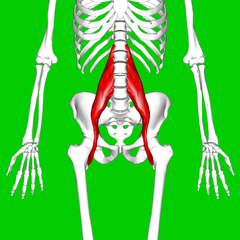
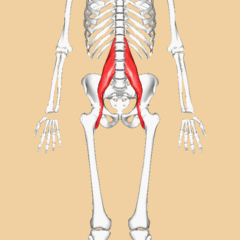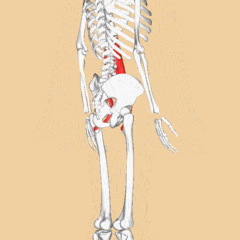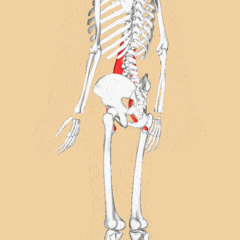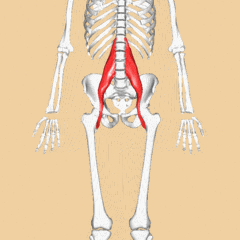
Psoas Major
Original Editor - Oyemi Sillo
Lead Editors - Vidya Acharya, Samrah khan, Lucinda hampton, Oyemi Sillo, Kim Jackson, George Prudden, Samson Chengetanai, Joao Costa, Maram Salem, Rachael Lowe and Kardelen Aktas
Description
[edit | edit source]
Psoas Major is a long fusiform muscle placed on the side of the lumbar region of the vertebral column and brim of the lesser pelvis. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Origin
[edit | edit source]
The psoas muscle is anatomically considered to have superficial and deep parts owing to the presence of branches of the lumbar plexus running through it.
Superficial part - overlies the lumbar plexus and takes origin from the sides of the T12 and L1 to L4 vertebrae including the intervening intervertebral discs.
The deep part which lies mainly deep to the branches of the lumbar plexus takes origin from the transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae L1 to L5.
Insertion[edit | edit source]
from this wide origin, the fibres of the muscle will converge as they descend on the posterior abdominal wall, cross the pelvic inlet/brim into the true, to form a long tendon. this tendon is joined within the pelvic region by musculotendinous fibres from the iliacus muscle to insert into the lesser trochanter of the femur.
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Branches from the ventral rami of lumbar spinal nerves (L1, L2, and L3) before they join to form the lumbar plexus.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
The muscle receives blood from the four lumbar arteries from the aorta, from small branches of the renal arteries, from small muscular branches of the common iliac artery, and from the deep circumflex iliac artery.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Action
[edit | edit source]
- Flexion of the thigh at the hip
- Minimal action in lateral rotation and abduction of the thighCite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Function
[edit | edit source]
Stabilizes the lumbar spine Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title, maintains erect posture when working in reverse action.
This muscle is also important clinically in that it can get injured and lead to what is called the psoas syndrome. This is relatively uncommon condition but is particularly difficult to diagnose because it mimicks the symptoms of other clinical conditions. this syndrome is often misdiagnosed
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1ZGxMH1ktXCPn8nGi0wDB8UkPgso1uhqbVv3CHnT3QaghuSQfS|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS