” on an MRI report. Patients may also have a long lateral facet and / or shallow inclination.[6]
If imaging is not available, you can assess the following:[6]
- Feel for passive glide, especially laterally (see video on left below)
- Look for J sign (see video on right below) for subluxation (i.e. increased lateral patellar deviation when moving from flexion to extension[11]) and poor engagement at the entrance to the trochlea
There is a spectrum of trochlear dysplasia. Ideally, a trochlea will be shaped liked a soup bowl. Individuals who have a saucer-shaped trochlea (i.e. shallow) are more likely to experience subluxation or dislocation. They may report that it feels like their patella is “skidding around” or “slipping”. At the more extreme end of the spectrum, patients can have a domed trochlea. These persons are most likely to dislocate and are unlikely to stabilise without surgery (e.g. trochleoplasty).[6]
“High-grade trochlear dysplasia is characterized by the combination of a flat and/or prominent trochlea proud of the anterior femoral cortex, which offers inadequate tracking during flexion and leads to patellar subluxation.”[10]
Trochleoplasty - Prevention of Rapid Wear[edit | edit source]
- Addresses trochlear morphology, Q angle and TT-TG distance (see below)
- Addresses a long patellar tendon (see below)
- Addresses the over-stretching of medial structures (see below)
Please note that trochleoplasty is major surgery and outcomes are better when this procedure is performed on pristine chondral surfaces (i.e. on individuals in their late teens).[6]
Non-Operative Rehabilitation[edit | edit source]
Individuals with patellofemoral instability may have multi-directional instability, but they may not always dislocate:[6]
- Look out for patients using descriptors such as ‘slipping’
- Robertson[6] notes that patellofemoral instability is often associated with small patellae and hypermobility
- It is important to try to establish if the individual is subluxing, dislocating or has general excess mobility
- If the problem is with engagement, look at rehabilitating in the early range of motion, avoiding pain
- Isometrics are very useful
- Robertson[6] also notes that individuals with multi-directional instability are often very puffy in their parapatellar soft tissues
- They often have medial and lateral fat pad oedema
- Can consider bracing (see below)
- Not always isolated to terminal extension instability
Bracing[edit | edit source]
It is essential to use clinical reasoning when considering bracing. Ask the following questions:[6]
- Is there any chondral damage or bone oedema? If yes where?
- Lateral facet / lateral trochlea, then consider Q brace[14]
- If no damage, then consider a patellar stabilising brace
Q Brace[edit | edit source]
Callaghan et al.[14] explored the use of a Bioskin Patellar Tracking Q Brace on patients with painful patellofemoral joint osteoarthritis (PFJOA):[14]
- MRI was used to monitor bone marrow lesions in lateral PFJOA
- Participants either wore a brace or had no brace (control)
- Participants in the brace group wore their braces for a mean of 7.4 hours per day
- At the six-week follow-up, Callaghan et al.[14] found that subjects using the Q brace had decreased pain, as well as a reduction in the volume of patellofemoral bone marrow lesions
Taping[edit | edit source]
- McConnell taping can be useful for lateral pathology (see video below)
- K tape can be used to stabilise the knee[6]
Position of the Tibial Tubercle[edit | edit source]
Ideally, the tibial tubercle will be positioned directly under the trochlea. However, some people present with a lateralised tibial tuberosity. When the quadriceps works, the position of the tibial tubercle creates an overall lateralising force, which can have an impact on stability.[6]
TT-TG distance (tibial tuberosity-trochlear groove) is measured on MRI to accurately determine the position of the tibial tubercle in relation to the trochlea.[6][16] The greater the distance, the more lateralised the tibial tuberosity.[16]
To measure TT-TG distance:[6]
- A line is made through the trochlea and tibial tuberosity
- The distance between these two lines is measured[6]
- Up to 15 mm is considered normal
- 15-20 mm may start to affect stability and potentially create pain
- ≥20 mm indicates individuals at risk for future instability[16]
When MRI is not available, it is possible to conduct a visual examination. You can then ask the patient to perform a static quadriceps hold and look to see if the patella moves laterally. While this is not an accurate measure, it can be useful when considered alongside the overall clinical picture.[6]
Non-Operative Management of a Large TT-TG[edit | edit source]
A lateralised tibial tuberosity causes a lateral valgus movement, which overloads the lateral facet and provides a lateral force. Thus, it is important for patients to avoid the following femoral positions:[6]
- Adduction
- Internal rotation
- Adduction with internal rotation
Check also if the patient is anteverted (using Craig's test - see video below). Other points to consider include:[6]
- Are patients aware of any issues with dynamic control (i.e. do they knock their knees when running?)
- Do they have weakness or poor neuromusculoskeletal (NMS) control?
- Can they correct this? What cues work best?
- Consider at what angle of hip flexion the rotation problem occurs
- Is the “medial collapse” driven from the foot?
- Care with orthotics is required for this group
The following exercises can be useful in the rehabilitation of individuals with a large TT-TG:[6]
Length of the Patellar Tendon[edit | edit source]
A patella alta is essentially a “high-riding” patella.[6] It can occur when individuals are born with long patellar tendons[6] and it is known to be associated with patellofemoral instability.[18]
The Insall-Salvati ratio is most often used to measure the height of the patella.[19] It compares patellar tendon length with patellar length.[19] An ideal ratio is 1:1. This can also be informally assessed in the clinic.[6]
Non-Operative Management of Patella Alta[edit | edit source]
In individuals with patella alta, the patella takes longer to enter the trochlea. Typically, the patella will engage in the trochlea at around 15 degrees of knee flexion. But this is delayed in individuals with patella alta.[18] Thus, their knee is relatively more unstable for the first 30 degrees of knee flexion.[6]
It is, therefore, important to target 0-30 degrees of knee flexion with dynamic stability. Conservative management should focus on making the Vastus Medialis Oblique (VMO) architecturally favourable - i.e. increase the fibre angle and the insertion ratio.[6][20]
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament[edit | edit source]
The medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) is the primary restraint to the patella, so it can have a significant impact on stability. While people do not tend to have a congenital problem with this ligament, it is disrupted after dislocation (either very stretched or ruptured).[6]
If a patient presents after a confirmed or potential dislocating event, look for:[6]
- Bruising
- Swelling
- Medial tenderness (just medial to the patella)
These will increase your suspicion of a MPFL injury.[6]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
The following outcome measures can be useful in this client group:[6]
- Norwich Instability Score: highlights degree of instability and impact on life
- Tampa Score of Kinesiophobia: highlights level of kinesiophobia (i.e. the fear of movement)
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Bailey MEA, Metcalfe A, Hing CB, Eldridge J; BASK Patellofemoral Working Group. Consensus guidelines for managing patellofemoral instability. Knee. 2021;29:305-12.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Vellios EE, Trivellas M, Arshi A, Beck JJ. Recurrent Patellofemoral Instability in the Pediatric Patient: Management and Pitfalls. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(1):58-68.
- ↑ Kim HK, Parikh S. Patellofemoral Instability in Children: Imaging Findings and Therapeutic Approaches. Korean J Radiol. 2022 Jun;23(6):674-687.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Jaquith BP, Parikh SN. Predictors of recurrent patellar instability in children and adolescents after first-time dislocation. J Pediatr Orthop. 2017;37(7):484-90.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Post WR, Fithian DC. Patellofemoral instability: a consensus statement from the AOSSM/PFF Patellofemoral Instability Workshop. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(1):2325967117750352.
- ↑ 6.00 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 6.16 6.17 6.18 6.19 6.20 6.21 6.22 6.23 6.24 6.25 6.26 6.27 6.28 6.29 6.30 6.31 6.32 Robertson C. Patellofemoral Joint Instability Course. Plus. 2022.
- ↑ Duthon VB. Acute traumatic patellar dislocation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(1 Suppl):S59-67.
- ↑ Monk AP, Doll HA, Gibbons CL, Ostlere S, Beard DJ, Gill HS, Murray DW. The patho-anatomy of patellofemoral subluxation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(10):1341-7.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Migliorini F, Oliva F, Maffulli GD, Eschweiler J, Knobe M, Tingart M, Maffulli N. Isolated medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for recurrent patellofemoral instability: analysis of outcomes and risk factors. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):239.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Batailler C, Neyret P. Trochlear dysplasia: imaging and treatment options. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3(5):240-47.
- ↑ Hayat Z, El Bitar Y, Case JL. Patella Dislocation. [Updated 2022 May 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538288/
- ↑ www.sportsinjuryclinic.net. Patellar Glide Test. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0VXNx4yuWEo [last accessed 14/6/2022]
- ↑ Claire Patella. J Sign Claire Patella. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/shorts/4dHF6LxhAMw [last accessed 14/6/2022]
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Callaghan MJ, Parkes MJ, Hutchinson CE, Gait AD, Forsythe LM, Marjanovic EJ, et al. A randomised trial of a brace for patellofemoral osteoarthritis targeting knee pain and bone marrow lesions. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(6):1164-70.
- ↑ McConnell Physiotherapy Group. MCCONNELL KNEE TAPING (OFFICIAL). Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WbHXYnwUwws [last accessed 14/6/2022]
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Heidenreich MJ, Camp CL, Dahm DL, Stuart MJ, Levy BA, Krych AJ. The contribution of the tibial tubercle to patellar instability: analysis of tibial tubercle-trochlear groove (TT-TG) and tibial tubercle-posterior cruciate ligament (TT-PCL) distances. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(8):2347-51.
- ↑ Clinical Physio. Craig's Test for Hip | Clinical Physio Premium. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qi41LYsVy1E [last accessed 14/6/2022]
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Patel RM, Gombosh M, Polster J, Andrish J. Patellar Tendon imbrication is a safe and efficacious technique to shorten the patellar tendon in patients with patella alta. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020;8(10):2325967120959318.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Gaillard F, Weerakkody Y. Insall-Salvati ratio. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org. Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/insall-salvati-ratio?lang=us (accessed 14 June 2022).
- ↑ Khoshkhoo M, Killingback A, Robertson CJ, Adds PJ. The effect of exercise on vastus medialis oblique muscle architecture: An ultrasound investigation. Clin Anat. 2016;29(6):752-8.