|
|
| (222 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| <div class="editorbox"> | | <div class="editorbox"> |
| '''Original Editors '''- [[User:Jason Chang|<font color="#000080">Jason Chang</font>]], [[User:Andrea Christoforou|Andrea Christoforou]], [[User:Maria Cuddihy|<font color="#000080">Maria Cuddihy</font>]], [[User:Christine Gorsek|Christine Gorsek]], [[User:Annika Hobler|Annika Höbler]] as part of the [[Current and Emerging Roles in Physiotherapy Practice|QMU Current and Emerging Roles in Physiotherapy Practice Project]] | | '''Original Editors '''- [[User:Jason Chang|Jason Chang]], [[User:Andrea Christoforou|Andrea Christoforou]], [[User:Maria Cuddihy|Maria Cuddihy]], [[User:Christine Gorsek|Christine Gorsek]], [[User:Annika Hobler|Annika Höbler]] as part of the [[Current_and_Emerging_Roles_in_Physiotherapy_Practice|Queen Margaret University's Current and Emerging Roles in Physiotherapy Practice Project]] |
| </div>
| |
| = INTRODUCTION TO RESOURCE =
| |
| | |
| NB: Currently under <u>'''HEAVY'''</u>construction. Please stand by. Thank you. (December 2013)
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| == Resource Aims ==
| |
| | |
| Tackling Physical Inactivity: A Resource for Raising Awareness in Physiotherapists has been developed based on the following three premises, each of which is addressed/supported/evidenced within the Resource:
| |
| | |
| '''1)''' Physical inactivity has become a public health priority as a result of its widespread prevalence and burden to public health.
| |
| | |
| '''2)''' Physiotherapists, upon qualification, are uniquely skilled and appropriately positioned to make a substantial contribution to promoting physical activity and easing this public health burden.
| |
| | |
| '''3)''' As a result of the cumulative evidence of the problem and of physical activity promotion as a means toward the solution and as a result of the recent widespread attention on the issue, an overwhelming amount of information has become available.
| |
| | |
| Thus, the Resource serves to facilitate the ‘everyday practitioner’ in his/her role in physical activity promotion. Through the identification and collation of some of the most relevant information, it aims to raise awareness of the problem (physical inactivity), the solution (physical activity) and the various approaches (individual, community and government) that may be taken to execute this role.
| |
| | |
| The Resource is by no means comprehensive, as this would be impossible and counterproductive given the amount of information that exists and is continuously being produced. Instead, it is a guide, or a starting point, with suggestions throughout the Resource for relevant Further Reading to enable further exploration. In addition, relevant [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Continuing_Professional_Development_/_Continuing_Education_%28CPD/CE%29 Continuing Professional Development (CPD)] opportunities are recommended to help the reader engage with the Resource and consolidate his/her learning. In particular, it is encouraged that the reader navigate this Resource while continuously reflecting upon its application to his/her own practice and recognising opportunities for physical activity promotion in his/her clinical specialty, population and setting and geographic location.
| |
| | |
| == Audience ==
| |
| | |
| The Resource is aimed at physiotherapists because of their unique skills and broad scope. However, it is not exclusive. Other healthcare professionals, academics or individuals with an interest in the topic may extract relevant and useful information from it.
| |
| | |
| == Learning Outcomes ==
| |
| | |
| The Resource aims to achieve the following Learning Outcomes:
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| = PHYSICAL INACTIVITY: 'THE BIGGEST PUBLIC HEALTH PROBLEM' =
| |
| | |
| Physical inactivity has been deemed "the biggest public health problem of the 21st century"<ref name="Blair 2009">Blair SN. Physical inactivity: the biggest public health problem of the 21st century [warm up].J Sports Med 2009;43(1):1-2.</ref> and has been shown to kill more people than smoking, diabetes and obesity combined (Figure 1)<ref name="Khan">Khan KM, Tunaiji HA. As different as Venus and Mars: time to distinguish efficacy (can it work?) from effectiveness (does it work?) [warm up]. Br J Sports Med 2011;45(10):759-760.</ref>. It is ranked as the fourth leading risk factor for global mortality, killing approximately 3.2 million people (~6% of the total deaths) annually and accounting for approximately 32.1 million disability adjusted life years (DALYs; ~2.1% of global DALYs) annually<ref name="GHO">Global Health Observatory (GHO). Prevalence of physical inactivity 2013. Available at: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/physical_activity_text/en/index.html Accessed 20 November 2013.</ref>.<br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Fig. 1 Obesity.jpg|thumb|left|160x183px|Figure 1. Percentage of deaths attributable to low fitness (i.e. inactivity) compared to smoking (s), diabetes (d) and obesity (o) combined - in men (m) and women (w).(Khan & Tunaiji 2011)]]
| |
| | |
| The major burden of disease attributed to physical inactivity is a result of its established role as one of the main risk factors for non-communicable diseases (NCDs), including cardiovascular disease, diabetes and cancer. In 2008, NCDs were responsible for 63% of the 57 million deaths worldwide<ref name="GHO2">Global Health Observatory (GHO). Noncommunicable diseases (NCD) 2013. Available at: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/en/index.html Accessed 20 November 2013.</ref>, with physical inactivity estimated to be directly responsible for 6% of the disease burden from coronary heart disease, 7% of type 2 diabetes and 10% of each of breast and colon cancers<ref name="Lee2012">Lee IM, Shiroma EJ, Lobelo F, Puska P, Blair SN, Katzmarzyk PT. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: an analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet 2012;380(9838):219-29.</ref>. If physical inactivity were eliminated, this would translate to an estimated 5.3 million lives being saved each year, or - more realistically - 533,000 or 1.3 million lives saved if physical inactivity were reduced by 10% or 25%, respectively<ref name="Lee2012">Lee IM, Shiroma EJ, Lobelo F, Puska P, Blair SN, Katzmarzyk PT. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: an analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet 2012;380(9838):219-29.</ref>. This is independent of the increased risk of morbidity and mortality due to other factors, such as adiposity, raised blood glucose concentrations and high blood pressure, which are directly influenced by physical inactivity<ref name="Hallal2012">Hallal PC, Bauman AE, Heath GW, Kohl HW, Lee IM, Pratt M. Physical activity: more of the same is not enough [comment]. Lancet 2012;380(9838):190-1.</ref>. In particular, [http://www.physio-pedia.com/The_Emerging_Role_of_the_Physiotherapist_in_the_Current_Obesity_Epidemic obesity] engages in a 'vicious cycle' with physical inactivity amplifying the burden to public health<ref name="Piet2008">Pietilainen KH, Kaprio J, Borg P, Plasqui G, Yki-Jarvinen H, Kujala UM, Rose RJ, Westerterp KR, Rissanen A. Physical inactivity and obesity: a vicious circle. Obesity 2008;16(2):409-414.</ref> (see ''Did You Know?''<ref name="Walpole2012">Walpole SC, Prieto-Merino D, Edwards P, Cleland J, Stevens G, Roberts I. The weight of nations: an estimation of adult human biomass. BMC Public Health 2012;12:439</ref>). <br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:DidYouKnowOb.jpg|thumb|right|Did You Know? (Walpole et al 2012)]]
| |
| | |
| <br>A recent analysis of global data collected by the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that 31.1% of adults (aged 15 years or older) worldwide are physically inactive<ref name="HallalGlobal">Hallal PC, Andersen LB, Bull FC, Guthold R, Haskell W, Ekelund U. Global physical activity levels: surveillance progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Lancet 2012;380(9838):247-57.</ref>. For this analysis, physical inactivity was defined as not achieving the equivalent of 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity at least 5 days per week or 20 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity at least 3 days per week<ref name="HallalGlobal" />. Inactivity was found to increase with age and socio-economic status<ref name="HallalGlobal" />. For adolescents aged 13 to 15 years old, the problem appears to be worse, with more than 80% reportedly not achieving the public health goal of 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity per day, and with girls being less active than boys<ref name="HallalGlobal" />. Figure 2 summarises the levels of inactivity, defined as not meeting the recommended national physical activity guidelines for the year listed, in the four UK nations<ref name="BHF2012">British Heart Foundation (BHF). Physical activity statistics 2012. Available at: http://www.bhf.org.uk/publications/view-publication.aspx?ps=1001983 (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref>, mimicking the global trends with respect to age and gender<ref name="HallalGlobal" />. The relationship between socio-economic status and physical inactivity, however, is reversed in the UK, with individuals in the lowest income bracket exhibiting higher levels of inactivity than those in the highest income bracket<ref name="BHF2012">British Heart Foundation (BHF). Physical activity statistics 2012. Available at: http://www.bhf.org.uk/publications/view-publication.aspx?ps=1001983 (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref>.<br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Final - % not meeting guideline.jpg|thumb|right|280x140px|Figure 2. Percentage of individuals not meeting the relevant recommended national physical activity guidelines. Stratified by UK country, age group and gender. Figure produced using data reported in (BHF 2012). No data was reported for children in Wales and N. Ireland.]]
| |
| | |
| The factors contributing to the 'pandemic of physical inactivity'<ref name="Kohl2012" /> extend beyond the individual. Increasingly, it is being recognised that social, cultural, environmental and national and global policy level factors also play a substantial role, as represented by the proposed ecological model of physical activity (Figure 3)<ref name="Bauman2012" />. Effective management of physical activity thus requires interventions targeted at all levels<ref name="Kohl2012">Kohl HW 3rd, Craig CL, Lambert EV, Inoue S, Alkandari JR, Leetongin G, Kahlmeier S The pandemic of physical inactivity: global action for public health. Lancet 2012;380(9838):294-305.</ref>. Accordingly, the [http://www.nice.org.uk/ National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)] have developed a comprehensive, multi-level Physical Activity Framework at which to target interventions (Figure 4)<ref name="NICEph8">National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Physical activity and the environment 2008. Available at: http://publications.nice.org.uk/physical-activity-and-the-environment-ph8/public-health-need-and-practice#physical-activity-framework (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref>.<br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Fig 3 Ecological model of PA.jpg|thumb|left|330x166px|Figure 3. The ecological model of physical activity.(Figure from Bauman et al 2012)]]
| |
| | |
| To that end, physical activity initiatives have propped up around the world. Leading the global forum, WHO have adopted the [http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/en/ ''WHO global strategy on diet, physical activity and health''], publishing recommended physical activity guidelines and providing implementation aids to support national policymakers<ref name="WHOStrategy">World Health Organization (WHO). Diet and physical activity: a public health priority. 2013. Available at: http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/en/ (Accessed 3 December 2013).</ref><ref name="Kohl2012" />. In the UK, [https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/start-active-stay-active-a-report-on-physical-activity-from-the-four-home-countries-chief-medical-officers ''Start active, stay active: a report on physical activity from the four home countries' Chief Medical Officers'' ]was recently published (in 2011), providing updated national guidelines, the evidence underpinning them and guidance for their local implementation<ref name="DOHSASA">Department of Health. Start active, stay active: a report on physical activity from the four home countries’ Chief Medical Officers. 2011. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/start-active-stay-active-a-report-on-physical-activity-from-the-four-home-countries-chief-medical-officers Accessed 20 November 2013.</ref>. Links to other examples of global and national initiatives are provided below. Physical activity is finally being recognised as a public health priority.<br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:NICE-Pathway Framework.jpg|thumb|right|296x194px|Figure 4. NICE Physical Activity Framework. (Figure from NICE 2008)]]
| |
| | |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:GAPALogo.jpg|Homepage (link)[http://www.globalpa.org.uk/]
| |
| Image:ParticipActionLogo.jpg|Homepage (link)[http://www.participaction.com/]
| |
| Image:GetIrelandActive1.jpg|Homepage (link)[http://www.getirelandactive.ie/]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| {| width="488" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" align="left"
| |
| |-
| |
| | valign="middle" align="center" | NB: Websites can be accessed via number beneath logo. Number does NOT correspond with reference list.<br>
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| === Further Reading ===
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| === CPD ===
| |
| | |
| <br><br>
| |
| | |
| = PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: 'THE BEST MEDICINE' =
| |
| | |
| ''All parts of the body which have a function if used in moderation and exercised in labour in which each is accustomed, become thereby healthy, well developed and age more slowly; but if unused and left idle they become liable to disease, defective in growth and age quickly.''<br> - Hippocrates, the Father of Medicine, ca 400 B.C.
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:PADefinition.jpg|center|565x140px]]
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| === Evidence ===
| |
| | |
| <br>In addition to the high prevalence of and risks associated with physical inactivity, physical activity has become a public health priority<ref name="Kohl2012" /> because of the overwhelming body of evidence supporting its effectiveness as a holistic health intervention <ref name="Warburton2006">Warburton DER, Nicol CW, Bredlin SSD. Health benefits of physical activity: the evidence. fckLRCan Med Assoc J 2006;174(6):801-09.</ref>. While physical activity has only recently (circa 2000) factored into the public health agenda<ref name="Kohl2012" />, quantitative evidence of its widespread health benefits has been formally emerging since 1950s. In the 1950s, Professor Morris and colleagues showed that men engaged in work requiring a level of physical activity (e.g. active conductors or postmen) were less likely to suffer from coronary heart disease than men with sedentary jobs (e.g. bus drivers or clerical workers)<ref name="Paff2001">Paffenbarger RS Jr, Blair SN, Lee IM. A history of physical activity, cardiovascular health and longevity: the scientific contributions of Jeremy N Morris, DSc, DPH, FRCP. Int J Epidemiol 2001;30(5):1184-92.</ref>. Sixty years later, the evidence continues to materialise, with a recent study suggesting that exercise can be as effective as pharmaceutical interventions in the prevention and rehabilitation of a number of health conditions, particularly stroke<ref name="Naci2013">Naci H, Ioannidis JPA. Comparative effectiveness of exercise and drug interventions on mortality outcomes: metaepidemiological study. BMJ 2013;347:f5577.</ref>.
| |
|
| |
|
| <br>Physical activity refers to “any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscle that uses energy” <ref name="WHOfacts">World Health Organization (WHO). 10 facts on physical activity 2013. Available at: http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/physical_activity/facts/en/index.html (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref> and can involve anything from daily household chores to structured exercise and sport. (It is important to note, however, that the terms 'physical activity' and 'exercise' are often used interchangeably<ref name="BlairLaMonte">Blair SN, LaMonte MJ, Nichaman MZ. The evolution of physical activity recommendation: how much is enough? Am J Clin Nutr 2004;79(5):913S-920S.</ref>.) The general benefits afforded by physical activity are not restricted to physical aspects of health (e.g. reduced risk of cardiovascular disease<ref name="Schuler2013">Schuler G, Adams V, Goto Y. Role of exercise in the prevention of cardiovascular disease: results, mechanisms and new perspectives. Eur Heart J 2013;34:1790-9.</ref>), nor are they restricted to any particular age-group or clinical population. Substantial evidence supports positive effects on cognition, mental health and well-being<ref name="Cotman2007">Cotman CW, Berchtold NC, Christie L. Exercise builds brain health: key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Trends in Neuroscience 2007;30(9):464-471.</ref><ref name="Lange2008">Lange-Assechenfeldt C, Kojda G. Alzheimer’s disease, cerebrovascular dysfunction and the benefits of exercise: from vessels to neurons. Exp Gerontology 2008;43:499-504.</ref><ref name="Hoffman2007">Hoffman MD, Hoffman DR. Does aerobic exercise improve pain perception and mood? a review of the evidence related to healthy and chronic pain subjects. Current Pain and Headache Reports 2007;11(2):93-7.</ref>. Futhermore, these physical and mental health benefits traverse the lifespan - from the very young to the very old <ref name="Hillman2008">Hillman CH, Erickson KI, Kramer AF. Be smart, exercise your heart: exercise effects on brain and cognition. Science and Society 2008;9:58-65.</ref><ref name="Warburton2006" /><ref name="Hyde2013">Hyde AL, Maher JP, Elavsky S. Enhancing our understanding of physical activity and wellbeing with a lifespan perspective. Int J Wellbeing 2013;3(1):98-115.</ref>. They also apply to various ‘clinical’ as well as non-clinical populations, including, for example, individuals living with chronic or long-term conditions, such as low back pain<ref name="Heneweer2009">Heneweer H, Vanhees L, Picavet HS. Physical activity and low back pain: a U-shaped relation? Pain 2009;143(1-2):21-5.</ref>, multiple sclerosis<ref name="Dalgas2008">Dalgas U, Stenager E, Ingemann-Hansen T. Review: multiple sclerosis and physical exercise: recommendations for the application of resistance-, endurance- and combined training. Mult Scler 2008;14(1):35-53.</ref> or cystic fibrosis<ref name="Williams2013">Williams CA, Stevens D. Physical activity and exercise training in young people with cystic fibrosis: current recommendations and evidence. J Sport and Health Science 2013;2(1):39-46.</ref> and the ‘generally well’ population<ref name="Warburton2006" />.
| | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> |
|
| |
|
| <br>The YouTube video by Dr. Mike Evans below provides a stimulating and compelling overview of the evidence, with some key points highlighted in the box to the right:<br> | | == Introduction == |
| | [[Physical Inactivity|Physical inactivity]] has been deemed "the biggest [[Public Health and Physical Activity|public health]] problem of the 21st century"<ref name="Blair 2009">Blair SN. Physical inactivity: the biggest public health problem of the 21st century [warm up].J Sports Med 2009;43(1):1-2.</ref> and has been shown to kill more people than [[Smoking Cessation and Brief Intervention|smoking]], [[diabetes]] and [[obesity]] combined (Figure 1)<ref name="Khan">Khan KM, Tunaiji HA. As different as Venus and Mars: time to distinguish efficacy (can it work?) from effectiveness (does it work?) [warm up]. Br J Sports Med 2011;45(10):759-760.</ref>. It is ranked as the fourth leading risk factor for global mortality, killing approximately 3.2 million people (~6% of the total deaths) annually and accounting for approximately 32.1 million disability adjusted life years (DALYs; ~2.1% of global DALYs) annually<ref name="GHO">Global Health Observatory (GHO). Prevalence of physical inactivity 2013. Available at: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/physical_activity_text/en/index.html (Accessed 20 November 2013).</ref>.[[Image:Fig. 1 Obesity.jpg|thumb|395x395px|Figure 1.Percentage of deaths attributable to low fitness (i.e. inactivity) compared to smoking (s), diabetes (d) and obesity (o) combined - in men (m) and women (w). |alt=|center]]See [[Physical Inactivity]] Link |
|
| |
|
| <br> | | <br>The YouTube video by Dr. Mike Evans below provides a stimulating and compelling overview of the evidence, with some key points highlighted in the box to the right:<div class="coursebox"> |
| <div class="coursebox"> | | {| class="FCK__ShowTableBorders" width="100%" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4" border="0" |
| {| width="100%" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4" border="0" class="FCK__ShowTableBorders" | |
| |- | | |- |
| | align="center" | | | | align="center" | |
| Line 120: |
Line 27: |
|
| |
|
| |} | | |} |
| </div> | | </div> |
| | == Sedentary Behaviour == |
|
| |
|
| === Sedentary Behaviour === | | As emphasised in the video ''23 and ½ Hours'' and embraced by the latest [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Tackling_Physical_Inactivity:_A_Resource_for_Raising_Awareness_in_Physiotherapists#Guidelines physical activity guidelines], the ‘dose’ of physical activity that seems to confer the majority of these health benefits (in adults) is 30 minutes of moderate to vigorous intensity on most days of the week<ref name="BlairLaMonte">Blair SN, LaMonte MJ, Nichaman MZ. The evolution of physical activity recommendation: how much is enough? Am J Clin Nutr 2004;79(5):913S-920S.</ref>. However, one aspect of physical activity promotion that this dose recommendation does not address is sedentary behaviour. See [[Sedentary Behaviour|Sedentary behaviour]] link. |
|
| |
|
| As emphasised in the video ''23 and ½ Hours'' and embraced by the latest [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Tackling_Physical_Inactivity:_A_Resource_for_Raising_Awareness_in_Physiotherapists#Guidelines physical activity guidelines], the ‘dose’ of physical activity that seems to confer the majority of these health benefits (in adults) is 30 minutes of moderate to vigorous intensity on most days of the week<ref name="BlairLaMonte" />. However, one aspect of physical activity promotion that this dose recommendation does not address is sedentary behaviour. Sedentary behaviour refers to the execution of activities involving sitting or lying that result in low levels of energy expenditure, such as sitting during a commute, at a desk at work or in front of the TV at home<ref name="Bussman2013">Bussmann JBJ, van den Berg-Emons RJG. To total amount of activity…..and beyond: perspectives on measuring physical behavior. Frontiers in Psychology 2013;4(463):1-6.</ref>. An overwhelming body of evidence is mounting to suggest that sedentary behaviour is associated with increased risk of chronic disease and death and has its own pathophysiological profile, independent of the execution of moderate to vigorous physical activity (Figure 5A)<ref name="Wilmot2012">Wilmot EG, Edwardson CL, Achana FA, Davies MJ, Gorely T, Gray LJ, Khunti K, Yates T, Biddle SJH. Sedentary time in adults and the association with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and death: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2012;55:2895-2905.</ref><ref name="Owen2012">Owen N, Healy GN, Matthews CE, Dunstan DW. Too much sitting: the population-health science of sedentary behavior. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 2012;38(3):105-113.</ref><ref name="Bankoski2011">Bankoski A, Harris TB, McClain JJ, Brychta RJ, Caserotti P, Chen KY, Berrigan D, Troiano RP, Koster A. Sedentary activity associated with metabolic syndrome independent of physical activity. Diabetes Care 2011;34(2):497-503.</ref>. Fortunately, given the amount of time potentially spent sitting each day (see ''Did You Know? ''below), there is also evidence to suggest that short breaks in sedentary time can confer substantial health benefits <ref name="Healy2008">Healy GN, Dunstan DW, Salmon J, Cerin E, Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, Owen N. Breaks in sedentary time: beneficial associations with metabolic risk. Diabetes Care 2008;31(4):661-6.</ref><ref name="Healy2011">Healy GN, Matthews CE, Dunstan DW, Winkler EAH, Owen N. Sedentary time and cardio-metabolic biomarkers in US adults: NHANES 2003-06. Eur Heart J 2011;32(5):590-7.</ref>, as highlighted in the short video below.
| | Given the amount of time potentially spent sitting each day evidence suggests that short breaks in sedentary time can confer substantial health benefits <ref name="Healy2008">Healy GN, Dunstan DW, Salmon J, Cerin E, Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, Owen N. Breaks in sedentary time: beneficial associations with metabolic risk. Diabetes Care 2008;31(4):661-6.</ref><ref name="Healy2011">Healy GN, Matthews CE, Dunstan DW, Winkler EAH, Owen N. Sedentary time and cardio-metabolic biomarkers in US adults: NHANES 2003-06. Eur Heart J 2011;32(5):590-7.</ref>, as highlighted in the short video below. <div class="coursebox"> |
| | | {| class="FCK__ShowTableBorders" width="100%" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4" border="0" |
| <br>
| |
| <div class="coursebox"> | |
| {| width="100%" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4" border="0" class="FCK__ShowTableBorders" | |
| |- | | |- |
| | align="center" | | | | align="center" | |
| '''Is Sitting On Your Backside Dangerous?''' | | '''Is Sitting On Your Backside Dangerous?'''<ref>Risk Bites. Is sitting on your backside dangerous?. Available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=COIGHiMveG4 (Accessed 26 November 2013).</ref> |
| | |
| <ref>Risk Bites. Is sitting on your backside dangerous?. Available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=COIGHiMveG4 (Accessed 26 November 2013).</ref> | |
|
| |
|
| <br> | | <br> |
| Line 141: |
Line 44: |
| <br> | | <br> |
|
| |
|
| | valign="baseline" |
| |
| <br> <br>
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:DidYouKnowBox.jpg|40x56px]] [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LaH8KVysHOI Did You Know? ]
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:HowMuchDoYouSite.jpg|center|325x182px]]<br>
| |
|
| |
| |}
| |
| </div>
| |
| [[Image:Efx of Sedentary Behaviour.jpg|thumb|left|380x187px|Figure 5. A. Hazard ratios for all-cause mortality given different combinations of physical (in)activity and sedentary behaviour levels. (Figure from Katzmarzyk 2010). B. Average steps per day among a sample of Old Order Amish men and women compared with two samples of modern populations. (Figure from Katzmarzyk 2010)]]The cumulative evidence of the risks and benefits of physical inactivity and activity, respectively, should not be surprising. Humans are built for movement. As hunters and gatherers for most of human history, our genes have evolved to accommodate the high energy expenditure levels required to be ‘the fittest’ and survive in those prehistoric conditions<ref name="Katzmarzyk2010">Katzmarzyk PT. Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and health: paradigm paralysis or paradigm shift? Diabetes 2010;59:2717-2725.</ref><ref name="Booth2002">Booth FW, Chakravarthy MV, Gordon SE, Spangenburg EE. Waging war on physical inactivity: using modern molecular ammunition against an ancient enemy. J Appl Physiol 2002;93:3-30.</ref>. Yet, since the industrial revolution and development of modern conveniences, modern-day humans have become less active overall (Figure 5B)<ref name="Katzmarzyk2010" />, thus disrupting that inherent homeostatic mechanism<ref name="Booth2002" /> and leading to the manifestation of 'the diseasome of physicial inactivity' (Figure 6)<ref name="Pedersen2009">Pedersen BK. The diseasome of physical inactivity-and the role of myokines in muscle-fat cross talk. J Physiol 2009;587(23):5559-5568.</ref><ref name="Khan2011Blog">Khan K. Canada lowers the bar for physical activity…to make people more active? 2011. Available at: http://blogs.bmj.com/bjsm/2011/02/09/canada-lowers-the-bar-for-physical-activity%E2%80%A6to-make-people-more-active/ (Accessed 26 November 2013).</ref>.
| |
|
| |
| <br> [[Image:EvolutionofMan.jpg|thumb|right|420x155px|Figure 6. Illustration of the evolution of the sedentary human resulting in 'the diseasome of physical inactivity'. (Figure from Khan 2011 [BMJ Group] blog (left) and Pedersen 2009 (right)]]
| |
|
| |
| Thus, it is clear that the physical activity paradigm should incorporate sedentary behaviour<ref name="Katzmarzyk2010" />, and physical activity initiatives and recommendations should adapt accordingly <ref name="Hamilton2008">Hamilton MT, Healy GN, Dunstan DW, Zderic TW, Owen N. Too little exericse and too much sitting: inactivity physiology and the need for new recommendations on sedentary behavior. Current Cardiovascular Risk Reports 2008;2(4):292-8.</ref><ref name="Yates2011">Yates T, Wilmot EG, Khunti K, Biddle S, Gorely T, Davies MJ. Stand up for your health: is it time to rethink the physical activity paradigm? Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2011;93(2):292-4.</ref>. To further aid in this endeavour, a new conceptual framework has evolved, redefining physical activity and representing the complex, multi-dimensional nature of physical activity and sedentary behaviour as components of human movement (Figure 7)<ref name="Pettee2012" /><ref name="Pettee2010PPT">Pettee Gabriel KK, Morrow JR. A framework for physical activity as a complex and multidimensional behavior. 2010. Available at: http://nccor.org/downloads/webinar_7-21-2010_Session_1_Gabriel_and_Morrow.pdf.(Accessed 4 December 2013).</ref>.
| |
|
| |
| <br>
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:HumanMovement Framework.jpg|thumb|center|440x224px|Figure 7. A novel conceptual framework for physical activity as 'a complex, multidimensional behavior' (Figure from Pettee Gabriel & Morrow 2010 [presentation])]]
| |
|
| |
| === The Development and Evolution of Physical Activity Guidelines ===
| |
|
| |
| Beginning with Morris’ work on occupational physical activity in the 1950s <ref name="Paff2001" />, the evidence emerging from the years of epidemiological research of the risks associated with inactivity or a sedentary lifestyle provided the rationale for the development of physical activity guidelines<ref name="BlairLaMonte" />. Identifying the appropriate ‘dose’ of physical activity that would extract the greatest reward in public health, however, required an ongoing examination of data emerging from both epidemiological and exercise training studies and the decision to focus these recommendations on the population who would benefit most, namely those who were most inactive and thus contributing most to the public health burden<ref name="Lee2001">Lee IM, Skerrett PJ. Physical activity and all-cause mortality: what is the dose-response relation? Med Sci Sports Exerc 2001;33(6):S459-71.</ref><ref name="BlairLaMonte" />.<br>
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:EvolutionofGuidelines.jpg|thumb|left|333x189px|Figure 8. The Evolution of Physical Activity Guidelines. (Figure created based on data primarily from Blair, LaMonte & Nichaman 2004)]]
| |
|
| |
| Figure 8 below summarises the evolution of the physical activity guidelines. The first, which came out in the 1970s, called for continuous, high-intensity physical activity, with the goal of achieving physical fitness rather than promoting health<ref name="BlairLaMonte" />. Subsequent studies, which revealed substantial health benefits from lower levels of intensity<ref name="BlairLaMonte" /> and the identification of a clear dose-response relationship between the amount of physical activity and the health benefits<ref name="Lee2001" /> allowed for flexibility in the achievement of the guidelines. It had become clear that the main contributor to health was not so much the intensity but the volume of physical activity executed, with those performing enough to expend on the order of 1000kcals per week reaping the majority of the health benefits<ref name="Lee2001" />.<br>
| |
|
| |
| More recently, additional evidence of the complimentary effects of resistance training, of the enhancing effects of flexibility training<ref name="Pollock2000">Pollock ML, Franklin BA, Balady GJ, Chaitman BL, Fleg JL, Fletcher B, Limacher M, Pina IL, Stein RA, Williams M, Bazzarre T. Resistance Exercise in Individuals With and Without Cardiovascular Disease Benefits, Rationale, Safety, and Prescription An Advisory From the Committee on Exercise, Rehabilitation, and Prevention, Council on Clinical Cardiology, American Heart Association. Circ 2000;101:828-33.</ref>, of [[Image:WHOSASAGuidelines.jpg|thumb|right|170x186px|Table 1. Comparison of current guidelines provided by WHO and the UK. Red text indicates differences between the two guidelines.]]the sufficiency of meeting the guidelines with as little as 10-minute bouts of physical activity<ref name="Loprinzi2013">Loprinzi PD, Cardinal BJ. Association between biologic outcomes and objectively measured physical activity accumulated in ≥ 10-minute bouts and &amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;lt;10-minute bouts. Am J Health Promot 2013;27(3):143-51.</ref> and the clear physical-activity-independent risks associated with sedentary behaviour (Figure 5A) has informed the current physical activity guidelines (Figure 8) provided by WHO and various nations worldwide. Table 1 compares the guidelines provided by WHO and the UK. Links to WHO's and various nations' physical activity guidelines are provided below.
| |
|
| |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:WHOFlag.png|WHO Guidelines (link)[http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/factsheet_recommendations/en/index.html]
| |
| Image:Flag of the United States.png|US Guidelines (link)[http://www.health.gov/paguidelines/guidelines/default.aspx]
| |
| Image:UKFlag.png|UK Guidelines (link)[https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/uk-physical-activity-guidelines]
| |
| Image:Flag of Ireland.jpg|Irish Guidelines (link)[http://www.getirelandactive.ie/get-the-guidlines/how-much-physical-activity-should-i-be-doing/]
| |
| Image:Flag of Canada.png|Canadian Guidelines (link)[http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/hp-ps/hl-mvs/pa-ap/03paap-eng.php]
| |
| Image:Flag of Australia.png|Australian Guidelines (link)[http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/content/health-pubhlth-strateg-phys-act-guidelines]
| |
| Image:Flag of New Zealand.png|New Zealand Guidelines (link)[http://www.health.govt.nz/our-work/preventative-health-wellness/physical-activity]
| |
| </gallery> <br>
| |
|
| |
| {| width="488" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" align="left"
| |
| |-
| |
| | valign="middle" align="center" | NB: Websites can be accessed via number beneath logo. Number does NOT correspond with reference list.<br>
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
| <br>
| |
| <br>
| |
|
| |
| = PHYSIOTHERAPISTS AS 'PHYSICAL ACTIVITY CHAMPIONS'<br> =
| |
|
| |
| ''First, do no harm...'' <br>
| |
|
| |
| - Hippocratic Oath
| |
|
| |
| <br>Physiotherapists have the potential to make a substantial impact on individual, community and public health. Their holistic, biopsychosocial<ref name="Sanders2013">Sanders T, Foster NE, Bishop A, Ong BN. Biopsychosocial care and the physiotherapy encounter: physiotherapists’ accounts of back pain consultations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2013;14:65</ref>, and non-invasive approach, professional autonomy<ref name="HCPC2013">Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC). Physiotherapists: standards of proficiency. 2013. Available at: http://www.hpc-uk.org/assets/documents/10000DBCStandards_of_Proficiency_Physiotherapists.pdf. (Accessed 3 December 2013).</ref>, specialist knowledge and skill set<ref name="WCPT2011">World Confederation for Physical Therapy. Policy statement: physical therapists as exercise experts across the life span. 2011. Available at: http://www.wcpt.org/policy/ps-exercise%20experts (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref>, relatively prolonged patient contact time and varied clinical practice populations and settings places the physiotherapist in the ideal position for the widespread promotion of physical activity (Figure 9)<ref name="Khan2013">Khan K. Guest editorial: physiotherapists as physical activity champions. Physiotherapy Practice 2013 Available at: http://sunshinephysio.com/resources/articles/PhysicalActivityChampions.pdf (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref><ref name="Dean2009-1">Dean E. Physical therapy in the 21st century (Part I): Toward practice informed by epidemiology and the crisis of lifestyle conditions. Physiother Theory Prac 2009;25(5-6):330-353.</ref><ref name="Europa2012">Europa. Presentation of ER-WCPT commitment in the EU platform on diet, physical activity and health. 2012. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/health/nutrition_physical_activity/docs/ev20121114_co04_en.pdf (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref>.<br>
| |
|
| |
| [[Image:WhyPhysios.jpg|thumb|left|380x210px|Figure 9. Summary of why physiotherapists are in an ideal position to take the lead as 'physical activity champions'. (Figure adapted from Europa 2012 [presentation])]]
| |
|
| |
| In the past, physiotherapy intervention, including exercise prescription, has predominantly focused on the restoration of function lost as a result of an acute incident or on the maintenance of function in neurological or cardio-respiratory disease<ref name="Verhagen2009">Verhagen E, Engbers L. The physical therapist’s role in physical activity promotion. Br J Sports Med 2009;43(2):99-101</ref>. However, a shift in the public health need toward the prevention or management of chronic lifestyle conditions, including NCDs, obesity, osteoarthritis and depression<ref name="GHO2" />, and toward the mitigation of the effects of ageing an increasing ageing population<ref name="Spijker2013">Spijker J, MacInnes J. Population ageing: the timebomb that isn’t? Brit Med J 2013;347:f6598.</ref> has demanded a shift in the role of the physiotherapist in addressing this need through the widespread promotion of physical activity (and other health-promoting lifestyle changes)<ref name="Dean2009-1" />. Recognising this emerging role and “professional and ethical responsibility”<ref name="Dean2009-1" />, physiotherapy professional bodies around the world have brought physical activity promotion to the forefront of their agenda with links to two clear examples provided below:<br>
| |
|
| |
| <br>
| |
|
| |
| <br>
| |
|
| |
| Notably, in Scotland, in association with the [http://www.scotland.gov.uk/Publications/2012/06/9095 Allied Health Professionals (AHP) National Delivery Plan (2012-2015)], which includes physiotherapists, the AHP Directors Group have formed the [http://www.paha.org.uk/Home Physical Activity and Health Alliance (PAHA)] and have pledged to “…work with a range of partners to increase the level of physical activity in Scotland”<ref name="PAHA2009">Physical Activity and Health Alliance. AHP directors physical activity pledge. 2009. Available at: http://www.paha.org.uk/Announcement/ahp-directors-physical-activity-pledge. (Accessed 3 December 2013).</ref><br>
| |
|
| |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:CSPLogo.jpg|Move For Health (link)[http://www.csp.org.uk/your-health/healthy-living/move-health-campaign]
| |
| Image:WCPTLogo.jpg|Physical Activity (link)[http://www.wcpt.org/node/33329]
| |
| Image:PAHA-AHPPledge.jpg|Pledge (link)[http://www.paha.org.uk/Announcement/ahp-directors-physical-activity-pledge]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
|
| |
| <br>
| |
|
| |
| Since physical activity participation is influenced by multiple factors, including individual, socio-cultural, environmental and government policy (Figures 3 and 4), there is potential for physiotherapists to intervene at all levels. The remainder of this resource offers guidance on how this may be achieved.<br><br>
| |
|
| |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:IndividualLogo.jpg|The Individual(link)[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Tackling_Physical_Inactivity:_A_Resource_for_Raising_Awareness_in_Physiotherapists#PHYSICAL_ACTIVITY_FOR_THE_INDIVIDUAL]
| |
| Image:CommunityLogo.jpg|The Community (link)[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Tackling_Physical_Inactivity:_A_Resource_for_Raising_Awareness_in_Physiotherapists#Community]
| |
| Image:GovernmentLogo.jpg|Government & Policy (link)[http://www.physio-pedia.com/Tackling_Physical_Inactivity:_A_Resource_for_Raising_Awareness_in_Physiotherapists#Government.2C_Policy_and_Clinical_Governance.C2.A0]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
|
| |
| ''<br>''
| |
|
| |
| {| width="488" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="0" align="left"
| |
| |-
| |
| | valign="middle" align="center" | ''NB: Websites can be accessed via number beneath logo. Number does NOT correspond with reference list.''<br>
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
| <br>
| |
|
| |
| <br>
| |
|
| |
| <br>
| |
|
| |
| = PHYSICAL ACTIVITY FOR THE INDIVIDUAL =
| |
|
| |
| Physical activity promotion at the level of the individual is not a novel concept. As first points of contact, primary care providers, particularly GPs, have acknowledged a necessary role in physical activity promotion for decades, with varying degrees of follow-through in different countries<ref name="Weiler2010">Weiler R, Stamatakis E. Physical activity in the UK: a unique crossroad? Brit J Sports Med 2010;44:912-4</ref>. The various medical-practitioner-based physical activity schemes developed have typically involved (1) links to commercial exercise centres; (2) the provision of simple advice on physical activity or (3) a behavioural counselling approach to the provision of physical activity advice<ref name="Handcock2003">Handcock P, Jenkins C. The Green Prescription: a field of dreams? J New Zealand Med Assoc, 2003;116(1187):1-5.. &amp;amp;lt;br&amp;amp;gt; fckLRfckLRServing as role models in such practioner-based physical activity promotion, Sweden have been providing 'Exercise on Prescription' since the 1980s&amp;amp;lt;ref name="Hellenius2011"&amp;amp;gt;Hellenius M, Sundberg CJ. Physical activity as medicine: time to translate evidence into clinical practice. Brit J Sports Med 2011;45:158</ref> (listen to ''Podcast'').<br>
| |
|
| |
| {| width="153" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="0" align="right"
| |
| |-
| |
| | [[Image:BMJPodcast.jpg|thumb|center|115x152px]] [http://soundcloud.com/bmjpodcasts/bjsm-podcast-exercise-on link to Podcast]
| |
| |} | | |} |
| | </div>Thus, it is clear that the physical activity paradigm should incorporate sedentary behaviour<ref name="Katzmarzyk2010">Katzmarzyk PT. Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and health: paradigm paralysis or paradigm shift? Diabetes 2010;59:2717-2725.</ref>, and physical activity initiatives and recommendations should adapt accordingly <ref name="Hamilton2008">Hamilton MT, Healy GN, Dunstan DW, Zderic TW, Owen N. Too little exericse and too much sitting: inactivity physiology and the need for new recommendations on sedentary behavior. Current Cardiovascular Risk Reports 2008;2(4):292-8.</ref><ref name="Yates2011">Yates T, Wilmot EG, Khunti K, Biddle S, Gorely T, Davies MJ. Stand up for your health: is it time to rethink the physical activity paradigm? Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2011;93(2):292-4.</ref>. |
| | == The Development and Evolution of Physical Activity Guidelines == |
|
| |
|
| <br> | | Beginning with Morris’ work on occupational physical activity in the 1950s <ref name="Paff2001">Paffenbarger RS Jr, Blair SN, Lee IM. A history of physical activity, cardiovascular health and longevity: the scientific contributions of Jeremy N Morris, DSc, DPH, FRCP. Int J Epidemiol 2001;30(5):1184-92.</ref>, the evidence emerging from the years of epidemiological research of the risks associated with inactivity or a sedentary lifestyle provided the rationale for the development of physical activity guidelines<ref name="BlairLaMonte" />. Identifying the appropriate ‘dose’ of physical activity that would extract the greatest reward in public health requires an ongoing examination of data emerging from both epidemiological and exercise training studies. It also requires the decision to focus these recommendations on the population who would benefit most, namely those who are inactive, thus contributing to the public health burden<ref name="Lee2001">Lee IM, Skerrett PJ. Physical activity and all-cause mortality: what is the dose-response relation? Med Sci Sports Exerc 2001;33(6):S459-71.</ref><ref name="BlairLaMonte" />. |
|
| |
|
| Similarly, New Zealand have participated with the provision of the 'Green Prescription' for the past 15 years<ref name="GPNZ2012">Ministry of Health. A prescription for good health: green prescriptions in action. 2012. Available at: http://www.health.govt.nz/publication/prescription-good-health-green-prescriptions-action. (Accessed 3 December 2013).</ref>. Most recently, Scotland have joined in and [http://blogs.bmj.com/bjsm/2013/09/26/scotland-launches-new-physical-activity-pathway-and-staff-training-resources/ launched a new physical activity pathway], in accordance with the AHP Director Group’s pledge to “[a]gree a form of questioning and brief intervention for each patient, every time and embed this in all AHP services”<ref name="PAHA2009" />.<br>
| | See [[Physical Activity]] link for guidelines and more.<br>Physiotherapists have the potential to make a substantial impact on individual, community and public health. Their holistic, biopsychosocial<ref name="Sanders2013">Sanders T, Foster NE, Bishop A, Ong BN. Biopsychosocial care and the physiotherapy encounter: physiotherapists’ accounts of back pain consultations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2013;14:65</ref>, and non-invasive approach, professional autonomy<ref name="HCPC2013">Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC). Physiotherapists: standards of proficiency. 2013. Available at: http://www.hpc-uk.org/assets/documents/10000DBCStandards_of_Proficiency_Physiotherapists.pdf. (Accessed 3 December 2013).</ref>, specialist knowledge and skill set<ref name="WCPT2011">World Confederation for Physical Therapy. Policy statement: physical therapists as exercise experts across the life span. 2011. Available at: http://www.wcpt.org/policy/ps-exercise%20experts (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref>, relatively prolonged patient contact time and varied clinical practice populations and settings (including [http://www.physio-pedia.com/An_overview_of_physiotherapy_in_UK_prisons prisons]) places the physiotherapist in the ideal position for the widespread promotion of physical activity (Figure 9)<ref name="Khan2013">Khan K. Guest editorial: physiotherapists as physical activity champions. Physiotherapy Practice 2013 Available at: http://sunshinephysio.com/resources/articles/PhysicalActivityChampions.pdf (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref><ref name="Dean2009-1">Dean E. Physical therapy in the 21st century (Part I): Toward practice informed by epidemiology and the crisis of lifestyle conditions. Physiother Theory Prac 2009;25(5-6):330-353.</ref><ref name="Europa2012">Europa. Presentation of ER-WCPT commitment in the EU platform on diet, physical activity and health. 2012. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/health/nutrition_physical_activity/docs/ev20121114_co04_en.pdf (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref>.<br> |
|
| |
|
| <br>
| | [[Image:WhyPhysios.jpg|thumb|575x575px|Figure 9. Summary of why physiotherapists are in an ideal position to take the lead as 'physical activity champions'. (Figure adapted from Europa 2012 [presentation])|center]] |
|
| |
|
| {| width="210" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="0" align="left"
| | In the past, physiotherapy intervention, including exercise prescription, has predominantly focused on the restoration of function lost as a result of an acute incident or on the maintenance of function in neurological or cardio-respiratory disease<ref name="Verhagen2009">Verhagen E, Engbers L. The physical therapist’s role in physical activity promotion. Br J Sports Med 2009;43(2):99-101</ref>. However, a shift in the public health agenda towards the prevention or management of chronic lifestyle conditions, including NCDs, obesity, osteoarthritis and depression<ref name="GHO2">Global Health Observatory (GHO). Noncommunicable diseases (NCD) 2013. Available at: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/en/index.html Accessed 20 November 2013.</ref>, and towards the mitigation of the effects of ageing in an increasingly ageing population<ref name="Spijker2013">Spijker J, MacInnes J. Population ageing: the timebomb that isn’t? Brit Med J 2013;347:f6598.</ref> has demanded a change in the role of the physiotherapist in addressing this need through the widespread promotion of physical activity (and other health-promoting lifestyle changes)<ref name="Dean2009-1" />. Recognising this emerging role and “professional and ethical responsibility”<ref name="Dean2009-1" />, physiotherapy professional bodies around the world have brought physical activity promotion to the forefront of their agenda with links to two clear examples - CSP and WCPT - provided below. |
| |-
| |
| |
| |
| [[Image:HealthierScotland.jpg|border|left|178x90px]][http://www.healthscotland.com/topics/settings/health/events.aspx NHS Physical Activity Promotion]<br>
| |
|
| |
|
| <br>
| | == Physical Activity For The Individual == |
|
| |
|
| |}
| | Physical activity promotion at the level of the individual is not a novel concept. As first points of contact, primary care providers, particularly GPs, have acknowledged a necessary role in physical activity promotion for decades, with varying degrees of follow-through in different countries<ref name="Weiler2010">Weiler R, Stamatakis E. Physical activity in the UK: a unique crossroad? Brit J Sports Med 2010;44:912-4</ref>. The various medical-practitioner-based physical activity schemes developed have typically involved (1) links to commercial exercise centres; (2) the provision of simple advice on physical activity or (3) a behavioural counselling approach to the provision of physical activity advice<ref name="Handcock2003">Handcock P, Jenkins C. The Green Prescription: a field of dreams? J New Zealand Med Assoc, 2003;116(1187):1-5.</ref>. |
|
| |
|
| In general, the past few years have seen a revitalisation in the push for physical activity promotion in primary<ref name="KhanBMJ2011" /> and secondary<ref name="Allison2013">Allison TG. Changing medical culture to promote physical activity in secondary prevention of coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J 2013;34(42):3245-7</ref> care. As multi-tier healthcare providers, physiotherapists can assume an active role by taking advantage of each patient encounter to assess and promote physical activity<ref name="Dean2009-1" /><ref name="Dean2009-2" />, as part of an established physical activity scheme or independantly. Three main features of physical activity promotion at the level of the individual are described below.
| | == Assessing Physical Activity == |
| | | Assessment is an important tool in the physiotherapist's arsenal, enabling the collection of relevant information for a clinically-reasoned, holistic and patient-centred approach to diagnosis and subsequent management. Despite the [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Tackling_Physical_Inactivity:_A_Resource_for_Raising_Awareness_in_Physiotherapists#Evidence evidence], patients’ habitual physical activity and sedentary levels are generally not assessed as part of the standard physiotherapy assessment<ref name="Petty2001">Petty N.J. Neuromusculoskeletal Examination and Assessment: A Handbook for Therapists. 2001. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.</ref>.Yet, all patients coming into contact with a physiotherapist suffer from and/or are susceptible to the effects of physical inactivity, regardless of their presenting complaint. Thus, the assessment of physical activity and sedentary levels has a relevant place in the physiotherapy examination<ref name="Hussey2003">Hussey J, Wilson F. Measurement of Activity Levels is an important part of physiotherapy assessment. Physiotherapy 2003;89(10):585-93.</ref>. |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br><br>
| |
| | |
| == The Physical Activity 'Vital Sign' ==
| |
| | |
| Assessment is an important tool in the physiotherapists arsenal, enabling the collection of relevant information for a clinically-reasoned, holistic and patient-centred approach to diagnosis and subsequent management. Despite the [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Tackling_Physical_Inactivity:_A_Resource_for_Raising_Awareness_in_Physiotherapists#Evidence evidence], patients’ habitual physical activity and sedentary levels are generally not assessed as part of the standard physiotherapy assessment<ref name="Petty2001">Petty N.J. Neuromusculoskeletal Examination and Assessment: A Handbook for Therapists. 2001. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.</ref>.Yet, all patients coming into contact with a physiotherapist suffer from and/or are susceptible to the effects of physical inactivity, regardless of their presenting complaint. Thus, the assessment of physical activity and sedentary levels has a relevant place in the physiotherapy examination<ref name="Hussey2003">Hussey J, Wilson F. Measurement of Activity Levels is an important part of physiotherapy assessment. Physiotherapy 2003;89(10):585-93.</ref>. <br> | |
| | |
| In the general medicine community, physical activity has been declared the fifth vital sign<ref name="Sallis2010">Sallis R. Developing healthcare systems to support exercise: exercise as the fifth vital sign. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45:473-74</ref> – a modifiable sign that should be assessed at every clinical encounter<ref name="Sallis2010" /><ref name="KhanBMJ2011" />. Different approaches may be used to measure levels of physical activity (e.g. observation, heart rate monitors, motion sensors), but questionnaires are likely to be the most appropriate in the context of a typical physiotherapy assessment, given time and resource constraints<ref name="Hussey2003" />. Three alternatives for the assessment of a patient’s physical activity levels are describes below.
| |
| | |
| === The General Practice Physical Activity Questionnaire [https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/general-practice-physical-activity-questionnaire-gppaq (GPPAQ)] ===
| |
| | |
| The GPPAQ was developed by the UK’s Department of Health in collaboration with the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine. It is a brief, validated screening tool for the assessment of adults’ (16 to 74 years) physical activity levels as they relate to their occupation and leisure time. It takes only 30 seconds to complete and additional few minutes to calculate the individual’s Physical Activity Index (PAI) and determine the level of intervention required<ref name="GPPAQ">National Collaborating Centre for Nursing and Supportive Care. Appendix J: the general practice physical activity questionnaire (GPPAQ). 2006. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK51962/. (Accessed 3 December 2013).</ref>.
| |
| | |
| {| width="200" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="0" align="center"
| |
| |-
| |
| | [[Image:GPPAQ.jpg|center|277x123px]] [https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/192450/GPPAQ_-_pdf_version.pdf Download the Questionnaire!]
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| === The Scottish Physical Activity Screening Question [http://www.healthscotland.com/topics/settings/health/events.aspx (Scot-PASQ)] ===
| |
| | |
| <br>The Scot-PASQ was developed and validated by NHS Health Scotland in collaboration with the University of Edinburgh<ref name="Scot-PASQ">Physical Activity and Health Alliance. Scottish physical activity screening question (Scot-PASQ). 2013. Available at: http://www.paha.org.uk/Resource/scottish-physical-activity-screening-question-scot-pasq. (Accessed 3 December 2013).</ref>. It has been implemented in Scotland’s new Physical Activity Pathway. It is a brief screening tool that consists of three questions, the first two of which specifically assess whether the patient is meeting the minimum national recommendations.
| |
| | |
| {| width="200" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="0" align="center"
| |
| |-
| |
| | [[Image:Scot-PASQ.jpg|center|277x123px]] [http://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&ved=0CDQQFjAB&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.paha.org.uk%2FFile%2FIndex%2F40eaecc1-c5ed-43af-93a4-a0f5010f786e&ei=US6dUuehJJDwhQfx54HgDQ&usg=AFQjCNHVSs9IR0mIs3drzwl5EtYQYCfpwA&bvm=bv.57155469,d.ZG4 Download the Questionnaire!]<br>
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
|
| |
|
| | In the general medicine community, physical activity has been declared the fifth vital sign<ref name="Sallis2010">Sallis R. Developing healthcare systems to support exercise: exercise as the fifth vital sign. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45:473-74</ref> – a modifiable sign that should be assessed at every clinical encounter<ref name="Sallis2010" /><ref name="KhanBMJ2011">Khan KM, Weiler R, Blair SN. Prescribing exercise in primary care. BMJ 2011;343</ref>. Different approaches may be used to measure levels of physical activity (e.g. observation, heart rate monitors, motion sensors), but questionnaires are likely to be the most appropriate in the context of a typical physiotherapy assessment, given time and resource constraints<ref name="Hussey2003" />. Three alternatives for the assessment of a patient’s physical activity levels are described below. |
| === The Kaiser Permanente Approach: The ‘Exercise Vital Sign’ === | | === The Kaiser Permanente Approach: The ‘Exercise Vital Sign’ === |
|
| |
|
| <br>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kaiser_Permanente Kaiser Permanente] are a not-for-profit, California-based integrated managed care consortium that have adopted a simple method for assessing physical activity levels in each patient, at every visit<ref name="Sallis2011">Sallis, R. Developing healthcare systems to support exercise: exercise as the fifth vital sign. Br J Sports Med 2011;45:473-4</ref>. Coined the ‘Exercise Vital Sign” (EVS), it is brief screening tool that consists of two questions and has shown good face and discriminant validity<ref name="Coleman2012">Coleman KJ, Ngor E, Reynolds K, Quinn VP, Koebnick C, Young DR, Sternfeld B, Sallis RE. Initial validation of an exercise “vital sign” in electronic medical records. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2012;44(11):2071-6</ref>. It is described in the 40-second video below.<br>
| | Kaiser Permanente is a not-for-profit, California-based integrated managed care consortium that have adopted a simple method for assessing physical activity levels in each patient, at every visit<ref name="Sallis2011">Sallis, R. Developing healthcare systems to support exercise: exercise as the fifth vital sign. Br J Sports Med 2011;45:473-4</ref>. Coined the ‘Exercise Vital Sign' (EVS), it is a brief screening tool that consists of two questions and has shown good face and discriminant validity<ref name="Coleman2012">Coleman KJ, Ngor E, Reynolds K, Quinn VP, Koebnick C, Young DR, Sternfeld B, Sallis RE. Initial validation of an exercise “vital sign” in electronic medical records. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2012;44(11):2071-6</ref>. It is described in the 40-second video below. |
| <div class="coursebox"> | | <div class="coursebox"> |
| {| width="100%" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4" border="0" class="FCK__ShowTableBorders" | | {| class="FCK__ShowTableBorders" width="100%" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4" border="0" |
| |- | | |- |
| | align="center" | | | | align="center" | |
| Kaiser Permanente: Making Exercise a Vital Sign | | '''Kaiser Permanente: ''' '''Making Exercise a Vital Sign'''<ref>AHIPResearch. Kaiser Permanente: Making Exercise a Vital Sign. Available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hxfp0LOaLMM Accessed 02 December 2013.</ref> |
| | |
| | <br> |
|
| |
|
| {{#ev:youtube|Hxfp0LOaLMM|350}} | | {{#ev:youtube|Hxfp0LOaLMM|350}} |
|
| |
|
| <ref>AHIPResearch. Kaiser Permanente: Making Exercise a Vital Sign. Available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hxfp0LOaLMM Accessed 02 December 2013.</ref> | | <br> |
|
| |
|
| | | | | |
| Key Points: | | <u>Key Points:</u> |
|
| |
|
| The EVS: "2 questions, 1 minute" <ref name="Sallis2010" /> | | The EVS: "2 questions, 1 minute" <ref name="Sallis2010" /> |
| Line 318: |
Line 89: |
|
| |
|
| |} | | |} |
| </div> | | </div> |
| Whether these or other assessment methods are applied, care should be taken that they are relevant to the patient’s age and clinical status to ensure accuracy in measurement<ref name="Hussey2003" />. It also should be borne in mind that one of the main limitations of using questionnaires to assess the overall physical activity levels of an individual is recall bias <ref name="Hussey2003" />. Most individuals (48-63%) tend to over-estimate their physical activity levels<ref name="Sluijs2007">Sluijs EMF, Griffin, SM, van Poppel MNM. A cross-sectional study of awareness of physical activity: associations with personal, behavioral and psychosocial factors. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2007; 4(53):1-9</ref>. It has also been observed with adolescents reporting their own physical activity levels<ref name="Corder2011">Corder K, van Sluijs EMF, Goodyer I, Ridgway CL, Steele RM, Bamber D, Dunn V, Griffin SJ, Ekelund U. Physical Activity Awareness of British Adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med; 2011; 165(7):603-609</ref> and with mothers reporting the activity levels of their young children<ref name="Hasketh2013">Hasketh KR, McMinn AM, Griffin SJ, Harvey NC, Godfrey KM, Inskip HM, Cooper C, van Sluijs EMF. Maternal awareness of young children’s physical activity: levels and cross-sectional correlates of overestimation. BMC Public Health 2013;13:924</ref>. The Physical Activity Resource Center for Public Health (PARC-PH) at the University of Pittsburgh have developed an excellent resource, containing up-to-date information on various physical activity and sedentary behaviour assessment tools, the link to which can be accessed via the University of Pittsburgh's logo.
| |
| | |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:UniofPitss.jpg|Physical Activity Resource Center for Public Health[http://www.parcph.org/assess.aspx]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| Finally, to enable follow-up and to adhere to the relevant professional record-keeping requirements (e.g. <ref name="CSPStandards">Chartered Society of Physiotherapy. Quality Assurance Standards 2012. Available at: http://www.csp.org.uk/professional-union/professionalism/csp-expectations-members/quality-assurance-standards (Accessed 3 November 2013).</ref>), the results of the assessment should be documented in the patient’s medical records<ref name="KhanBMJ2011" />. Appropriate management can then be implemented<ref name="Sallis2010" />. While it is debateable whether querying a patient’s activity level challenges their behaviour and perspective, it serves as a starting point and provides the opportunity to - at the very least - inform the patient of the potential consequences of his/her behaviour<ref name="Sallis2010" />.<br><br> CPD – Suggest ‘Raising the Issue of Physical Activity’
| |
| | |
| == Mobilising Behaviour Change == | | == Mobilising Behaviour Change == |
|
| |
|
| Line 333: |
Line 96: |
| A summary of these models and approaches is provided below.<br> | | A summary of these models and approaches is provided below.<br> |
|
| |
|
| === Theoretical Models of Health Behaviour Change<br> === | | === Theoretical Models of Health Behaviour Change === |
| | | Table 2 provides a brief description of and practical suggestions for some of the most prominent theoretical models<ref name="Dean2009-2" /><ref name="Elder1999" />. Among these, the Transtheoretical Model (TTM)<ref name="Pro1983">Prochaska JO, DiClemente CC. Stages and processes of self-change of smoking: toward an integrative model of change. J Consult Clin Psychol 1983;51(3):390-95.</ref> has received the most attention in the field due to its ease and utility in clinical practice<ref name="Dean2009-2" /><ref name="Nigg2011">Nigg CR, Geller KS, Motl RW, Horwath CC, Wertin KK, Dishman RK. A research agenda to examine the efficacy and relevance of the transtheoretical model for physical activity behaviour. Psychol Sport Exerc 2011;12(1):7-12.</ref>. It assumes that a patient’s readiness to change falls within one of five stages, based on his/her level of engagement with the particular health behaviour<ref name="Pro1983" /> |
| [[Image:SummaryofModels.jpg|thumb|left|140x225px|Table 2. Summary of several theoretical models of behaviour change. (Table adapted from Dean 2009 [Part II] and Elder et al 1999)]]
| | |
| | |
| Table 2 provides a brief description of and practical suggestions for some of the most prominent theoretical models<ref name="Dean2009-2" /><ref name="Elder1999" />. Among these, the Transtheoretical Model (TTM)<ref name="Pro1983">Prochaska JO, DiClemente CC. Stages and processes of self-change of smoking: toward an integrative model of change. J Consult Clin Psychol 1983;51(3):390-95.</ref> has received the most attention in the field due to its ease and utility in clinical practice<ref name="Dean2009-2" /><ref name="Nigg2011">Nigg CR, Geller KS, Motl RW, Horwath CC, Wertin KK, Dishman RK. A research agenda to examine the efficacy and relevance of the transtheoretical model for physical activity behaviour. Psychol Sport Exerc 2011;12(1):7-12.</ref>. It assumes that a patient’s readiness to change falls within one of five stages, based on his/her level of engagement with the particular health behaviour<ref name="Pro1983" /> (Tables 2 and 3): | |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:TTMmodels.jpg|thumb|center|631x117px|Table 3. Summary of the five TTM ‘stages of readiness’. (Table adapted from Dean 2009 [Part II])]]
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| Determining the patient’s stage of readiness through a series of specific questions facilitates the identification of strategies or subsequent interventions that will be most effective in guiding the patient to progress to the next stage <ref name="Elder1999" /><ref name="Nigg2011" />. The Health Behavior Change Research (HBCR) workgroup at the University of Hawai’i at Mānoa provide a series of relevant questionnaires for applying the TTM to physical activity. The American Council on Exercise® (ACE) offers practical guidance on how to use the TTM to help a patient make healthy behaviour changes. In particular, motivational interviewing, described below, has gained wide acceptance as an effective means of motivating behaviour change within the TTM framework<ref name="Shin2001">Shinitzky HE, Kub J. The art of motivating behavior change: the use of motivational interviewing to promote health. Public Health Nurs 2001;18(3):178-85.</ref>.
| |
| | |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:HBCRLogo.jpg|Questionnaires (link)[http://manoa.hawaii.edu/hbcr/index.php/tools-and-measures-mobile/68-insert-word-doc-test]
| |
| Image:ACELogo.jpg|Guidance (link)[http://www.acefitness.org/blog/3171/how-to-use-the-transtheoretical-model-to-help]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| While the TTM and other health behaviour models suffer from limitations<ref name="Nigg2011" />, they are useful in helping to understand the potentially modifiable factors that underlie behaviour and behaviour change. Taken together, these theoretical models converge on key, interrelated determinants of behaviour change<ref name="Elder1999" /><ref name="Rhodes2009">Rhodes RE, Fiala B. Building motivation and sustainability into the prescription and recommendations for physical activity and exercise therapy: the evidence. Physiother Theory Prac 2009;25(5-6):424-41.</ref>. In particular, self-efficacy (i.e. one’s perceived ability to execute the behaviour) <ref name="Bandura1997">Bandura A. Self-efficacy: The Exercise of Control. 1997. New York: Freeman.</ref><ref name="Ohea2004">O’Hea EL, Boudreaux ED, Jeffries SK, Carmack Taylor CL, Scarinci IC, Brantley PJ. Stage of change movement across three health behaviors: the role of self-efficacy. Am J Health Promot 2004;19(2):94-102.</ref><ref name="Nigg2011" /><ref name="Dishman2005">Dishman RK, Motl RW, Sallis JF, Dunn AL, Birnbaum AS, Welk GJ, Bedimo-Rung AL, Voorhees CC, Jobe JB. Self-management strategies mediate self-efficacy and physical activity. Am J Prev Med 2005;29(1):10-8.</ref>, barrier identification and negotiation<ref name="Al2013">Al-Otaibi HH. Measuring stages of change, perceived barriers and self efficacy for physical activity in Saudi Arabia. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev 2013;14(2):1009-16.</ref><ref name="Sluijs1993" /> (Table 4)<ref name="Hsu2011">Hsu Y, Chou C, Nguyen-Rodriguez ST, McClain AD, Belcher BR, Spruijt-Metz D. Influences of social support, perceived barriers, and negative meanings of physical activity on physical activity in middle school students. J Phys Act and Health 2011;8:210-219.</ref><ref name="BHF2012" /><ref name="WHOFactsheet2013">World Health Organization. Physical inactivity: a global public health problem. 2013. Available at: http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/factsheet_inactivity/en/index.html (Accessed 4 December 2013).</ref><ref name="Godin1994">Godin G, Desharnais R, Valois P, Lepage L, Jobin J, Bradet R. Differences in perceived barriers to exercise between high and low intenders: observations among different populations. Am J Health Prom 1994;8:279-285.</ref><ref name="Johnson1990">Johnson CA, Corrigan SA, Dubert PM, Gramling, SE. Perceived barriers to exercise and weight control practices in community women. Women Health 1990;16:177-91.</ref><ref name="Chinn1999">Chinn DJ, White M, Harland J, Drinkwater C, Raybould S. Barriers to physical activity and socioeconomic position: implications for health promotion. J Epidemiol Commun H 1999;53:191-192.</ref>, S.M.A.R.T, patient-centred goal-setting<ref name="Not2007">Nothwehr F, Yang J. Goal setting frequency and the use of behavioural strategies related to diet and physical activity. Health Educ Res 2007;22(4):532-8.</ref><ref name="Shilts2004">Shilts MK, Horowitz M, Townsend MS. Goal setting as a strategy for dietary and physical activity behaviour change: a review of the literature. Am J Health Promot 2004;19(2):81-93.</ref> and feedback, including reinforcement and follow-up<ref name="Dean2009-2" /><ref name="Sluijs1993" /><ref name="Di2001">DiClemente CC, Marinilli AS, Singh M, Bellino LE. The role of feedback in the process of health behaviour change. Am J Health Behav 2001;25(3):217-27.</ref> have been found to significantly impact physical activity behaviour change. A physiotherapist can work with the patient to modulate these factors to promote behaviour change<ref name="Dean2009-2" /><ref name="Rhodes2009" />, using various approaches<ref name="CSPFac">CSP Facilitating behaviour change, evidence briefing. Available at: http://www.csp.org.uk/publications/facilitating-behaviour-change-evidence-briefing (Accessed 19 Nov 2013).</ref>, some of which are described below.<br><br>
| |
|
| |
|
| {| width="200" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" align="center"
| | Determining the patient’s stage of readiness through a series of specific questions facilitates the identification of strategies or subsequent interventions that will be most effective in guiding the patient to progress to the next stage <ref name="Elder1999" /><ref name="Nigg2011" />. The Health Behavior Change Research (HBCR) workgroup at the University of Hawai’i at Mānoa provide a series of relevant questionnaires for applying the TTM to physical activity. The American Council on Exercise® (ACE) offers practical guidance on how to use the TTM to help a patient make healthy behaviour changes. Links to both the HBCR and ACE are provided below. In particular, [[Motivational Interviewing|motivational interviewing]], has gained wide acceptance as an effective means of motivating behaviour change within the TTM framework<ref name="Shin2001">Shinitzky HE, Kub J. The art of motivating behavior change: the use of motivational interviewing to promote health. Public Health Nurs 2001;18(3):178-85.</ref>. |
| |-
| |
| | valign="top" rowspan="2" | [[Image:PracticalBarriers.jpg|center|289x343px]]
| |
| | valign="top" | [[Image:PsychologicalBarriers.jpg|center|300x250px]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |
| |
| Table 4. Table 4. Various barriers reported by patients with respect to physical activity. (Compiled from references Johnson et al 1990; Godin et al 1994; Chinn et al. 1999; Hsu et al 2011; BHF 2012; WHO 2013)
| |
| | |
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
| === Methods to Promote Behaviour Change === | | === Methods to Promote Behaviour Change === |
|
| |
|
| Behavioural counselling encompasses a spectrum of interventions, which can be rooted in one or more behavioural theories<ref name="Steptoe2001" />. Two approaches - Brief Advice and Brief Intervention - do not require extensive training to be effectively executed<ref name="CSPBrief">Chartered Society of Physiotherapy. Brief Interventions: Evidence Briefing. Available at: http://www.csp.org.uk/publications/brief-interventions-evidence-briefing (Accessed 24 Nov 2013).</ref> and are integrated as part of [http://www.healthscotland.com/uploads/documents/20387-PractitionerGuide.pdf Scotland's new Physical Activity Pathway]<ref name="NHSPAP">NHS Health Scotland. Physical activity pathway for secondary care. Available at: http://www.healthscotland.com/documents/21759.aspx (Accessed 21 Nov 2013).</ref>. A third approach, motivational interviewing, is also recommended, although it requires additional training <ref name="Miller2009">Miller WR and Rollnick S. Ten things that motivational interviewing is not. Behav Cog Psych 2009;37(2):129-40.</ref>. | | Behavioural counselling encompasses a spectrum of interventions, which can be rooted in one or more behavioural theories<ref name="Steptoe2001" />. Two approaches - Brief Advice and Brief Intervention - do not require extensive training to be effectively executed<ref name="CSPBrief">Chartered Society of Physiotherapy. Brief Interventions: Evidence Briefing. Available at: http://www.csp.org.uk/publications/brief-interventions-evidence-briefing (Accessed 24 Nov 2013).</ref> |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| ==== Brief Advice ==== | | ==== Brief Advice ==== |
|
| |
|
| Brief Advice consists of a short (~3 minute), structured conversation with the patient aimed at raising awareness of the benefits of physical activity, exploring barriers and identifying some solutions. It may be suitable for a patient in the early stages of readiness, namely precontemplation and contemplation<ref name="Elder1999" />, or for a patient in the maintenance stage, requiring only reinforcement to maintain the behaviour<ref name="Steptoe2001" />. <br> | | Brief Advice consists of a short (~3 minute), structured conversation with the patient aimed at raising awareness of the benefits of physical activity, exploring barriers and identifying some solutions. It may be suitable for a patient in the early stages of readiness, namely precontemplation and contemplation<ref name="Elder1999" />, or for a patient in the maintenance stage, requiring only reinforcement to maintain the behaviour<ref name="Steptoe2001" />. |
|
| |
|
| ==== Brief Intervention ==== | | ==== Brief Intervention ==== |
|
| |
|
| Brief Interventions are longer (~3-20 minutes) structured conversations, which delve deeper into the patient’s needs, preferences and circumstances with the aim of motivating and supporting the patient toward the behaviour change in a non-judgmental and positive manner. More time is spent discussing the benefits of the behaviour change, addressing barriers, setting goals and building confidence.<br> | | Brief Interventions are longer (~3-20 minutes), structured conversations, which delve deeper into the patient’s needs, preferences and circumstances with the aim of motivating and supporting the patient toward the behaviour change in a non-judgmental and positive manner. More time is spent discussing the benefits of the behaviour change, addressing barriers, setting goals and building confidence. |
| | | === Motivational Interviewing === |
| The [http://www.knowledge.scot.nhs.uk/home/portals-and-topics/health-improvement/hphs/nhs-physical-activity-promotion.aspx NHS Scotland Knowledge Network] have produced short videos describing these two approaches as part of their ''Every Step Counts ''Learning pack, in which they describe the new Physical Activity Pathway.
| |
| | |
| <br> <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:NHSEduforScot.jpg|[http://www.knowledge.scot.nhs.uk/home/portals-and-topics/health-improvement/hphs/nhs-physical-activity-promotion.aspx]
| |
| </gallery><br>
| |
| | |
| ==== Motivational Interviewing ====
| |
| | |
| Motivational interviewing is a behaviour change intervention that has been most recently defined as “…a collaborative, person-centred form of guiding to elicit and strengthen motivation for change”<ref name="Miller2009" />. This short interview with William R Miller, the founder of Motivational Interviewing, describes the approach’s beginnings:<br>
| |
| <div class="coursebox">
| |
| {| width="100%" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4" border="0" class="FCK__ShowTableBorders"
| |
| |-
| |
| | align="center" |
| |
| Background of Motivational Interviewing<ref name="CASAT">CASAT. Background of MI. Available at: http://vimeo.com/20901845#at=0 (Accessed 03 December 2013).</ref>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| {{#ev:vimeo|20901845|350}}
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| |
| |
| [[Image:5GenPrinciples.jpg|thumb|center|160x249px|Table 5. Summary of five general principles of motivational interviewing. (Table adapted from Shinitzky & Kub 2001)]]
| |
| | |
| |}
| |
| </div>
| |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| Motivational interviewing consists of two phases, the first in which intrinsic motivation is reinforced and the second in which commitment to change is enhanced<ref name="Martins2009">Martins RK, McNeil DW. Review of motivational interviewing in promoting health behaviors. Clin Psychol Rev 2009;29(4):283-93.</ref>. It is based on five general principles<ref name="Shin2001" /> (Table 5). Monash University in Australia have developed a learning resource, which includes videos in which the five general principles are modelled.
| |
| | |
| Motivational interviewing is an approach which aims to challenge the patient in a supportive and self-reflective manner, working under the assumption that the patient knows what is best for him/herself. The clinician’s role is to collaborate with, guide and support the patient through his/her journey of behaviour change. Although distinct from the Transtheoretical Model<ref name="Miller2009" />, Motivational Interviewing is often used in conjunction with it, as it has been shown to facilitate progression through the stages<ref name="Shin2001" />. In particular, it has been shown to be effective in those who are in the low stages of readiness to change<ref name="Res2002">Resnicow K, DiIlorio C, Soet JE, Borrelli B, Hecht J, Ernst D. Motivational interviewing in health promotion: it sounds like something is changing. Health Psychol 2002;21(5):444-451.</ref> and in a range of health settings<ref name="Martins2009" />.
| |
| | |
| As motivational interviewing requires standardised training for optimal delivery <ref name="Martins2009" />, it presents an excellent CPD opportunity for physiotherapists<ref name="KhanBMJ2011">Khan KM, Weiler R, Blair SN. Prescribing exercise in primary care. BMJ 2011;343</ref>. Click on the Motivational Interviewing tab below to get started. <br> <br> <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:MonashUni.jpg|Monash U Learning Resource (link)[http://www.monash.edu.au/pharm/current/step-up/motivational-interviewing/]
| |
| Image:MI.jpg|Motivational Interviewing (link)[http://www.motivationalinterview.org/]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| == Further Reading ==
| |
| | |
| == CPD ==
| |
| | |
| = PA on prescription temp header<br> =
| |
|
| |
|
| | [[Motivational Interviewing|Motivational interviewing]] is a behaviour change intervention that has been most recently defined as “…a collaborative, person-centred form of guiding to elicit and strengthen motivation for change”<ref name="Miller2009">Miller WR and Rollnick S. Ten things that motivational interviewing is not. Behav Cog Psych 2009;37(2):129-40.</ref>. See link. |
| == Physical Activity 'On Prescription' == | | == Physical Activity 'On Prescription' == |
|
| |
|
| Having assessed the patient’s physical activity levels and having begun to develop a behavioural approach and partnership with the patient, the final major component of physical activity promotion at the level of the individual is the actual substance of the intervention – the health education, physical activity prescription and other ‘stuff’ received by the patient to be able to adopt and/or maintain a more physically active and less sedentary lifestyle<ref name="KhanBMJ2011" />. Interestingly, while it is generally acknowledged that physiotherapists have a significant role here<ref name="WCPT2011" />, physiotherapists’ perceptions of this role varies<ref name="ODon2012">O’Donaghue G, Cusack T, Doody C. Contemporary undergraduate physiotherapy education in terms of physical activity and exercise prescription: practice tutors’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs. Physio 2012;98(2):167-73.</ref><ref name="Shirley2010">Shirley D, van der Ploeg, HP, Bauman AE. Physical activity promotion in the physical therapy setting: perspectives from practitioners and students. Phys Ther 2010; 90:1311-22.</ref>. The next few subsections are intended to facilitate physiotherapists in achieving this role. | | Having assessed the patient’s physical activity levels and having begun to develop a behavioural approach and partnership with the patient, the final major component of physical activity promotion at the level of the individual is the actual substance of the intervention – the health education, physical activity prescription and other ‘stuff’ received by the patient to be able to adopt and/or maintain a more physically active and less sedentary lifestyle<ref name="KhanBMJ2011" />. Interestingly, while it is generally acknowledged that physiotherapists have a significant role in health promotion and prescription<ref name="WCPT2011" />, physiotherapists’ perceptions of this role varies<ref name="ODon2012">O’Donaghue G, Cusack T, Doody C. Contemporary undergraduate physiotherapy education in terms of physical activity and exercise prescription: practice tutors’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs. Physio 2012;98(2):167-73.</ref><ref name="Shirley2010">Shirley D, van der Ploeg, HP, Bauman AE. Physical activity promotion in the physical therapy setting: perspectives from practitioners and students. Phys Ther 2010; 90:1311-22.</ref>. The next few subsections provide relevant information intended to facilitate physiotherapists in achieving this role. |
|
| |
|
| === Education === | | === Education === |
| | <br> Patient education has become an essential part of health care for the patient, enabling him/her to participate in the decision-making<ref name="Hoving2010">Hoving C, Visser A, Mullen PD, van den Borne B. A history of patient education by health professionals in Europe and North America: from authority to shared decision making education. Patient Educ Couns 2010 Mar;78(3):275-81.</ref>. Critically, it is also the responsibility of physiotherapists to educate their patients. Given their unique patient contact and broad patient access (Figure 9), they are advantageously positioned to do so – in every patient, across the lifespan and among all settings<ref name="Dean2009-1" />. Furthermore, education as a physiotherapy intervention has proven to be successful for the management of low back pain<ref name="Engers2008">Engers A, Jellema P, Wensing M, van der Windt DA, Grol R, van Tulder MW. Individual patient education for low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jan 23;(1):CD004057.</ref> and other conditions, with a recent report of patient waiting times being cut by half as a result of a [http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/news/press-releases/2012/october/patient-education-pilot-cuts-physiotherapy-waiting-times-in-half.aspx patient education pilot].<br> |
|
| |
|
| [[Image:LowAwarenessPARec.jpg|thumb|right|Did You Know?]]
| | <br>Thus, by combining effective education, which should be tailored in content and delivery to the patient’s individual learning needs<ref name="Dean2009-1" />, and the principles of behavioural change, physiotherapists have the potential to achieve:<br> |
| | |
| <br> Patient education has become an essential part of health care for a patient, enabling him/her to participate in the decision-making<ref name="Hoving2010">Hoving C, Visser A, Mullen PD, van den Borne B. A history of patient education by health professionals in Europe and North America: from authority to shared decision making education. Patient Educ Couns 2010 Mar;78(3):275-81.</ref>. Critically, it is also the responsibility of physiotherapists to educate their patients. Given their unique patient contact and broad patient access (Figure 9), they are advantageously positioned to do so – in every patient, across the lifespan and among all settings<ref name="Dean2009-1" />. Furthermore, education as a physiotherapy intervention has proven to be successful for the management of low back pain<ref name="Engers2008">Engers A, Jellema P, Wensing M, van der Windt DA, Grol R, van Tulder MW. Individual patient education for low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jan 23;(1):CD004057.</ref> and other conditions, with a recent report of patient waiting times being cut by half as a result of a [http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/news/press-releases/2012/october/patient-education-pilot-cuts-physiotherapy-waiting-times-in-half.aspx patient education pilot].<br>
| |
| | |
| <br>Thus, by combining effective education, which should be tailored in content and delivery to the patient’s individual learning needs<ref name="Dean2009-1" />, and the principles of behavioural change, physiotherapists have the potential to achieve: | |
| | |
| <br> | |
| | |
| *Increased knowledge and awareness of risks of physical inactivity and the benefits of physical activity.<br> | | *Increased knowledge and awareness of risks of physical inactivity and the benefits of physical activity.<br> |
| *Increased knowledge and awareness of physical activity, what it can entail and how it can be achieved, including by use of the services available, thus increasing self-efficacy and the potential of increasing adherence of new lifestyle. | | *Increased knowledge and awareness of physical activity, what it can entail and how it can be achieved, including use of the services available, hence increasing self-efficacy and potentiating adherence to a new lifestyle. |
| *A change in attitudes and motivations for engaging in physical activity. | | *A change in attitudes and motivations for engaging in physical activity. |
| *A change in beliefs and perceptions about physical activity, sedentary behaviour and social norms.<br> | | *A change in beliefs and perceptions about physical activity, sedentary behaviour and social norms. |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| '''Physical Activity – The Definition Revisited'''<br>
| |
| | |
| A good place to begin in educating the patient on physical activity is to define it for him/her and clarify the hierarchical structure<ref name="ACSM2013" /> (below) to which “exercise” belongs. <br>A possible misconception may arise as the term 'physical activity' and 'exercise' are often used interchangeably<ref name="ACSM2013">American College of Sports Medicine. Exercise Prescription. In: ACSM’s GuidelinesfckLRfor Exercise Testing and Prescription. London: Williams &amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp; Wilkins; 2013.</ref>. Thus, barriers may play to whatever preconceptions an individual may have about physical activity and/or exercise.<br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:PA definition.jpg|border|center|625x558px]]<br>
| |
| | |
| ==== The Risks and Benefits ====
| |
| | |
| Two key aspects of one’s intent to change that should be considered when working with a patient to achieve a behavioural change, such as becoming more physically active, are<br>
| |
| | |
| <br>1. the extent to which a person perceives their own behaviour as ‘unhealthy’. <br>2. the belief that a change in behaviour will decrease the health risks.<ref name="Sluijs2007" /><br>
| |
| | |
| <br>Thus, building on these two key principles of ‘intention to change’, education can be tailored to obtain the greatest impact, informing patients of the relevant risk and benefits that pertain to physical (in)activity.<br>
| |
| | |
| ==== The Risks of Physical Inactivity<br> ====
| |
| | |
| The risks of physical inactivity have been previously described. The main message that should be relayed to the patient is the inverse relationship between inactivity and health (Figure 10).<br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Dose-Response curve.jpg|thumb|left|Figure 10. Representation of dose-response relationship between physical activity and health risk. (Figure adapted from DOH 2011)]]
| |
| | |
| ==== The Benefits of Physical Activity ====
| |
| | |
| [[Image:EffectsOfEXSTraining.jpg|thumb|right|Figure 11. Summary of various physiological effects of physical activity/exercise. (Figure adapted from Gielen et al 2010; Henriksson & Sundberg 2010)]]
| |
| | |
| The prevailing and growing list of evidence concerning the physiological benefits (Figure 11<ref name="Swedish2010" /><ref name="Gielen2010">Gielen S, Schuler G, Adams V. Cardiovascular effects of exercise training: molecular mechanisms. Circulation 2010;122:1221-1238.</ref>) derived from physical activity as seen in adults can also be seen in children<ref name="Janssen2010">Janssen I, LeBlanc GA. Systematic review of the health benefits of physical activity and fitness in school-aged children and youth. International Journal of Behavioural Nutrition and Physical Activity 2010;7(40):1-12.</ref> and older adults<ref name="Haapanen">Haapanen-Niemi N, Miilunpalo S, Pasanen M, Vuori I, Oja P, Malmberg J. Body mass index, physical inactivity and low level of physical fitness as determinants of all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality - 16y follow-up of middle-aged and elderly men and women. International Journal of Obesity 2000;24:1465-1474</ref>, although with some variation between individuals and through the lifespan.
| |
| | |
| Thus, while we could educate all age groups on the global biological benefits of physical activity, there are age-specific motivators that can be targeted to make the education intervention more effective. Importantly, the educational content can go beyond the physical/biological and address other psychosocial proprieties, such as self-esteem, socialising, making the school team.<br>
| |
| | |
| <u>'''Children & Preadolescents'''</u>
| |
| | |
| Education for individuals in this age group may benefit more if the advantages of physical activity were delivered with context such as Sports Days, outdoor teambuilding exercises.
| |
| | |
| <br>The early developmental years of children are vital in building a healthy foundation for their body to grow into. In fact the same benefits shown in Figure (big poster), albeit with differing magnitudes, are true for children and preadolescents<ref name="ACSM2013" /><ref name="DOHSASA" />. <br>
| |
| | |
| Our muscles, bones and other structures adapt under different stresses of movement, thereby increasing in endurance and strength (ref: Petty anatomy). Similarly, physical activity is vital in improving the neurological development of the brain such as increased hippocampal volume and its related affects on relational memory tasks<ref name="Chaddock2010">Chaddock L, Kirk IE, Prakash RS, Kim JS, Voss MW, VanPatter M, Pontifex MB, Raine LB, Konkel A, Killman CH, Cohen NJ, Kramer AF. A neuroimaging investigation of the association between aerobic fitness, Hippocampal volume, and memory performance in preadolescent children. Brain Research 2010;1358:172-183.</ref>.
| |
| | |
| <br>It would be unjust to assume that children have no stress since the causes of such may be wholly subjective. We can address the psychosocial issues through physical activity which can target certain physiological changes that may contribute/result from stress, counterbalancing its effect<ref name="APAstress2013">American Psychological Association. Identifying Signs of Stress in Your Children and Teens. 2013. Available at: http://www.apa.org/helpcenter/stress-children.aspx (Accessed 04/12/2013)</ref>.<br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:RoleofPAEduChild.jpg|thumb|left|Figure 12. The indirect effects of physical activity on psychosocial wellbeing. (Figure adapted from Malina et al 2004)]]Figure 12 <u>''summarises the psychosocial issues relatively well in the context of the perception of oneself''</u><ref name="Malina2004">Malina RM, Bouchard C, Bar-Or O. Growth, Maturation, and Physical Activity. 2nd ed. 2004. Ilinois: Human Kinetics [viewed 28 November 2013]. Available from: http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=VqFcFsykj6EC&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false</ref>. Physical activity can have an effect on all of the components of growth and development<ref name="Janssen2010" /><ref name="KortButler2012">Kort-Butler LA. Extracurricular Activity Involvement and Adolescent Self-Esteem. The Prevention Researcher 2012;19(2):13-16.</ref>. Whilst some of the issues may be of lesser relevance concerning a toddler than a preadolescent it is important to encourage habitual physical activity.
| |
| | |
| The body has naturally come to expect and need a certain amount of activity to thrive<ref name="Booth2002" />; it must therefore be nurtured to prevent later-life issues.<br>
| |
| | |
| '''<u>Adolescent & Adults</u>'''
| |
| | |
| Physical activity has a role in rehabilitative and preventative medicine. Considerations must also be given to an individual’s mental health. Decrease in self-esteem in early adolescence has been observed to occur (Baldwin & Hoffman 2002). If coupled with poor body image, social stigmas attached to overweight and obesity, mental health can suffer, possibly leading to a cycle of reduced social interactions and increased sedentary behaviour. Pursuit of physical activity through extracurricular activities for example, may alleviate some of the psychological stresses<ref name="KortButler2012" />.
| |
| | |
| <br>Furthermore, physical activity has been observed as a factor in the development and maintenance of the brain (ref:LifeEextensions). Studies have shown moderate intensity cycling as having a positive effect on the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) whether it’s in healthy individuals or those suffering from chronic conditions such as multiple sclerosis (Gold et al. 2003). This can have implications regarding the reduction of the risks in developing conditions such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.<br>
| |
| | |
| <u>'''Older Adults'''</u><br>
| |
| | |
| Older adults can benefit from the positive habitual effects of physical activity, maintenaning and developing cognitive functions (Gold et al. 2003).<br>Additionally, it is important to consider decreasing sedentary behaviour as physical inactivity leads to increased risk of all-cause mortality whether it’s an increase in risk of developing cardiovascular disease or respiratory complications (Katzmarzyk and Lee, 2012).
| |
| | |
| Maintaining physical activity is also the cornerstone of maximising self-sufficiency<ref name="Szeklicki2013">Szeklicki R, Osinski W, Maciaszek J, Stemplewski R, Salamon A. Correlations Between Habitual Physical Activity And Self-Perceived Functional Fitness, Self-Sufficiency Fitness And Health Among Men Over 60 Years Old. Human Movement 2013;14(1):27-34</ref>. This may seem paradoxical at first for those with decreased mobility, but some activity is still better than none. Habitual activity ensures the maintenance of adequate levels of flexibility, dexterity, balance and exercise tolerance (Nelson et al. 2007) so as to negotiate activities of daily living and falls risk prevention (ref;).
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:CSPLogo.jpg|Easy Exercise Guide (link)[http://www.csp.org.uk/publications/easy-exercise-guide]
| |
| Image:CSPLogo.jpg|Do you sit at a desk all day? Information Leaflets (link)[http://www.csp.org.uk/publications/do-you-sit-desk-all-day]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| ==== Guidelines ====
| |
| | |
| [[Image:NewPAPyramid.jpg|thumb]]Physical Activity Pyramid (Figure 13) provides a quick glimpse of the main features of current national recommendations, with illustrations of options on how they may be achieved.<br>
| |
| | |
| Specific guidelines are in circulation that are categorised by age group as well as by special population group in the boxes below.<br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| {| width="200" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" align="left"
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="5" | '''UK Start Active, Stay Active - Factsheets'''<br>
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="5" | [[Image:GuidelineFactsheets.jpg|center|600x207px]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | [http://www.paha.org.uk/File/Index/dfa28bb9-dd2a-416c-ad53-9f1d00fbac82 link]
| |
| | [http://www.paha.org.uk/File/Index/9912501c-f2b4-480e-b1b8-9f1d00fbe3e6 link]
| |
| | [http://www.paha.org.uk/File/Index/61433356-38cc-462d-a796-9f1d00fc0a30 link]
| |
| | [http://www.paha.org.uk/File/Index/5d8bf34a-8e9e-456d-8369-9f1d00fc4165 link]
| |
| | [http://www.paha.org.uk/File/Index/df14c3ef-d194-4d4e-b6c1-9f1d00fc69f9 link]
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| Various countries and organisations have published guidelines outlining the benefits of physical activity, and the ways in which it may be pursued.
| |
| | |
| Knowledge of the relevant guidelines would help enhance the overall patient journey, so as to keep to specific and relevant goals of the individual. <br>
| |
| | |
| Specific guidelines have also been published by The Canadian Society of Exercise Physiology providing recommendations for special populations that can benefit from increasing or improving levels of physical activity.
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:CDCLogo.jpg|US Physical Activity for Everyone Info sheets (link)[http://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/everyone/guidelines/index.html]
| |
| Image:CSEP.jpg|Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour Info sheets (link)[http://www.csep.ca/english/view.asp?x=804]
| |
| Image:CSEP.jpg|CSEP Special Populations Info sheets (link)[http://www.csep.ca/english/view.asp?x=943]
| |
| </gallery><br>
| |
| | |
| === The Prescription ===
| |
| | |
| An exercise prescription may be thought of as having the following basic components but should always be considered in tandem:<br>
| |
| | |
| ==== Mode ====
| |
| | |
| '''The mode''' is the type/form of physical activity that may be undertaken after consultation with the patient. Taking into account of their:
| |
| | |
| <br>• Personal goals<br>• Interests<br>• Hobbies
| |
| | |
| <br>Encouraging individuals to take the stairs instead of lifts or cycle to work once a week are some of the simple first steps in determining a suitable ‘Mode’. The Mode may be guided by considering the '''F'''requency, '''I'''ntensity and '''T'''ime ('''FIT''') components that make up Physical Activity.
| |
| | |
| <br>The approach to the '''FIT''' components is highly dependent on the patient’s current levels of activity and stage of readiness.
| |
| | |
| <br>• For the generally inactive or sedentary individual, the guidelines may be long-term goals – something to strive towards. A ‘small changes’ approach and recommendation of appropriate activities may be warranted<ref name="Hills2013">Hills AP, Byrne NM, Lindstrom R, Hill JO. ‘Small Changes' to Diet and Physical Activity Behaviors for Weight Management. Obes Facts 2013;6:228-238.</ref>.
| |
| | |
| • For the generally active individual or individual looking to maintain or exceed the guidelines and optimise the health benefits by avoiding a fitness plateau<ref name="Garber2011">Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM, Nieman DC, Swain DP, American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. The quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2011;43(7):1334-1359.</ref>, providing advice and recommending alternative activities to facilitate variation may suffice<ref name="Steptoe2001" />.
| |
| | |
| In both cases, it is essential that the physiotherapist is familiar with the local activity resources, including the people and the places<ref name="KhanBMJ2011" />. For example (see Did You Know?). <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| <div class="coursebox">
| |
| {| width="802" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4" border="0" class="FCK__ShowTableBorders"
| |
| |-
| |
| | align="center" |
| |
| Did You Know? [[Image:EdinburghLeisure.jpg|center|199x50px]]
| |
| | |
| '''Purpose, Vision and Values''' <ref name="EdinburghLeisureTV">EL AtoZ Film Available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WcKWvlI6qug#t=27 (Accessed 04 December 2013).</ref><br>
| |
| | |
| {{#ev:youtube|WcKWvlI6qug|350}}
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| | [[Image:ActiveScotland.jpg|thumb|center|Active Scotland]] [http://www.activescotland.org.uk/ Active Scotland]
| |
| |}
| |
| </div>
| |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| ==== Frequency ====
| |
| | |
| The frequency is the number of occurrences of a particular physical activity during the day OR the number of days dedicated to a particular physical activity programme. Current guideline for physical activity targeting cardiorespiratory endurance (aerobic) recommendeds 3-5 days a week<ref name="ACSM2013" /><ref name="Swedish2010">Henriksson J, Sundberg CJ. General effects of physical activity. In: Börjesson, M., Hellenius, M. L., Jansson, E., Karlsson, J., Leijon, M., Ståhle, A., Sundberg, C. J. and Taube, J, eds. Physical Activity in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease. Sweden: Swedish National Institute of Public Health;2010.</ref>. A good sense of pacing should also be highlighted especially for someone who has previously been sedentary (ref:). <br>Individuals can be encouraged to stand and/or have a walkabout when television adverts are in progress or, if working behind a computer, to take regular 15 minute breaks every hour to stretch ones legs and have a walk. It is a matter of strategising and prioritising what is feasible and what the patient is ready to commit to.
| |
| | |
| ==== Intensity ====
| |
| | |
| The intensity is how ‘vigorous’ a physical activity is. There exists a positive dose response of derived health benefits from increasing physical activity intensity (Garber et al. 2011). Knowledge of the applicability of the “progressive overload” principle with regards to intensity levels may be of use. Much like training a particular muscle, physical activity levels below certain minimum intensity is unlikely to elicit any beneficial physiological changes (Garber 2011; Mason 2013).
| |
| | |
| There are a number of measures scientists and health professionals have used to quantify the relative intensity levels of differing physical activities. These have included:<br><br>
| |
| | |
| * VO<sub>2</sub>R = Percentage of oxygen uptake reserve.
| |
| * HRR = Heart Rate Reserve.
| |
| * VO<sub>2</sub> = Oxygen consumption.
| |
| * HR = Heart Rate.
| |
| * MET = Metabolic Equivalents.
| |
| | |
| Whilst each of these relative methods of quantifying intensity has its advantages and disadvantages being acquainted with the concept of Metabolic Equivalents (MET) may help in giving an overview of what may be suitable.
| |
| | |
| Whilst each of these relative methods of quantifying intensity has its advantages and disadvantages, the Metabolic Equivalents (MET) is a convenient way of conceptualising the energy cost of physical activities as a multiple of resting metabolic rates (Jetté et al. 1990). <br>The following tables summarises the relative Intensity with respect to the Mode of activity.<br>
| |
| | |
| {| width="200" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" align="center"
| |
| |-
| |
| | [[Image:METHike.jpg|center]]
| |
| | [[Image:METWalkJogRun.jpg|350x195px]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | [[Image:METChore.jpg|center]]
| |
| | [[Image:METHousehold.jpg|350x198px]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | [[Image:METSport.jpg|center|188x240px]]
| |
| | [[Image:METLeisure.jpg|350x320px]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="2" | Figure. <br>
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| Current evidence as highlighted in the guidelines and handbooks<ref name="DOHSASA" />; Swedish) suggests moderate intensity activities are enough to elicit beneficial physiological changes that are of the ‘right’ dose, especially for someone who has been sedentary. The phrase, “moderate but often” is a good rule of thumb when considering any physical activity prescription. By toning down the intensity of the physical activity, the goal of long-term participation becomes more achievable. <br>
| |
|
| |
|
| ==== Time ==== | | ==== Physical Activity ==== |
| | See [[Physical Activity]] link for more information including guidelines [[Image:NewPAPyramid.jpg|thumb|Figure 13. Physical Activity Pyramid |alt=|center|809x809px]] |
|
| |
|
| The Time is the measure in minutes or hours expended for a particular physical activity or activity programme. <br>A great majority living a sedentary lifestyle or those working to become more physically active often quote time as a barrier (ref: to barriers section?). It is vital for physiotherapists and patients to have an honest discussion as to what is achievable and appealing so that realistic goals can be implemented around that person’s life. <br>The Start Active, Stay Active report published in 2011 recommends that adults should aim to accumulate at least 150 minutes of physical activity of moderate intensity on at least 5 days of the week. There is also the added flexibility in breaking this down into sessions and don’t necessarily have to be greater than 10 minutes. Patients that are previously sedentary and needing to ease into a more active lifestyle pursuing just 20 minutes of exercise per day can already elicit certain health benefits<ref name="ACSM2013" />.
| | == Physical Activity and Exercise Prescription == |
| | See [[Physical Activity and Exercise Prescription]] for information. See also [[Barriers to Physical Activity]] |
|
| |
|
| <br>[[Image:Time.jpg|thumb|left|300x300px|Figure x. Accessed http://www.bikewalkdurham.org/BPAC_resources.html]]<br>
| | == Summary == |
|
| |
|
| <br> | | [[Image:ICFCircMod.jpg|thumb|right|Figure 16. Illustration of the process of the physical activity prescription in the context of the ICF.]]While this section on physical activity promotion at the level of the individual has been presented in a linear or sequential fashion, the phases are intertwined and continuous (Figure 16). The assessment of physical activity and stage of readiness and the provision of the prescription occur using a relevant behavioural counselling approach in the context of the patient’s biopsychosocial status, as guided by the International Classification of Function and Disability (ICF)<ref name="Rimmer2005">Rimmer JH. Use of the ICF in identifying factors that impact participation in physical activity/rehabilitation among people with disabilities. Disability and Rehab 2005;28(17):1087-95.</ref>. |
|
| |
|
| <br>
| | In forming a partnership with the patient, the physiotherapist aims to understand the barriers preventing the patient from engaging in a more physically active lifestyle and begin to consider ways in which the patient may negotiate them. These barriers are not only the practical ones, such as time and equipment, but also physical and mental. In particular, identification of the patient’s physical and mental barriers, including disease or disorder, and proper, ongoing risk assessment (e.g. [http://www.csep.ca/CMFiles/publications/parq/par-q.pdf PAR-Q]) in the process of physical activity promotion is essential and the essence of why physiotherapists are ideal candidates for this role<ref name="WCPT2011" />. While risk assessment is essential it falls outside the scope of the current topic but with regards to promoting physical activity in the the following groups: |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br> <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| === Summary<br> ===
| |
| | |
| While this section on physical activity promotion at the level of the individual has been presented in a linear or sequential fashion, the phases are intertwined and continuous (Figure). The assessment of physical activity and stage of readiness and the provision of the prescription occur using a relevant behavioural counselling approach in the context of the patient’s biopsychosocial status, as guided by the International Classification of Function and Disability (ICF) (ref Rimmer2005: http://informahealthcare.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09638280500493860?journalCode=dre).
| |
| | |
| [[Image:ICFCircMod.jpg|thumb|right|ICF model for Physical Activity Prescription]]
| |
| | |
| In forming a partnership with the patient, the physiotherapist aims to understand the barriers preventing the patient from engaging in a more physically active lifestyle and begin to consider ways in which the patient may negotiate them (Table of Barriers). These barriers are not only the practical ones, such as time and equipment, but also physical and mental. In particular, identification of the patient’s physical and mental barriers, including disease or disorder, and proper, ongoing risk assessment in the process of physical activity promotion is essential and the essence of why physiotherapists are ideal candidates for this role<ref name="WCPT2011" />. While risk assessment is essential it falls outside the scope of the current topic but with regards to promoting physical activity in the the following groups: | |
|
| |
|
| <br>• Individuals who are healthy but sedentary.<br>• Individuals that are apparently health and sedentary.<br>• Individuals with comorbidities.<br>• Individuals with a disability. | | <br>• Individuals who are healthy but sedentary.<br>• Individuals that are apparently health and sedentary.<br>• Individuals with comorbidities.<br>• Individuals with a disability. |
| Line 690: |
Line 150: |
| Finally, it is important that clinicians avoid the assumption that: | | Finally, it is important that clinicians avoid the assumption that: |
|
| |
|
| <br>• “If you recommend exercise, they will do it…”<br>• “If you write a programme, they will follow it…”<ref name="Handcock2003" /><br> | | <br>• “If you recommend exercise, they will do it…”<br>• “If you write a programme, they will follow it…”<ref name="Handcock2003" /><br> |
|
| |
|
| == Resources ==
| | Support, guidance and follow-up are critical to the maintenance of the patient’s physical activity behaviour. Guides and leaflets, such as those produced by the CSP (below), are options of support that may be provided.<br> <br> |
|
| |
|
| = PHYSICAL ACTIVITY BEYOND THE INDIVIDUAL = | | <gallery mode="packed-hover"> |
| | | Image:CSPLogo.jpg|Easy Exercise Guide (link)[http://www.csp.org.uk/publications/easy-exercise-guide] |
| [[Image:NICEPAP.jpg|thumb|right|Figure x. NICE Physical Activity Pathway (NICE Pathways 2013)]]The emergence of physical activity at the heart of the public health agenda has unveiled unforeseen opportunities and unprecedented roles for physiotherapists<ref name="Eaton2012">Eaton, L. Public health presents physios with an unprecedented opportunity [Views and opinions]. 2012. Available at: http://www.csp.org.uk/frontline/article/views-opinions (Accessed 7 November 2013).</ref>. The various branches of the [http://pathways.nice.org.uk/pathways/physical-activity NICE Physical Activity Pathway] (Figure)<ref name="NICEpathway">National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Pathways. Physical activity overview. Available at: http://pathways.nice.org.uk/pathways/physical-activity (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref> reflect the diverse paths physiotherapists may take beyond the individual patient. In particular, this includes roles within the community and in national health and government policy. As this is relatively unchartered territory, general guidance is provided below, with suggestions based on transferable applications of current roles and UK-based examples of unique initiatives.
| | Image:CSPLogo.jpg|Do you sit at a desk all day? Information Leaflets (link)[http://www.csp.org.uk/publications/do-you-sit-desk-all-day] |
| | | </gallery> |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| == Community ==
| |
| | |
| While physiotherapists already contribute to the health of the community through their care of each individual, physiotherapists may also participate in the development and/or execution of community-wide interventions. Community-wide programmes focusing on health education, school-based physical education, and social support and interventions that promote physical activity, such as signs that encourage stair use and school-based interventions that limit TV and video-game time have proven successful<ref name="Kahn2002">Kahn EB, Ramsey LT, Brownson RC, Heath GW, Howze EH, Powell KE, Stone EJ, Rajab MW, Corso P, and the Task Force on Community Preventive Services. The effectiveness of interventions to increase physical activity: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med 2002;22(4S):73-107</ref>.
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
| Physiotherapists may be creative in the way in which they assume this role (ref: http://bjsm.bmj.com/content/43/1/44.full.pdf+html). In the UK, the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy (CSP)<hyperlink their website> have been engaged in the Move For Health Campaign <hyperlink: http://www.csp.org.uk/your-health/healthy-living/move-health-campaign>, highlighting the contributions of physiotherapists to the health of the nation (refMFH?). Through this initiative, various activities have been organised to promote individual community health, such as Workout at Work Day <hyperlink http://www.csp.org.uk/news-events/events/workout-work-day-2013>. A recent ‘seasonal’ initiative <hyperlink 'Seas Init'> had physiotherapists out in the streets promoting physical activity and other lifestyle changes to shoppers passing by. [http://www.csp.org.uk/frontline/article/street-physios-ease-shoppers%E2%80%99-pain http://www.csp.org.uk/frontline/article/street-physios-ease-shoppers%E2%80%99-pain]
| |
|
| |
|
| | | == Physical Activity Beyond The Individual == |
| | The emergence of physical activity at the heart of the public health agenda has unveiled unforeseen opportunities and unprecedented roles for physiotherapists<ref name="Eaton2012">Eaton, L. Public health presents physios with an unprecedented opportunity [Views and opinions]. 2012. Available at: http://www.csp.org.uk/frontline/article/views-opinions (Accessed 7 November 2013).</ref>. |
|
| |
|
| Other examples of physiotherapist-led community programmes that promote physical activity and target populations across the lifespan and with varying needs are offered below. <br>
| | See [[Physical Activity Promotion in the Community]] |
| | |
| Infants to teenagers:<br>
| |
| | |
| *[http://www.thephysiotherapycentre.com/ Kidilates] - pilates for infants and young children, including those with disabilities
| |
| *[http://www.rsgk.co.uk/ Ready Steady Go Kids] - a preschool multi-sport programme
| |
| *[http://www.physiocise.com.au/programs_for_kids.htm Physiocise] - targeted at children and teenagers
| |
| | |
| <br>Adults:<br>
| |
| | |
| *[http://www.physioledpilates.com/?page Physioled]Pilates
| |
| *[http://www.cheltenham.gov.uk/info/10096/healthy_living/1060/nhs-classes_in_the_community Back to Fitness] - an NHS service <br>
| |
| | |
| <br>Older Adults:<br>
| |
| | |
| *[http://www.edinburghparkinsons.org/training-care-programs/physio-led-exercise-class/ Parkinson’s Disease Exercise Class]
| |
| *[http://www.solent.nhs.uk/service-info.asp?id=120&utype= Community Falls Prevention ]<br>
| |
| | |
| Various opportunities for CPD exist to equip physiotherapists for this emerging role in community-based health intervention. These include Pilates certification, pregnancy and postnatal exercise instructor (http://postnatalexercise.co.uk/ ) and postural stability instructor <hyperlink: http://www.laterlifetraining.co.uk/courses/postural-stability-instructor/>.
| |
| | |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| === Volunteering === | | === Volunteering === |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| In general, [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Volunteering%3F_Keep_this_in_sight%E2%80%A6the_future_is_bright volunteering is an ever-emerging role for physiotherapists]. It can entail anything from volunteering locally to travelling abroad. | | In general, [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Volunteering%3F_Keep_this_in_sight%E2%80%A6the_future_is_bright volunteering is an ever-emerging role for physiotherapists]. It can entail anything from volunteering locally to travelling abroad. |
|
| |
|
|
| | Home:Physiotherapists can volunteer in their local communities in various ways from programme administration to teaching classes in the promotion of physical activity. <br> Abroad: With rising prevalence in physical inactivity and the rising need of NCD prevention and control in underdeveloped nations, the need for targeted physical activity promotion is being realised<ref name="GAPA2013">Global Advocacy for Physical Activity (GAPA). Global Advocacy for Physical Activity: Advocacy Council of ISPAH. 2013. Available at: http://www.globalpa.org.uk/ (Accessed 5 December 2013).</ref>, and the value of volunteering for initiatives such as GAPA cannot be dismissed. In addition, it has been estimated by the United Nations Development Programme that over 80% of the world’s 650 million disabled people reside in impoverished countries with little access to rehabilitation facilities, education, and employment. Overseas organisations are constantly looking for physiotherapists for the promotion of health and the development of rehabilitation services both in hospitals and in community-based clinics<ref name="VSO">VSO. Physiotherapists: Volunteer opportunities overseas for physiotherapists. Available at: http://www.vso.org.uk/volunteer/opportunities/community-and-social-development-health/physiotherapists (Accessed 23 November 2013).</ref>. |
| | |
| ==== Home ====
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
| Physiotherapists can volunteer in their local communities in various ways from programme administration to teaching classes in the promotion of physical activity. In the UK alone, 111 volunteering roles in the health and social care sectors exist [newref]. Some opportunities include | |
|
| |
|
|
| | == Conclusion == |
|
| |
|
| *community-based programmes, such as those supported by [http://www.edinburghleisure.co.uk/opportunities-edinburgh-leisure/become-volunteer Edinburgh Leisure] and other community-based leisure centres;
| | The Resource was created as a guide for physiotherapists and others interested in the physical activity agenda. Collating information from various sources in various media formats, it provides an overview of the relevant underpinning evidence supporting physical activity as a public health priority and the means by which it may be addressed. In particular, it focuses on the significance of the role of the physiotherapist in the promotion of physical activity at the level of the individual, in the community and in government and policy. Within each section, it offers relevant guidance and useful tools. It also offers suggestions for relevant further reading and CPD opportunities to encourage further exploration and consolidation of learning. In conclusion, given the significance of the role of the physiotherapist in the physical activity agenda, one issue remains and calls for further reflection. |
| *CRISIS, the national charity for homeless individuals, seek out physiotherapists to volunteer and provide services such as assessments, advice and health promotion, treatments and referrals to additional services for their clients, particularly over the Christmas period<ref name="CRISIS">Crisis. Specialist Volunteers: Physiotherapy. Available at: http://www.crisis.org.uk/pages/service-volunteers.html#physiotherapy (Accessed 24 November 2013).</ref>;
| |
| *the Riding for the Disabled Association, which has a selection of volunteering positions varying from administrative duties, riding instruction and physiotherapy, with the aim of promoting physical activity<ref name="CSPMoveHealth">CSP Move for Health. Physiotherapy Public Health Service Examples. 2013. Available at: http://www.csp47.co.uk/framework/sites/default/files/Move%20for%20Health%20exemplars1-5.pdf (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref>.<br>
| |
|
| |
|
| <br>
| | == References == |
| | |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:VolunteeringEngland.jpg|[http://www.crisis.org.uk/pages/service-volunteers.html#physiotherapy]
| |
| Image:RDA.jpg|[http://www.rda.org.uk/volunteering/]
| |
| Image:VolunteerCRISIS.jpg|[http://www.crisis.org.uk/pages/service-volunteers.html]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| ==== Abroad ==== | |
| | |
| <br>With rising prevalence in physical inactivity and the rising need of NCD prevention and control in underdeveloped nations, the need for targeted physical activity promotion is being realised (ref GAPAsite), and the value of volunteering for initiatives such as GAPA cannot be dismissed. In addition, it has been estimated by the United Nations Development Programme that over 80% of the world’s 650 million disabled people reside in impoverished countries with little access to rehabilitation facilities, education, and employment. Overseas organisations are constantly looking for physiotherapists for the promotion of health and the development of rehabilitation services both in hospitals and in community-based clinics<ref name="VSO">VSO. Physiotherapists: Volunteer opportunities overseas for physiotherapists. Available at: http://www.vso.org.uk/volunteer/opportunities/community-and-social-development-health/physiotherapists (Accessed 23 November 2013).</ref>.
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
| <gallery mode="packed-hover">
| |
| Image:AbroadVSO.jpg|[http://www.vso.org.uk/volunteer/opportunities/community-and-social-development-health/physiotherapists]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
| == Government, Policy and Clinical Governance ==
| |
| | |
| === Physiotherapists as Consultants in Policy <br> ===
| |
| | |
| It is well-established that government and policy level factors influence physical activity national and worldwide (Figure ) (Bauman2012?). Thus, physiotherapists, as experts on the issue of physical activity promotion, have a role in serving as consultants to community planners, local businesses, legislation and the NHS or the equivalent health services in other countries<ref name="Dean2009-1" />. An exemplar of this role is [http://www.physiotherapyuk.org.uk/visiting/speakers/karen-middleton-cbe-0 Karen Middleton], a qualified physiotherapist who has been serving as the chief AHP officer and has recently been appointed new [http://www.physiospot.com/2013/10/02/karen-middleton-appointed-as-new-csp-chief-executive/ CSP chief executive], applying her knowledge and experience as a physiotherapist to help guide policy in national health and in the profession. Another example of this role, coming from the other end of the journey of the physiotherapist, previous students at Queen Margaret University developed a business proposal to convince the NHS for support of a community-based pulmonary rehabilitation class, called [http://www.physio-pedia.com/SecondWind:_Business_Case SecondWind], which would serve to facilitate a more physically activity lifestyle in individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD).<br>
| |
| | |
| === Clinical Governance ===
| |
| | |
| <br>"Clinical governance is a system through which NHS organizations are accountable for continuously improving the quality of their services and safeguarding high standards of care by creating an environment in which excellence in clinical care will flourish."<ref name="Scally1998">Scally G, Donaldson LJ. Clinical governance and the drive for quality improvement in the new NHS in England. British Medical Journal.1998; 317(7150): 61-65.</ref><br> <br>Clinical governance is a term used to describe the broad range of activities that assist in the sustenance and improvement of high quality patient care. It is the responsibility of healthcare organisations, to the public they serve, that care delivered is safe and of the highest quality. In regards to implemented systems, structures and actions implemented healthcare organizations are required to produce evidence that standards are being maintained. In order to determine whether physiotherapists are delivering best quality of care in regards to physical activity, an active role in service evaluation, clinical audit and research is crucial.<br>
| |
| | |
| Pillars of Clinical Governance<ref name="Nicholls2000">Nicholls S, Cullen R, O’Neill S, Halligan A. Clinical governance: its origins and its foundations. British Journal of Clinical Governance. 2000. 5 (3):72 – 178.</ref>:<br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Pillars.jpeg|center]]<br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| ==== Service Evaluation ====
| |
| | |
| <br>Service evaluation aims to interpret and evaluate current care. It is designed to identify what type of standard a current service achieves<ref name="NRES2006">National Research Ethics Service. Differentiating audit, service evaluation and research. 2006. Available at:fckLRhttp://www.nres.nhs.uk/applications/guidance/?EntryId62=66988 (Accessed 24 November 2013).</ref>[104]. As Scotland’s new physical activity pathway and other similar physical activity interventions at the level of the individual are adopted throughout various physiotherapy services, it will be necessary to evaluate these services.<br>
| |
| | |
| ==== Clinical Audit ====
| |
| | |
| <br>Carried out in order to provide information to better equip the delivery of best practice and care for the patient, clinical audit addresses the question whether a service meets a predetermined standard<ref name="NRES2006" />. It addresses the quality of care and whether best practice is being implemented, if what needs to be done is being applied and how well is being done <ref name="HQIP2012">Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership. What is the difference between clinical audit and research? 2012 [online] Available at: http://www.hqip.org.uk/what-is-the-difference-between-clinical-audit-and-research/ (Accessed 24 November 2013).</ref>. Similar to the scenario of service evaluation, should physical activity become a standard component of physiotherapy assessment and evaluation, an audit of the process will be required to ensure that it meets the established guidelines. Even if physical activity assessment and intervention does not become a national standard, if it is applied as part of a local initiative, accurate documentation is necessary (ref CSPdocumentation), and such audits of clinical documentation are performed regularly (ref in fb mess?). <br>
| |
| | |
| Clinical Audit Process<ref name="ClinicalAudit">Research &amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp; Professional Development. Available at: http://www.rpd-research.org.uk/about.html (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref><br>
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Clinical audit cycle2.jpg|center|320x217px]]<br>
| |
| | |
| ==== <br> <br><br>Research ====
| |
| | |
| <br>Research involves the acquisition of new information and the discovery of which treatments and mode of care produce the best effects. It provides direction in clinical practice [102]. This Resource has been produced based on evidence emerging over years and years of research and thus offers several examples of areas in which a physiotherapist may get involved – from the basic biological to the public health impact [[Image:TranslationalPhys.jpg|thumb|right|Summary of Translational Physiology. (Figure from Seals 2013)]]of physical activity and all of the psychosocial aspects surrounding it. With respect to the former, a novel concept, ‘translational physiology’ has been proposed to integrate these multiple levels of physiology toward a common understanding (Figure )<ref name="Seals2013">Seals D.R. Translational physiology: from molecules to public health. Topical Review. The Journal of Physiology. 2013; 591(14):3457-69.</ref>.<br>
| |
| | |
| <br>
| |
| | |
| Other examples of public health research taking place in the UK include the following projects<ref name="CSPMoveHealth">CSP Move for Health. Physiotherapy Public Health Service Examples. 2013. Available at: http://www.csp47.co.uk/framework/sites/default/files/Move%20for%20Health%20exemplars1-5.pdf (Accessed 28 November 2013).</ref>:
| |
| | |
| 1) Designing an education programme to promote physiotherapy’s role in public health (add locations to each??)<br>2) Supporting physiotherapists in advising on physical activity<br>3) Working with Exercise on Prescription Instructors in Chronic Pain Services<br>4) Promoting the use of stairs in an NHS hospital<br>5) Daytime yoga classes for people with a physical disability<br>
| |
| | |
| = KEY RESOURCES =
| |
| | |
| = REFERENCES =
| |
|
| |
|
| <references /> | | <references /> |
|
| |
|
| <br><br>
| | [[Category:Current_and_Emerging_Roles_in_Physiotherapy_Practice]] |
| | | [[Category:Physical_Activity]] |
| References will automatically be added here, see [[Adding References|adding references tutorial]].
| | [[Category:Physical Activity Content Development Project]] |
| | |
| [[Category:Queen_Margaret_University_Project]] | | [[Category:Queen_Margaret_University_Project]] |
| | [[Category:Course Pages]] |
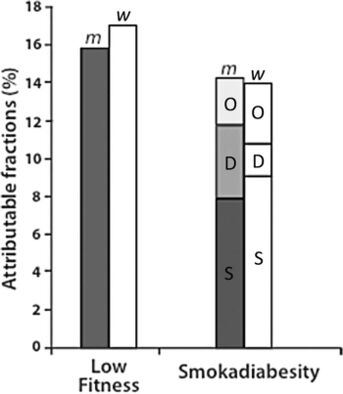
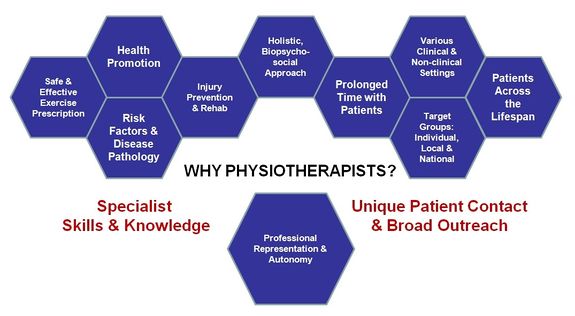
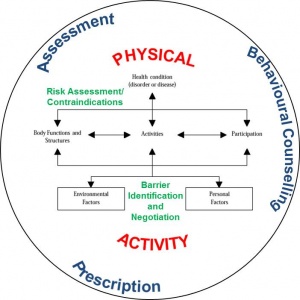
![Easy Exercise Guide (link)[1]](/images/7/76/CSPLogo.jpg)






