Quadratus Plantae: Difference between revisions
Leana Louw (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[Dry needling" to "[[Dry Needling") |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
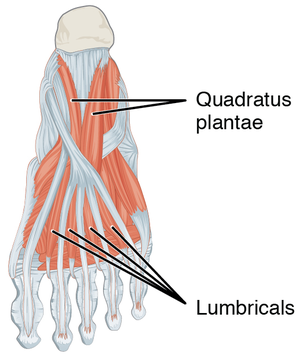
Quadratus plantae | Quadratus plantae is one of the 20 individual foot muscles. It is situated in the second layer of muscles at the sole of the foot.<ref name=":0">Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.</ref> The muscle consists of a lateral and medial head, coming together to form the bulk of this muscle.<ref>Schroeder KL, Rosser BW, Kim SY. [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13047-014-0054-5 Fiber type composition of the human quadratus plantae muscle: a comparison of the lateral and medial heads.] Journal of foot and ankle research 2014;7(1):54.</ref>The lateral head tends to be smaller than the medial head. | ||
[[File:Intrinsicfoot mm.png|none|thumb]] | [[File:Intrinsicfoot mm.png|none|thumb]] | ||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
The lateral head originates at the lateral border of the [[calcaneus]]. The medial head originates on the medial surface of the calcaneus. <ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /> | |||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
Before reaching it's insertion at the posterolateral margin of tendon of [[flexor digitorum longus]]<ref name=":0" />, the two heads of the quadratus plantae join and form a flat band.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
=== Nerve === | === Nerve === | ||
Lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3).<ref name=":0" /> | [[Lateral Plantar Nerve|Lateral plantar nerve]] (S2, S3).<ref name=":0" /> | ||
=== Artery === | === Artery === | ||
Lateral plantar artery.<ref name=":0" /> | Lateral plantar artery .<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The muscles of the foot are arranged in compartments and layers, but function together to support the foot during stance phase and maintaining the arch of the foot. Quadratus plantae mainly functions by assisting [[flexor digitorum longus]] with flexion of the lateral 4 digits of the [[Foot Anatomy|foot]].<ref name=":0" /> | The muscles of the foot are arranged in compartments and layers, but function together to support the foot during stance phase and maintaining the arch of the foot. Quadratus plantae mainly functions by assisting [[flexor digitorum longus]] with flexion of the lateral 4 digits of the [[Foot Anatomy|foot]].<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Clinical | == Clinical Relevance == | ||
Quadratus plantae increase the stability of the foot during the stance phase of gait to resist toe extension. It is thus an important foot muscle to consider in the [[Gait Cycle|gait pattern]] and with gait retraining after foot injuries. | Quadratus plantae increase the stability of the foot during the stance phase of gait to resist toe extension. It is thus an important foot muscle to consider in the [[Gait Cycle|gait pattern]] and with gait retraining after foot injuries.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
Related pathologies:<ref name=":1">Sooriakumaran P, Sivananthan S. [https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f051/1368acfdf227be873672246f474f5227620f.pdf Why does man have a quadratus plantae? A review of its comparative anatomy.] Croatian medical journal 2005;46(1).</ref> | Related pathologies:<ref name=":1">Sooriakumaran P, Sivananthan S. [https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f051/1368acfdf227be873672246f474f5227620f.pdf Why does man have a quadratus plantae? A review of its comparative anatomy.] Croatian medical journal 2005;46(1).</ref> | ||
* [[Calcaneal Fractures|Calcaneus | * [[Calcaneal Fractures|Calcaneus fractures]]: Can lead to contractures of quadratus plantae causing clawing of the 2nd to 5th toes. | ||
* [[Diabetes|Diabetic]] foot: Untreated abscesses in | * [[Diabetes|Diabetic]] foot: Untreated abscesses in the central plantar space can lead to necrosis of quadratus plantae. | ||
** Heel pain: Can be the result of entrapment of the lateral plantar nerve between the two heads of quadratus | ** Heel pain: Can be the result of entrapment of the lateral plantar nerve between the two heads of quadratus plantae. | ||
== Assessment == | == Assessment == | ||
* Palpation | * Palpation - Start just distal to the plantar aspect of the calcaneus and move distally along the middle portion of the foot. Resistance of the MTPs at the distal phalanx will lead to contraction of the muscle to confirm you are palpating the quadratus plantae. | ||
* [[Gait Cycle|Gait]] assessment | * [[Gait Cycle|Gait]] assessment | ||
* Muscle Length | |||
* Manual Muscle Testing | |||
{{#ev:youtube|c2OOTf2ANYs|300}}<ref>Blackriver and Bootsma Education. Manual Muscle Test and Lengthening - Quadratus Plantae & Lumbricals Pedis. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c2OOTf2ANYs [last accessed 20/1/2022]</ref> | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
* [[Myofascial Release|Myofascial release]]<ref name=":1" /> | * [[Myofascial Release|Myofascial release]]<ref name=":1" /> | ||
* [[Trigger Points|Trigger point]] therapy<ref name=":1" /> | * [[Trigger Points|Trigger point]] therapy<ref name=":1" /> | ||
* [[Dry | * [[Dry Needling]] | ||
* Gait training<ref name=":2">The Gait Guys. The QP....What's the deal? Available from: https://www.thegaitguys.com/thedailyblog/2018/1/2/the-qpwhats-the-deal (accessed 31/03/2020).</ref> | * Gait training<ref name=":2">The Gait Guys. The QP....What's the deal? Available from: https://www.thegaitguys.com/thedailyblog/2018/1/2/the-qpwhats-the-deal (accessed 31/03/2020).</ref> | ||
* Exercises (in combination with other intrinsic foot muscles):<ref name=":2" /> | * Exercises (in combination with other intrinsic foot muscles):<ref name=":2" /> | ||
** Short-foot exercise | ** Short-foot exercise | ||
** Toes spread out | ** Toes spread out | ||
** 1st toe extension | ** 1st toe extension while stabilizing through 2nd-5th toes | ||
** 2nd - 5th toe | ** 2nd - 5th toe flexion | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
| Line 58: | Line 62: | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Muscles]] | [[Category:Muscles]] | ||
[[Category:Foot - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Foot]] | |||
[[Category:Foot - Muscles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:53, 29 January 2024
Original Editor - Leana Louw
Top Contributors - Leana Louw, Patti Cavaleri and Kim Jackson
Description[edit | edit source]
Quadratus plantae is one of the 20 individual foot muscles. It is situated in the second layer of muscles at the sole of the foot.[1] The muscle consists of a lateral and medial head, coming together to form the bulk of this muscle.[2]The lateral head tends to be smaller than the medial head.
Origin[edit | edit source]
The lateral head originates at the lateral border of the calcaneus. The medial head originates on the medial surface of the calcaneus. [1][3]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Before reaching it's insertion at the posterolateral margin of tendon of flexor digitorum longus[1], the two heads of the quadratus plantae join and form a flat band.[3]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3).[1]
Artery[edit | edit source]
Lateral plantar artery .[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
The muscles of the foot are arranged in compartments and layers, but function together to support the foot during stance phase and maintaining the arch of the foot. Quadratus plantae mainly functions by assisting flexor digitorum longus with flexion of the lateral 4 digits of the foot.[1]
Clinical Relevance[edit | edit source]
Quadratus plantae increase the stability of the foot during the stance phase of gait to resist toe extension. It is thus an important foot muscle to consider in the gait pattern and with gait retraining after foot injuries.[3]
Related pathologies:[3]
- Calcaneus fractures: Can lead to contractures of quadratus plantae causing clawing of the 2nd to 5th toes.
- Diabetic foot: Untreated abscesses in the central plantar space can lead to necrosis of quadratus plantae.
- Heel pain: Can be the result of entrapment of the lateral plantar nerve between the two heads of quadratus plantae.
Assessment[edit | edit source]
- Palpation - Start just distal to the plantar aspect of the calcaneus and move distally along the middle portion of the foot. Resistance of the MTPs at the distal phalanx will lead to contraction of the muscle to confirm you are palpating the quadratus plantae.
- Gait assessment
- Muscle Length
- Manual Muscle Testing
Treatment[edit | edit source]
- Myofascial release[3]
- Trigger point therapy[3]
- Dry Needling
- Gait training[5]
- Exercises (in combination with other intrinsic foot muscles):[5]
- Short-foot exercise
- Toes spread out
- 1st toe extension while stabilizing through 2nd-5th toes
- 2nd - 5th toe flexion
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinial oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2010.
- ↑ Schroeder KL, Rosser BW, Kim SY. Fiber type composition of the human quadratus plantae muscle: a comparison of the lateral and medial heads. Journal of foot and ankle research 2014;7(1):54.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Sooriakumaran P, Sivananthan S. Why does man have a quadratus plantae? A review of its comparative anatomy. Croatian medical journal 2005;46(1).
- ↑ Blackriver and Bootsma Education. Manual Muscle Test and Lengthening - Quadratus Plantae & Lumbricals Pedis. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c2OOTf2ANYs [last accessed 20/1/2022]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 The Gait Guys. The QP....What's the deal? Available from: https://www.thegaitguys.com/thedailyblog/2018/1/2/the-qpwhats-the-deal (accessed 31/03/2020).