Popliteal Fossa: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[File:Popliteal_picture.jpg|frameless|right]] | [[File:Popliteal_picture.jpg|frameless|right]] | ||
=== Description === | === Description === | ||
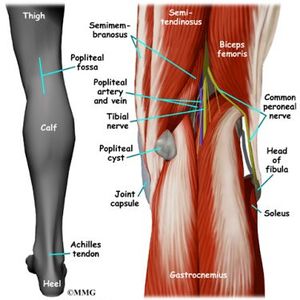
The Popliteal Fossa is a diamond- shaped space behind the [[knee]] joint .<ref name=":1">Chummy, | The Popliteal Fossa is a diamond- shaped space behind the [[knee]] joint .<ref name=":1">Chummy SS, editor. Last's Anatomy. Twelfth Edition. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2011. | ||
</ref> It is formed between the muscles in the posterior compartments of the thigh and leg.This anatomical landmark is the major route by which structures passes between the thigh and leg.<ref name=":0">Richard LD, Wayne VA, Adam WM, editors. Grays' Anatomy for Students. Second Edition. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2010.</ref> | |||
=== Margins/Borders === | === Margins/Borders === | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
* The Popliteal vein: It is superficial to the and travels with the Popliteal artery. | * The Popliteal vein: It is superficial to the and travels with the Popliteal artery. | ||
* The [[Tibial Nerve|Tibia nerve]] and common Fibular nerve: These are the two major branches of the [[Sciatic Nerve|Sciatic]] nerve. They are the most superficial of the neurovascular structures in the Popliteal fossa. They appears under the margin of the [[Biceps Femoris]] muscles. | * The [[Tibial Nerve|Tibia nerve]] and common Fibular nerve: These are the two major branches of the [[Sciatic Nerve|Sciatic]] nerve. They are the most superficial of the neurovascular structures in the Popliteal fossa. They appears under the margin of the [[Biceps Femoris]] muscles. | ||
{{#ev:youtube}} | |||
{{#ev:youtube | |||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
* Popliteal Aneurysm | * Popliteal Aneurysm | ||
* Popliteal nerve block | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 02:43, 24 September 2020
Original Editor - User:Ochia Lilian Chidera
Top Contributors - Ochia Lilian Chidera, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane, Lucinda hampton and Kim Jackson
Description[edit | edit source]
The Popliteal Fossa is a diamond- shaped space behind the knee joint .[1] It is formed between the muscles in the posterior compartments of the thigh and leg.This anatomical landmark is the major route by which structures passes between the thigh and leg.[2]
Margins/Borders[edit | edit source]
The Popliteal Fossa has 2 upper margins and 2 lower margins[2]
- The margins of the upper part are formed by the Semimembranosus and Semitendinosus muscles on the medial side and the Biceps Femoris on the lateral side.
- The margins of the lower parts are formed by the medial head of the Gastrocnemius muscle and the laterally by the Plantaris muscle and the lateral head of the Gastrocnemius muscle.
Floor[edit | edit source]
The floor of the fossa is formed by the Popliteal surface of the Femur, capsule of the Knee reinforced by the oblique Popliteal ligament and the Popliteus muscle covered by its Fascia[1].
Roof[edit | edit source]
The roof of the Popliteal fossa is covered by the Fascia Lata which is strongly reinforced by the tranverse fibers. Thus,the roof is pierced by the small Saphenous vein and the posterior Femoral cutaneous nerve[1].
Content[edit | edit source]
The major content of the Popliteal fossa are[2]:
- The Popliteal artery ; This is the deepest of the neurovascular structures in the Popliteal fossa. It is a continuation of the Femoral artery and appears on the upper medial side under the margin of the Semimembranosus muscle.
- The Popliteal vein: It is superficial to the and travels with the Popliteal artery.
- The Tibia nerve and common Fibular nerve: These are the two major branches of the Sciatic nerve. They are the most superficial of the neurovascular structures in the Popliteal fossa. They appears under the margin of the Biceps Femoris muscles.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
- Popliteal Pulse
- Popliteal Aneurysm
- Popliteal nerve block