Nerve Injury Rehabilitation: Difference between revisions
(added video and text) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process == | == Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process == | ||
Watch the below to grasp the concepts of nerve damage and repair | Peripheral nerve injuries have numerous causes including: traumatic injuries; infections; metabolic problems ( one of the most common causes is [[Diabetes|diabetes mellitus]]); inherited causes; exposure to toxins; tumours; iatrogenic causes.<ref name=":0">Mayo clinic. [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20352061 Peripheral neuropathy.] Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20352061 (last accessed 24.3.2019)</ref> | ||
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OlNyp0RfiBg&feature=youtu.be|width}}<ref>Dr. Simon Freilich. Nerve damage and repair. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OlNyp0RfiBg&feature=youtu.be (last accessed 24.3.2019)</ref> | |||
Watch the below to grasp the concepts of nerve damage and repair{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OlNyp0RfiBg&feature=youtu.be|width}}<ref>Dr. Simon Freilich. Nerve damage and repair. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OlNyp0RfiBg&feature=youtu.be (last accessed 24.3.2019)</ref> | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Clinical presentation varies according to the nerve affected ie sensory, motor, or combined). | |||
Signs and symptoms may include<ref name=":0" /> | |||
* Gradual onset of numbness, prickling or tingling in your feet or hands, which can spread upward into your legs and arms | |||
* Sharp, jabbing, throbbing, freezing or burning pain | |||
* Extreme sensitivity to touch | |||
* Lack of coordination and falling | |||
* Muscle weakness or paralysis if motor nerves are affected | |||
* Neuromatous or causalgia pain.<ref>Medscape. [https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1270360-clinical Peripheral nerve injuries clinical presentation]. Available from: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1270360-clinical (last accessed 24.3.2019)</ref> | |||
== | == Assessment == | ||
After a diagnosis of a peripheral nerve injury a full subjective and objective examination is required to get a clear picture of the way the lesion is affecting the client. The examination should focus on | |||
* Pain assessment | |||
* Sensation deficit and skin condition | |||
* Muscle strength/loss | |||
* Functional deficits | |||
* Joint stiffness | |||
* Emotional stress | |||
== Outcome Measures == | == Outcome Measures == | ||
Revision as of 07:42, 24 March 2019
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Lead Editors
Clinically Relevant Anatomy 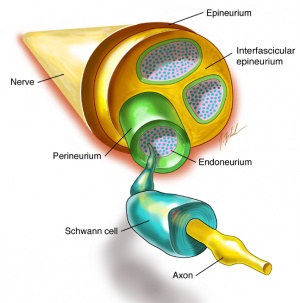 [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Nerve regrowth in the peripheral nervous system is dependant on type of injury. Functional disability due to nerve lesions is intertwined with severity of lesion. Before reading this article it would be advised to have a good knowledge of the type of lesion and the denervation consequences[1] . Please read Classification of Peripheral Nerve Injury as an introduction to this page.
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process[edit | edit source]
Peripheral nerve injuries have numerous causes including: traumatic injuries; infections; metabolic problems ( one of the most common causes is diabetes mellitus); inherited causes; exposure to toxins; tumours; iatrogenic causes.[2]
Watch the below to grasp the concepts of nerve damage and repair
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Clinical presentation varies according to the nerve affected ie sensory, motor, or combined).
Signs and symptoms may include[2]
- Gradual onset of numbness, prickling or tingling in your feet or hands, which can spread upward into your legs and arms
- Sharp, jabbing, throbbing, freezing or burning pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Lack of coordination and falling
- Muscle weakness or paralysis if motor nerves are affected
- Neuromatous or causalgia pain.[4]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
After a diagnosis of a peripheral nerve injury a full subjective and objective examination is required to get a clear picture of the way the lesion is affecting the client. The examination should focus on
- Pain assessment
- Sensation deficit and skin condition
- Muscle strength/loss
- Functional deficits
- Joint stiffness
- Emotional stress
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to management approaches to the condition
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Resources[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Reza Salman Roghani and Seyed Mansoor Rayegani (2012). Basics of Peripheral Nerve Injury Rehabilitation, Basic Principles of Peripheral Nerve Disorders, Dr. Seyed Mansoor Rayegani (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-0407-0, InTech, Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/basic-principles-of-peripheral-nervedisorders/basics-of-peripheral-nerve-injury-rehabilitation (last accessed 24.3.2019)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Mayo clinic. Peripheral neuropathy. Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20352061 (last accessed 24.3.2019)
- ↑ Dr. Simon Freilich. Nerve damage and repair. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OlNyp0RfiBg&feature=youtu.be (last accessed 24.3.2019)
- ↑ Medscape. Peripheral nerve injuries clinical presentation. Available from: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1270360-clinical (last accessed 24.3.2019)






