Sporting Hand and Wrist - Why Power and Pinch Grips Matter: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class=" | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User:Mariam Hashem|Mariam Hashem]] | |||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | |||
</div> | |||
< | == Types of Grips == | ||
[https://physio-pedia.com/Category:Hand_-_Anatomy?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal The hand anatomy] is efficiently organized to carry out a variety of complex tasks combining intricate movements and finely controlled force production. The soft tissue structure of the hand is complicated. Any injury to any of these, even very small structures, can alter the overall function of the hand and thereby complicate therapeutic management. <ref name=":3">Duruoz MT. Hand function. Springer-Verlag New York; 2016.</ref> [https://physio-pedia.com/Hand_Function#sts=Functional%20Position%20of%20Hand?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Hand function] and strength are important elements in day to day life and participation in sports. <ref name=":0">Gatt I, Smith-Moore S, Steggles C, Loosemore M. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5987983/pdf/10.1177_1558944717707831.pdf The takei handheld dynamometer: an effective clinical outcome measure tool for hand and wrist function in boxing.] HAND. 2018 May;13(3):319-24.</ref> The ability to grasp and manipulate objects highly correlates with the quality of life satisfaction. <ref>Romano P, Pournajaf S, Ottaviani M, Gison A, Infarinato F, Mantoni C, De Pandis MF, Franceschini M, Goffredo M. [https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/21/11/3823 Sensor network for analyzing upper body strategies in Parkinson’s disease versus normative kinematic patterns.] Sensors. 2021 May 31;21(11):3823.</ref>The American Society of Hand Therapists (ASHT) considers hand strength as one of the components required to evaluate the overall strength of the upper limb. <ref>El-samad A, Ahmed A, El-Meniawy GH, Nour El-Din SM, Mohamed NE. Pinch grip strength and fine manual control in children with diplegic cerebral palsy: a cross-sectional study. Bulletin of Faculty of Physical Therapy. 2021 Dec;26(1):1-8.</ref> | |||
Gripping or the ability to fold the fingers into the palms supported by the thenar and hypothenar eminences to make a club-like structure is exclusive to humans. <ref name=":2" /> | |||
The grip function of the hand is of great importance in professional and daily life activities. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the grip strength measurement for the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF). <ref>Lo VE, Chiu YC, Tu HH. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7908096/pdf/ijerph-18-00856.pdf Can We Use Grip Strength to Predict Other Types of Hand Exertions? An Example of Manufacturing Industry Workers.] Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jan 20;18(3):856.</ref>Professional and daily life activities require a combination of different types of grips<ref name=":3" />. | |||
'''There are two types of grips''': power grip and pinch grip.<ref>Gatt I. Hand and wrist injuries: a focus on boxing. A Comprehensive Guide to Sports Physiology and Injury Management E-Book: An Interdisciplinary Approach. 2020 Nov 28:315.</ref> | |||
=== Power Grip === | |||
Closing a hand with the thumb in opposition to all other fingers together generates a power grip. <ref name=":1">Gatt I. Sporting Hand & Wrist - Why Power & Pinch Grips Matter. Plus Course 2020</ref> | |||
A-Lumbrical grip | A-Lumbrical grip | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
! scope="col" | [[File:Lumbrical grip.png|center|thumb|229x229px]] Lumbrical grip | ! scope="col" | [[File:Lumbrical grip.png|center|thumb|229x229px]] Lumbrical grip | ||
! scope="col" | [[File:Spherical grip.png|center|thumb|253x253px]]Spherical grip | ! scope="col" | [[File:Spherical grip.png|center|thumb|253x253px]]Spherical grip | ||
! scope="col" | [[File:Hammer grip.png | ! scope="col" | [[File:Hammer grip.png|thumb|249x249px|center]] Hammer grip | ||
! scope="col" | [[File:Hook grip.png | ! scope="col" | [[File:Hook grip.png|thumb|210x210px|none]] Hook grip | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== Pinch grip === | |||
The holding of an object between the thumb and fingers of a single hand. | |||
A-Tip Pinch: index pressing against the thumb: holding an object between thumb and a fingertip is used for fine manipulation<ref name=":3" /> | A-Tip Pinch: index pressing against the thumb: holding an object between the thumb and a fingertip is used for fine manipulation. <ref name=":3" /> | ||
B-Tripod Pinch (Chuck pinch): increases | B-Tripod Pinch (Chuck pinch): increases stability by utilizing two fingertips instead of one. | ||
C-Lateral Pinch, also known as key pinch<ref name=":1" />: achieved by pressing the thumb pulp against the lateral aspect of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the index finger. In this grip, the thumb | C-Lateral Pinch, also known as key pinch<ref name=":1" />: achieved by pressing the thumb pulp against the lateral aspect of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the index finger. In this grip, the thumb goes into adduction and flexion. <ref name=":1" /> | ||
The peak forces generated with the three | The peak forces generated with the three digits and lateral pinch grips are about 40% greater than that produced with the tip pinch. <ref name=":3" /> | ||
Lateral pinch is the strongest type of pinch followed by tripod pinch. Tip pinch is used for more sophisticated processes requiring fine coordination. | Lateral pinch is the strongest type of pinch, followed by tripod pinch. Tip pinch is used for more sophisticated processes requiring fine coordination. | ||
{| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | {| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="col" | [[File:Tip Pinch.png|none|thumb]] | ! scope="col" | [[File:Tip Pinch.png|none|thumb]] | ||
! scope="col" | [[File:Tripod Pinch.png|none|thumb]] | ! scope="col" | [[File:Tripod Pinch.png|none|thumb]] | ||
! scope="col" | [[File:Lateral Pinch.png|none|thumb|215x215px]] | ! scope="col" | [[File:Lateral Pinch.png|none|thumb|215x215px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Grip Strength in Day to Day Life == | == Grip Strength in Day-to-Day Life == | ||
Daily activities require a combination of different movements in the upper limb. Hand function is | Daily activities require a combination of different movements in the upper limb. Hand function is a vital component of these movements. The loss of grip strength is associated with several pathologies. [https://physio-pedia.com/Wrist_and_Hand_Osteoarthritis?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Hand Osteoarthritis] is a common chronic condition involving one or more joints of the thumb and fingers. It is associated with pain, reduced grip strength, loss of range of motion (ROM), and joint stiffness leading to impaired hand function and difficulty with daily activities. <ref>Magni NE, McNair PJ, Rice DA. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5470180/pdf/13075_2017_Article_1348.pdf The effects of resistance training on muscle strength, joint pain, and hand function in individuals with hand osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.] Arthritis research & therapy. 2017 Dec 1;19(1):131.</ref> [https://physio-pedia.com/Stroke:_Hand_Rehabilitation?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Stroke] is another condition that impacts the upper limb and hand function. Addressing these conditions requires an understanding of hand anatomy and biomechanics. | ||
There are numerous factors such as sex, age, and hand | There are numerous factors, such as sex, age, and hand preference, that contribute to grip strength, and they should be considered when making clinical decisions. The average grip strength of women is approximately 60% of that of men, and for both sexes, grip strength reaches a maximum during the fourth decade of life and declines thereafter with increasing age. <ref name=":3" /> | ||
Cold weather causes reduced muscle contraction and affects grip strength and function of the hand<ref name=":3" /> | Cold weather causes reduced muscle contraction and affects the grip strength and function of the hand.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
It is believed that the difference between the dominant and non-dominant hand in strength is 10% (known as the 10% rule). This applies to right-handed people. For left-handed persons, grip strength is considered equivalent in both hands<ref name=":3" /> | It is believed that the difference between the dominant and non-dominant hand in strength is 10% (known as the 10% rule). This applies to right-handed people. For left-handed persons, grip strength is considered equivalent in both hands. <ref name=":3" /> | ||
'''The hand strength in daily activities is classified into three main functional groups'''<ref>Duruöz MT, Poiraudeau S, Fermanian J, | '''The hand strength in daily activities is classified into three main functional groups:''' <ref>Duruöz MT, Poiraudeau S, Fermanian J, Menkes CJ, Amor B, Dougados M, Revel M. Development and validation of a rheumatoid hand functional disability scale that assesses functional handicap. J Rheumatol. 1996 Jul;23(7):1167-72. </ref> | ||
* Activities | * Activities requiring force and rotation (e.g., unscrewing the jar lid) | ||
* Activities | * Activities require dexterity and precision (e.g., peeling fruits) | ||
* Dynamic activities, primarily based on pinching and performed with the first two or three fingers of the dominant hand (e.g., writing with a pencil) | * Dynamic activities, primarily based on pinching and performed with the first two or three fingers of the dominant hand (e.g., writing with a pencil) | ||
== Grip in Sports == | == Grip in Sports == | ||
The combination of grips differs according to the type of | The combination of grips differs according to the type of sport and hand dominance. If you are involved in sports rehabilitation, understanding the type of grip and involvement of the thumb is important to measure the strength and address any related injuries. <ref name=":1" /> | ||
'''Here are some examples of different grips used in various sports<ref name=":1" /> | '''Here are some examples of different grips used in various sports: <ref name=":1" />''' | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Sport | !Sport | ||
| Line 73: | Line 76: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Bow and arrow''' | |'''Bow and arrow''' | ||
| The lead hand holding the bow and keeping it stable in a power grip. Whereas the backhand, pulling the string, also in power grip but the thumb is less involved | | The lead hand holding the bow and keeping it stable in a power grip. Whereas the backhand, pulling the string, is also in power grip, but the thumb is less involved in more adduction. | ||
|[[File:Bow and Arrow grip.png|thumb|300x300px]] | |[[File:Bow and Arrow grip.png|thumb|300x300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Racquet sports such as tennis:''' | |'''Racquet sports such as tennis:''' | ||
| Hand holding the racket using a power grip and the other | | Hand holding the racket using a power grip and the other holding the ball in a pinch grip. By changing the grip, the movement and the force changes. | ||
|[[File:Tennis grip.jpg|center|thumb|360x360px]] | |[[File:Tennis grip.jpg|center|thumb|360x360px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 89: | Line 92: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Weight lifting''' | |'''Weight lifting''' | ||
|The use of a hook grip is recommended in weightlifting movements<ref>Oranchuk DJ, Drinkwater EJ, Lindsay RS, Helms ER, Harbour ET, Storey AG. Improvement of kinetic, kinematic, and qualitative performance variables of the power clean with the hook grip. International journal of sports physiology and performance. 2019 Mar 1;14(3):378-84.</ref> | |The use of a hook grip is recommended in weightlifting movements. <ref>Oranchuk DJ, Drinkwater EJ, Lindsay RS, Helms ER, Harbour ET, Storey AG. Improvement of kinetic, kinematic, and qualitative performance variables of the power clean with the hook grip. International journal of sports physiology and performance. 2019 Mar 1;14(3):378-84.</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Boxing:''' | |'''Boxing:''' | ||
|Power grip is used. Injury at the base of the CMC joints of the index and middle fingers is common causing instability and interferes with the gripping power<ref name=":1" /> | |Power grip is used. Injury at the base of the CMC joints of the index and middle fingers is common causing instability and interferes with the gripping power. <ref name=":1" /> | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
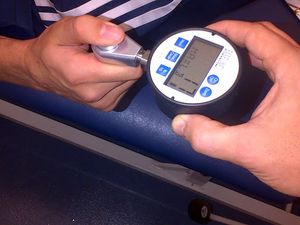
== Measuring Grip Strength == | == Measuring Grip Strength == | ||
Measuring grip strength is commonly used in research and sports to measure the efficacy of an intervention. | Measuring grip strength is commonly used in research and sports to measure the efficacy of an intervention. Implementing in-hand rehabilitation is a good practice to help with decision-making and reporting outcomes. [[File:Grip test elbow bent.jpg|thumb|233x233px]] | ||
'''Dynamometers'''<ref name=":0" />''':''' the Jamar and the Takei are the most | '''Dynamometers'''<ref name=":0" />''':''' the Jamar and the Takei are the most commonly studied dynamometers in the literature. | ||
''The Jamar dynamometer'' is the gold standard for documenting manual grip strength. It is comprised of the following: | |||
* an adjustable anatomical rigid handle | * an adjustable anatomical rigid handle | ||
* hydraulic system | * hydraulic system | ||
* analogue display | * analogue display | ||
''The Takei'' is a valid and reliable tool to measure power grip. It is comprised of the following: | |||
* Adjustable rectified | * Adjustable rectified | ||
* Complacent handle shape | * Complacent handle shape | ||
* Electromechanical system | * Electromechanical system | ||
* A digital or analogue display | * A digital or analogue display | ||
''Important points to consider when testing grip strength'': <ref name=":1" />[[File:Grip test elbow extended.jpg|thumb|210x210px]] | |||
* Note the associated symptoms such as pain or instability. The timing of the symptoms also matters whether they accompany the movement or start after the testing. | * Note the associated symptoms, such as pain or instability. The timing of the symptoms also matters whether they accompany the movement or start after the testing. | ||
* The difference between the right and left hands. Consider the element of chronicity could lead to weakness due to reciprocal inhibition. | * The difference between the right and left hands. Consider the element of chronicity that could lead to weakness due to reciprocal inhibition. | ||
* Repeat the test | * Repeat the test 3 times, starting with the non-painful side, then move on to the other hand and alternate the testing between hands three times | ||
* Look for the peak force (the best number | * Look for the peak force (the best number to be achieved on testing). Some people might be able to generate a high number on the strength test, but then the number lowers due to fatigue, or they take a few repetitions to generate the force | ||
* Testing position: | * Testing position: | ||
# Elbow | # Elbow at a 90-degree angle: helps to generate the highest peak. However, having the forearm in mid-position could lead to contraction of the brachioradialis muscle, and the movement will not be generated purely from the hand. | ||
# Testing from straight elbow position and wrist in neutral. This position is recommended by Gatt I.<ref name=":1" /> to isolate hand muscles. | # Testing from straight elbow position and wrist in neutral. This position is recommended by Gatt I.<ref name=":1" /> to isolate hand muscles. | ||
Note: When different elbow position is used for testing, even when the same measurement system is used, the results cannot be compared.<ref>Marković S, Dopsaj M, Veljković V. [https://www.measurement.sk/2020/msr-2020-0008.pdf Reliability of Sports Medical Solutions Handgrip and Jamar Handgrip Dynamometer.] Measurement Science Review 2020; 20 (2):59-64.</ref> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|-jmWNKUek3o|300}}<ref>Hand Grip Dynamometer. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-jmWNKUek3o[last accessed 28/12/2020]</ref> | |||
[https://physio-pedia.com/Hand_and_Wrist_Sports_Injuries?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal ''' | == Injuries and Grip Strength == | ||
A study by Loosemore et al. <ref name=":2">Loosemore M, Lightfoot J, Gatt I, Hayton M, Beardsley C. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5349401/pdf/10.1177_1558944716642756.pdf Hand and wrist injuries in elite boxing: a longitudinal prospective study (2005-2012) of the Great Britain Olympic Boxing Squad.] Hand. 2017 Mar;12(2):181-7.</ref> explored hand and wrist injuries in both training and competitions in boxing found: | |||
[[Hand Pulleys|Pulley]] | * [https://physio-pedia.com/Traumatic_Extensor_Hood_Rupture?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Boxer's Knuckles] (Finger carpometacarpal instability and finger metacarpophalangeal joint extensor hood and capsule sprain) to be the most common injury. | ||
* The incidence of training injuries was similar to that of competition injuries. | |||
[https://physio-pedia.com/Thumb_Ligament_Injuries?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Thumb ligament injuries] | The study also measured the grip strength in the right and left hands at baseline and after injuries and concluded: | ||
* A difference of 15% between both hands is considered normal | |||
[https://physio-pedia.com/Bennett's_fracture?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Bennett's fracture] | * Boxers with a difference of 20% are likely to have an injury. | ||
* A higher than 20% difference places the athlete at a higher risk for pathologies. | |||
[[Traumatic Extensor Hood Rupture]] | * Following an injury, an 87% difference in bilateral hand-gripping strength was observed. | ||
Example of [https://physio-pedia.com/Hand_and_Wrist_Sports_Injuries?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal '''injuries affecting Grip strength:'''] | |||
[[Flexor Tendon Injuries]] | * [[Hand Pulleys|Pulley ruptures]] | ||
* [https://physio-pedia.com/Thumb_Ligament_Injuries?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Thumb ligament injuries] | |||
[[Skier's thumb|skier’s thumb]] | * [https://physio-pedia.com/Bennett's_fracture?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal Bennett's fracture] | ||
* [[Traumatic Extensor Hood Rupture]] | |||
[[Ulnar Impaction Syndrome|Ulnar abutment]] | * [[Extensor tendon injuries of the fingers and hand|Extensor Tendon Injuries of the Fingers and Hand]] | ||
* [[Flexor Tendon Injuries]] | |||
[[Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injuries|Triangular fibrocartilage complex tears]] | * [[Skier's thumb|skier’s thumb]] | ||
* [[Ulnar Impaction Syndrome|Ulnar abutment]] | |||
[[Metacarpal Fractures|Metacarpal fractures]] | * [[Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injuries|Triangular fibrocartilage complex tears]] | ||
* [[Metacarpal Fractures|Metacarpal fractures]] | |||
== Rehabilitation of Grip Strength == | |||
As mentioned earlier, it's essential to understand the factors contributing to grip strength. | |||
Handgrip measuring should be a key component during the rehabilitation process to measure effectiveness. <ref name=":1" /> | |||
The available interventions to rehabilitate grip strength are numerous. The selection of the intervention depends on the individual factors, type of sport and used grip, the type of injury, chronicity, severity and also the associated pathologies. | |||
A case study of a boxing injury conducted by Gatt<ref name=":1" /> reported a threefold increase in handgrip strength and a drop of right-left hands strength difference from 87% to 15% following three weeks of conservative management. A functional rehabilitation approach is recommended with monitoring of symptoms and gradual progression into functional and power grip training. | |||
'''Examples of power grip interventions:''' | |||
1-Isokinetic training machine: | |||
Expensive but valuable kinetic machine. It could be implemented as testing and as training equipment for different wrist and hand muscles at eccentric and concentric measures with speed variations. | |||
Crushes: is another tool that could be used to improve the power grip. | 2-Rubber tools, also known as flex bars. Different colours could be deployed for varying strength and targeting the wrist and forearm muscles. [[File:Flex bar-power grip.png|thumb|300x300px|center]]3-Crushes: this is another tool that could be used to improve the power grip. Intensity could be adjusted by the number of springs. | ||
[[File:Crushes.png|center|thumb]] | [[File:Crushes.png|center|thumb]] | ||
4-Talon grips: could be added to pull-ups. A tool that is designed ergonomically to adapt to the shape of the hand and give a uniform loading on the tendons, | |||
[[File:Talon grip.jpg| | [[File:Talon grip.jpg|thumb|center]] | ||
'''Examples of pinch grip interventions:''' <ref name=":1" /> | |||
Pinch grip dynamometer or handheld dynamometer: there are two positions to | 1-Pinch grip dynamometer or handheld dynamometer: there are two positions to perform the exercise from as in the image:[[File:Pinch grip handheld dynamometer.png|center|thumb|Handheld dynamometer for pinch grip strength|250x250px]]2-key grip dynamometer: places the thumb joint in a closed position. Useful for strengthening the thumb flexors [[File:Key grip.jpg|center|thumb|Key Grip]] | ||
. | |||
The | The decision on which grip (key or pinch) depends on the onset and severity of the injury. | ||
3- Holding a plate: Different variations depend on the targeted muscles. The time to hold can be adjusted on the type of training, e.g. conditioning or endurance, and also could be used to check the difference in the maximum hold between right and left hands. Monitoring the symptoms associated with holding the plate, such as pain, the timing of the signs and the effect on holding, can be helpful data in management. | |||
[[File:Key grip with plate.jpg|center|thumb| | [[File:Key grip with plate.jpg|center|thumb| | ||
Key grip | Key grip | ||
| Line 196: | Line 184: | ||
[[File:Pinch grip with plate.jpg|center|thumb| | [[File:Pinch grip with plate.jpg|center|thumb| | ||
Pinch grip | Pinch grip | ||
]] | ]] | ||
Putty: | 4-Putty: for pinch or power grip using different variations: | ||
{{#ev:youtube|QxaP5P9CSWc|300}}<ref>Pinch grip strength putty R. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QxaP5P9CSWc[last accessed 28/12/2020]</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|QxaP5P9CSWc|300}}<ref>Pinch grip strength putty R. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QxaP5P9CSWc[last accessed 28/12/2020]</ref> | ||
{{#ev:youtube|DufAYWGidsc|300}}<ref>Power grip strength putty R. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DufAYWGidsc[last accessed 28/12/2020]</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|DufAYWGidsc|300}}<ref>Power grip strength putty R. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DufAYWGidsc[last accessed 28/12/2020]</ref> | ||
5-Flipping Plates: good exercise to improve thumb and wrist proprioception. | |||
{{#ev:youtube|Z-qNThP5Sjw|300}}<ref>Plate Flip | Better Grip | Forearm Strength | Move and Perform Better. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z-qNThP5Sjw[last accessed 28/12/2020]</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|Z-qNThP5Sjw|300}}<ref>Plate Flip | Better Grip | Forearm Strength | Move and Perform Better. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z-qNThP5Sjw[last accessed 28/12/2020]</ref> | ||
| Line 217: | Line 203: | ||
[[Category:Hand - Conditions]] | [[Category:Hand - Conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Course Pages]] | [[Category:Course Pages]] | ||
[[Category:Plus Content]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:09, 28 December 2022
Original Editor - Mariam Hashem Top Contributors - Mariam Hashem, Tarina van der Stockt, Kim Jackson and Ewa Jaraczewska
Types of Grips[edit | edit source]
The hand anatomy is efficiently organized to carry out a variety of complex tasks combining intricate movements and finely controlled force production. The soft tissue structure of the hand is complicated. Any injury to any of these, even very small structures, can alter the overall function of the hand and thereby complicate therapeutic management. [1] Hand function and strength are important elements in day to day life and participation in sports. [2] The ability to grasp and manipulate objects highly correlates with the quality of life satisfaction. [3]The American Society of Hand Therapists (ASHT) considers hand strength as one of the components required to evaluate the overall strength of the upper limb. [4]
Gripping or the ability to fold the fingers into the palms supported by the thenar and hypothenar eminences to make a club-like structure is exclusive to humans. [5]
The grip function of the hand is of great importance in professional and daily life activities. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the grip strength measurement for the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF). [6]Professional and daily life activities require a combination of different types of grips[1].
There are two types of grips: power grip and pinch grip.[7]
Power Grip[edit | edit source]
Closing a hand with the thumb in opposition to all other fingers together generates a power grip. [8]
A-Lumbrical grip
B-Spherical grip
C-Hammer grip
D-Hook grip
| Lumbrical grip | Spherical grip | Hammer grip | Hook grip |
|---|
Pinch grip[edit | edit source]
The holding of an object between the thumb and fingers of a single hand.
A-Tip Pinch: index pressing against the thumb: holding an object between the thumb and a fingertip is used for fine manipulation. [1]
B-Tripod Pinch (Chuck pinch): increases stability by utilizing two fingertips instead of one.
C-Lateral Pinch, also known as key pinch[8]: achieved by pressing the thumb pulp against the lateral aspect of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the index finger. In this grip, the thumb goes into adduction and flexion. [8]
The peak forces generated with the three digits and lateral pinch grips are about 40% greater than that produced with the tip pinch. [1]
Lateral pinch is the strongest type of pinch, followed by tripod pinch. Tip pinch is used for more sophisticated processes requiring fine coordination.
Grip Strength in Day-to-Day Life[edit | edit source]
Daily activities require a combination of different movements in the upper limb. Hand function is a vital component of these movements. The loss of grip strength is associated with several pathologies. Hand Osteoarthritis is a common chronic condition involving one or more joints of the thumb and fingers. It is associated with pain, reduced grip strength, loss of range of motion (ROM), and joint stiffness leading to impaired hand function and difficulty with daily activities. [9] Stroke is another condition that impacts the upper limb and hand function. Addressing these conditions requires an understanding of hand anatomy and biomechanics.
There are numerous factors, such as sex, age, and hand preference, that contribute to grip strength, and they should be considered when making clinical decisions. The average grip strength of women is approximately 60% of that of men, and for both sexes, grip strength reaches a maximum during the fourth decade of life and declines thereafter with increasing age. [1]
Cold weather causes reduced muscle contraction and affects the grip strength and function of the hand.[1]
It is believed that the difference between the dominant and non-dominant hand in strength is 10% (known as the 10% rule). This applies to right-handed people. For left-handed persons, grip strength is considered equivalent in both hands. [1]
The hand strength in daily activities is classified into three main functional groups: [10]
- Activities requiring force and rotation (e.g., unscrewing the jar lid)
- Activities require dexterity and precision (e.g., peeling fruits)
- Dynamic activities, primarily based on pinching and performed with the first two or three fingers of the dominant hand (e.g., writing with a pencil)
Grip in Sports[edit | edit source]
The combination of grips differs according to the type of sport and hand dominance. If you are involved in sports rehabilitation, understanding the type of grip and involvement of the thumb is important to measure the strength and address any related injuries. [8]
Here are some examples of different grips used in various sports: [8]
| Sport | Grip | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Bow and arrow | The lead hand holding the bow and keeping it stable in a power grip. Whereas the backhand, pulling the string, is also in power grip, but the thumb is less involved in more adduction. | |
| Racquet sports such as tennis: | Hand holding the racket using a power grip and the other holding the ball in a pinch grip. By changing the grip, the movement and the force changes. | |
| Golf: | Lateral pinch or key grip is used but that could change during the game depending on the movement and how much strength is required. | |
| Wheelchair sports, for example, basketball | The hand holding the wheelchair would require more strength from the thumb for stability. the other hand holding the ball would use a spherical grip in which there will be cupping at the wrist and adduction at the thumb. | |
| Weight lifting | The use of a hook grip is recommended in weightlifting movements. [11] | |
| Boxing: | Power grip is used. Injury at the base of the CMC joints of the index and middle fingers is common causing instability and interferes with the gripping power. [8] |
Measuring Grip Strength[edit | edit source]
Measuring grip strength is commonly used in research and sports to measure the efficacy of an intervention. Implementing in-hand rehabilitation is a good practice to help with decision-making and reporting outcomes.
Dynamometers[2]: the Jamar and the Takei are the most commonly studied dynamometers in the literature.
The Jamar dynamometer is the gold standard for documenting manual grip strength. It is comprised of the following:
- an adjustable anatomical rigid handle
- hydraulic system
- analogue display
The Takei is a valid and reliable tool to measure power grip. It is comprised of the following:
- Adjustable rectified
- Complacent handle shape
- Electromechanical system
- A digital or analogue display
Important points to consider when testing grip strength: [8]
- Note the associated symptoms, such as pain or instability. The timing of the symptoms also matters whether they accompany the movement or start after the testing.
- The difference between the right and left hands. Consider the element of chronicity that could lead to weakness due to reciprocal inhibition.
- Repeat the test 3 times, starting with the non-painful side, then move on to the other hand and alternate the testing between hands three times
- Look for the peak force (the best number to be achieved on testing). Some people might be able to generate a high number on the strength test, but then the number lowers due to fatigue, or they take a few repetitions to generate the force
- Testing position:
- Elbow at a 90-degree angle: helps to generate the highest peak. However, having the forearm in mid-position could lead to contraction of the brachioradialis muscle, and the movement will not be generated purely from the hand.
- Testing from straight elbow position and wrist in neutral. This position is recommended by Gatt I.[8] to isolate hand muscles.
Note: When different elbow position is used for testing, even when the same measurement system is used, the results cannot be compared.[12]
Injuries and Grip Strength[edit | edit source]
A study by Loosemore et al. [5] explored hand and wrist injuries in both training and competitions in boxing found:
- Boxer's Knuckles (Finger carpometacarpal instability and finger metacarpophalangeal joint extensor hood and capsule sprain) to be the most common injury.
- The incidence of training injuries was similar to that of competition injuries.
The study also measured the grip strength in the right and left hands at baseline and after injuries and concluded:
- A difference of 15% between both hands is considered normal
- Boxers with a difference of 20% are likely to have an injury.
- A higher than 20% difference places the athlete at a higher risk for pathologies.
- Following an injury, an 87% difference in bilateral hand-gripping strength was observed.
Example of injuries affecting Grip strength:
- Pulley ruptures
- Thumb ligament injuries
- Bennett's fracture
- Traumatic Extensor Hood Rupture
- Extensor Tendon Injuries of the Fingers and Hand
- Flexor Tendon Injuries
- skier’s thumb
- Ulnar abutment
- Triangular fibrocartilage complex tears
- Metacarpal fractures
Rehabilitation of Grip Strength[edit | edit source]
As mentioned earlier, it's essential to understand the factors contributing to grip strength.
Handgrip measuring should be a key component during the rehabilitation process to measure effectiveness. [8]
The available interventions to rehabilitate grip strength are numerous. The selection of the intervention depends on the individual factors, type of sport and used grip, the type of injury, chronicity, severity and also the associated pathologies.
A case study of a boxing injury conducted by Gatt[8] reported a threefold increase in handgrip strength and a drop of right-left hands strength difference from 87% to 15% following three weeks of conservative management. A functional rehabilitation approach is recommended with monitoring of symptoms and gradual progression into functional and power grip training.
Examples of power grip interventions:
1-Isokinetic training machine:
Expensive but valuable kinetic machine. It could be implemented as testing and as training equipment for different wrist and hand muscles at eccentric and concentric measures with speed variations.
2-Rubber tools, also known as flex bars. Different colours could be deployed for varying strength and targeting the wrist and forearm muscles.
3-Crushes: this is another tool that could be used to improve the power grip. Intensity could be adjusted by the number of springs.
4-Talon grips: could be added to pull-ups. A tool that is designed ergonomically to adapt to the shape of the hand and give a uniform loading on the tendons,
Examples of pinch grip interventions: [8]
1-Pinch grip dynamometer or handheld dynamometer: there are two positions to perform the exercise from as in the image:
2-key grip dynamometer: places the thumb joint in a closed position. Useful for strengthening the thumb flexors
.
The decision on which grip (key or pinch) depends on the onset and severity of the injury.
3- Holding a plate: Different variations depend on the targeted muscles. The time to hold can be adjusted on the type of training, e.g. conditioning or endurance, and also could be used to check the difference in the maximum hold between right and left hands. Monitoring the symptoms associated with holding the plate, such as pain, the timing of the signs and the effect on holding, can be helpful data in management.
4-Putty: for pinch or power grip using different variations:
5-Flipping Plates: good exercise to improve thumb and wrist proprioception.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Duruoz MT. Hand function. Springer-Verlag New York; 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Gatt I, Smith-Moore S, Steggles C, Loosemore M. The takei handheld dynamometer: an effective clinical outcome measure tool for hand and wrist function in boxing. HAND. 2018 May;13(3):319-24.
- ↑ Romano P, Pournajaf S, Ottaviani M, Gison A, Infarinato F, Mantoni C, De Pandis MF, Franceschini M, Goffredo M. Sensor network for analyzing upper body strategies in Parkinson’s disease versus normative kinematic patterns. Sensors. 2021 May 31;21(11):3823.
- ↑ El-samad A, Ahmed A, El-Meniawy GH, Nour El-Din SM, Mohamed NE. Pinch grip strength and fine manual control in children with diplegic cerebral palsy: a cross-sectional study. Bulletin of Faculty of Physical Therapy. 2021 Dec;26(1):1-8.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Loosemore M, Lightfoot J, Gatt I, Hayton M, Beardsley C. Hand and wrist injuries in elite boxing: a longitudinal prospective study (2005-2012) of the Great Britain Olympic Boxing Squad. Hand. 2017 Mar;12(2):181-7.
- ↑ Lo VE, Chiu YC, Tu HH. Can We Use Grip Strength to Predict Other Types of Hand Exertions? An Example of Manufacturing Industry Workers. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jan 20;18(3):856.
- ↑ Gatt I. Hand and wrist injuries: a focus on boxing. A Comprehensive Guide to Sports Physiology and Injury Management E-Book: An Interdisciplinary Approach. 2020 Nov 28:315.
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 8.10 Gatt I. Sporting Hand & Wrist - Why Power & Pinch Grips Matter. Plus Course 2020
- ↑ Magni NE, McNair PJ, Rice DA. The effects of resistance training on muscle strength, joint pain, and hand function in individuals with hand osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis research & therapy. 2017 Dec 1;19(1):131.
- ↑ Duruöz MT, Poiraudeau S, Fermanian J, Menkes CJ, Amor B, Dougados M, Revel M. Development and validation of a rheumatoid hand functional disability scale that assesses functional handicap. J Rheumatol. 1996 Jul;23(7):1167-72.
- ↑ Oranchuk DJ, Drinkwater EJ, Lindsay RS, Helms ER, Harbour ET, Storey AG. Improvement of kinetic, kinematic, and qualitative performance variables of the power clean with the hook grip. International journal of sports physiology and performance. 2019 Mar 1;14(3):378-84.
- ↑ Marković S, Dopsaj M, Veljković V. Reliability of Sports Medical Solutions Handgrip and Jamar Handgrip Dynamometer. Measurement Science Review 2020; 20 (2):59-64.
- ↑ Hand Grip Dynamometer. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-jmWNKUek3o[last accessed 28/12/2020]
- ↑ Pinch grip strength putty R. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QxaP5P9CSWc[last accessed 28/12/2020]
- ↑ Power grip strength putty R. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DufAYWGidsc[last accessed 28/12/2020]
- ↑ Plate Flip | Better Grip | Forearm Strength | Move and Perform Better. Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z-qNThP5Sjw[last accessed 28/12/2020]