HELLP Syndrome: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[Edema" to "[[Oedema") |
||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox">'''Original Editors '''- Carolyn S. Furdek [[Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems|from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.]] | |||
'''Original Editors '''- Carolyn S. Furdek [[Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems|from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.]] | |||
''' | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} </div> | ||
</div> | |||
[[ | == Introduction == | ||
[[File:Birth.jpeg|right|frameless|399x399px]] | |||
HELLP syndrome is a life-threatening condition that can potentially complicate pregnancy. It is named for 3 features of the condition: Hemolysis, [[Liver Function Tests|Elevated Liver enzyme levels]], and Low Platelet levels. It typically occurs in the last 3 months of pregnancy but can also start soon after delivery. | |||
< | * A wide range of non-specific symptoms may be present in women with HELLP syndrome. Symptoms may include fatigue; malaise; fluid retention and excess weight gain; [[headache]]; nausea and vomiting; pain in the upper right or middle of the abdomen; blurry vision; and rarely, nosebleed or seizures. | ||
* The cause of HELLP syndrome is not known, but certain risk factors have been associated with the condition. It is most common in women with preeclampsia or eclampsia. If not diagnosed and treated quickly, HELLP syndrome can lead to serious complications for the mother and baby. | |||
* The main treatment is to deliver the baby as soon as possible, even if premature, if there is distress of the mother or the baby. Treatment may also include medications needed for the mother or baby, and [[blood]] transfusion for severe bleeding problems.<ref>Rare Diseases hellp syndrome Available: https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/8528/hellp-syndrome (accessed 5.9.2021)</ref> | |||
== Etiology/Causes == | |||
The aetiology and pathophysiology remain incompletely understood with multiple theories: | |||
* Immune-mediated: maternal acute rejection reaction to fetal antigens | |||
* Placenta-mediated liver injury | |||
* [[SIRS / Sepsis / Septic Shock|Systemic inflammatory response syndrome]] in the setting of pre-eclampsia<ref name=":0">Radiopedia [https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hellp-syndrome HELLP syndrome] Available:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hellp-syndrome (accessed 6.10.2021)</ref> | |||
== Epidemiology == | |||
HELLP syndrome has a prevalence of 0.5% to 0.9%. About 70% of cases occur in the third trimester of pregnancy, and the remainder occurs within 48 hours of delivery. The mortality rate of women with HELLP syndrome is 0 to 24%, with a perinatal death rate of up to 37%<ref name=":1">Khalid F, Tonismae T. [https://www.statpearls.com/articlelibrary/viewarticle/22684/ HELLP Syndrome]. StatPearls [Internet]. 2020 Jul 31.Available:https://www.statpearls.com/articlelibrary/viewarticle/22684/ (accessed 5.10.2021)</ref> | |||
== Clinical Presentation == | |||
The presentation can be variable and can include malaise, epigastric and/or right upper quadrant pain, and nausea and vomiting. Some may have non-specific viral-like symptoms. The symptoms continuously progress. | |||
< | * [[Hypertension in Pregnancy|Hypertension]] and proteinuria (classic symptoms of pre-eclampsia) may be absent or slight.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
* The average gestational age of presentation of HELLP syndrome is 34 weeks. | |||
* Patients are usually multiparous and over the age of 35 years old. | |||
* Patients are often overweight and have [[Oedema Assessment|edema]] in 50% of the cases. | |||
* The condition exacerbates during the night. <ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Radiographic features == | |||
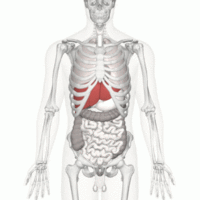
[[File:Liver gif.gif|right|frameless|200x200px]] | |||
General features predominantly involve hepatic (liver) sequelae: | |||
= | * hepatomegaly: especially the right lobe | ||
* haemorrhage, subcapsular haematoma, rupture | |||
* hepatic infarction<ref name=":0" /> | |||
Image 2: Liver position | |||
== Treatment / Management == | |||
[[File:Neonatal intensive care.jpeg|right|frameless|399x399px]] | |||
HELLP syndrome has the potential to quickly turn life-threatening for both mother and fetus. Therefore the recommendation is always to hospitalize patients for strict monitoring of laboratory values. | |||
* During hospitalization, patients should be treated as severely pre-eclamptic and should receive magnesium sulfate for seizure prophylaxis along with [[Blood Pressure|blood pressure]] control. | |||
* Maternal-fetal monitoring should be performed throughout each step of management as typically, immediate delivery is recommended for true HELLP patients | |||
* Those with stable maternal-fetal conditions between 24 to 34 weeks gestation a recommendation is to give [[Corticosteroid Medication|corticosteroids]] then deliver 24 hours after the last dose. See also [[Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome]]. Steroid administration is not only beneficial to the fetus for lung maturity but also for improvement of [[Laboratory Tests|laboratory values]] in patients, particularly in elevating platelet counts. | |||
* Some patients may benefit from transfusions of red cells, platelets, and plasma<ref name=":1" />. | |||
| |||
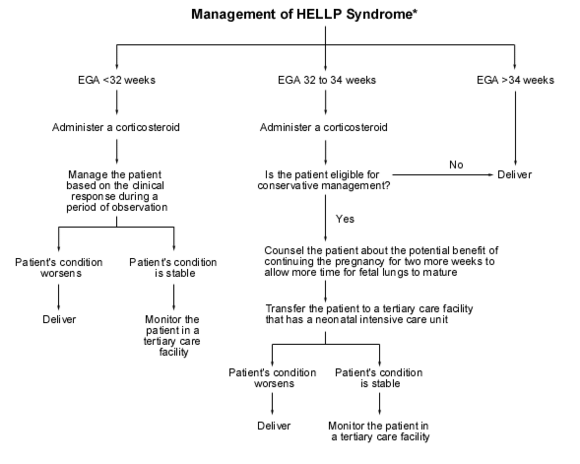
[[Image:HELLP Chart.gif|center|Figure: Suggested protocol in treating pts with HELLP Syndrome|alt=|thumb|580x580px]] | |||
[Chart courtesy of Journal of The American Family Physician: [http://www.aafp.org/afp/990901ap/829.html HELLP Syndrome]<ref>Padden MO. HELLP syndrome: recognition and perinatal management. American family physician. 1999 Sep;60(3):829-36.</ref>] | |||
== Prognosis == | |||
HELLP syndrome is a life-threatening condition. Early diagnosis and treatment, along with maternal and neonatal intensive care, can help to reduce the mortality in HELLP syndrome. | |||
* The mortality rate of women with HELLP syndrome is 0%-24%, with a perinatal death rate of up to 37% (poor perinatal prognosis is because of placental abruption, intrauterine hypoxia and asphyxia, prematurity, and low birth weight). | |||
Maternal death occurs due to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), placental abruption, postpartum hemorrhage, or acute renal failure. | |||
# DIC occurs in 15% to 62.5% of the cases. | |||
# Placental abruption occurs in 11% to 25% of women with HELLP syndrome. | |||
# Postpartum hemorrhage occurs in 12.5% to 40% | |||
# Acute renal failure in 36% to 50% of the cases. | |||
Patients with HELLP syndrome have a 19%-27% risk of developing HELLP syndrome in subsequent pregnancies<ref name=":1" />. | |||
== | == Physical Therapy Management == | ||
Due to the severity and risk of maternal mortality, conservative management is not recommended in the treatment of HELLP syndrome.<ref name="Haram">Haram, K. Svendsen, E. Abildgaard, U. The HELLP syndrome: Clinical issues and management. A Review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth [serial online]. 2009; 9:8.</ref> | |||
* | * [[Abdominal Muscles|Abdominal]] weakness and deconditioning may be seen in patients after a [[Cesarean Section|caesarean]] section. | ||
* Most patients are advised to wait 4-6 weeks before resuming [[Physical Activity|physical activity]] and [[Therapeutic Exercise|exercise]].<ref name="C-section">Cesarean Birth; Post Partum Patient Education Material: Ohio State University Medical Center. Can be located online at http://medicalcenter.osu.edu/PatientEd/Materials/PDFDocs/women-in/post-par/cesarean.pdf. Accessed 25 March 2011.</ref> | |||
* | |||
== Differential Diagnosis == | == Differential Diagnosis == | ||
| Line 135: | Line 80: | ||
HELLP Syndrome my be misdiagnosed as any of the below conditions:<ref name="Haram" /> | HELLP Syndrome my be misdiagnosed as any of the below conditions:<ref name="Haram" /> | ||
*Viral Hepatitis | *Viral [[Hepatitis A, B, C|Hepatitis]] | ||
*Cholangitis | *Cholangitis | ||
*Acute fatty liver of pregnancy | *Acute fatty liver of pregnancy | ||
*Haemolytic uremic syndrome | *Haemolytic uremic syndrome | ||
*Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura | *Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura | ||
*Systemic lupus erythematosus | *[[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus|Systemic lupus erythematosus]] | ||
== Case | == Case Report == | ||
*Subscapular Liver Hematoma in HELLP Syndrome: Case Report.<ref name="Kapan">Kapan M. Evsen MS. Gumas M.. Onder A. Tekbas G., Subscapular Liver Hematoma in HELLP Syndrome: Case Report. Gastroenterology Research. June 2010. 3(3). 144-146.</ref> [[http://www.gastrores.org/index.php/Gastrores/article/viewArticle/205/246 view article in Gastroenterology Research]] | *Subscapular Liver Hematoma in HELLP Syndrome: Case Report.<ref name="Kapan">Kapan M. Evsen MS. Gumas M.. Onder A. Tekbas G., Subscapular Liver Hematoma in HELLP Syndrome: Case Report. Gastroenterology Research. June 2010. 3(3). 144-146.</ref> [[http://www.gastrores.org/index.php/Gastrores/article/viewArticle/205/246 view article in Gastroenterology Research]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Bellarmine_Student_Project]] | [[Category:Bellarmine_Student_Project]] | ||
[[Category:Womens_Health]] | |||
[[Category:Pregnancy]] | |||
[[Category:Postpartum]] | |||
[[Category:Pelvis]] [[Category:Conditions]] [[Category:Pelvis - Conditions]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:45, 3 August 2022
Introduction[edit | edit source]
HELLP syndrome is a life-threatening condition that can potentially complicate pregnancy. It is named for 3 features of the condition: Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzyme levels, and Low Platelet levels. It typically occurs in the last 3 months of pregnancy but can also start soon after delivery.
- A wide range of non-specific symptoms may be present in women with HELLP syndrome. Symptoms may include fatigue; malaise; fluid retention and excess weight gain; headache; nausea and vomiting; pain in the upper right or middle of the abdomen; blurry vision; and rarely, nosebleed or seizures.
- The cause of HELLP syndrome is not known, but certain risk factors have been associated with the condition. It is most common in women with preeclampsia or eclampsia. If not diagnosed and treated quickly, HELLP syndrome can lead to serious complications for the mother and baby.
- The main treatment is to deliver the baby as soon as possible, even if premature, if there is distress of the mother or the baby. Treatment may also include medications needed for the mother or baby, and blood transfusion for severe bleeding problems.[1]
Etiology/Causes[edit | edit source]
The aetiology and pathophysiology remain incompletely understood with multiple theories:
- Immune-mediated: maternal acute rejection reaction to fetal antigens
- Placenta-mediated liver injury
- Systemic inflammatory response syndrome in the setting of pre-eclampsia[2]
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
HELLP syndrome has a prevalence of 0.5% to 0.9%. About 70% of cases occur in the third trimester of pregnancy, and the remainder occurs within 48 hours of delivery. The mortality rate of women with HELLP syndrome is 0 to 24%, with a perinatal death rate of up to 37%[3]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
The presentation can be variable and can include malaise, epigastric and/or right upper quadrant pain, and nausea and vomiting. Some may have non-specific viral-like symptoms. The symptoms continuously progress.
- Hypertension and proteinuria (classic symptoms of pre-eclampsia) may be absent or slight.[2]
- The average gestational age of presentation of HELLP syndrome is 34 weeks.
- Patients are usually multiparous and over the age of 35 years old.
- Patients are often overweight and have edema in 50% of the cases.
- The condition exacerbates during the night. [3]
Radiographic features[edit | edit source]
General features predominantly involve hepatic (liver) sequelae:
- hepatomegaly: especially the right lobe
- haemorrhage, subcapsular haematoma, rupture
- hepatic infarction[2]
Image 2: Liver position
Treatment / Management[edit | edit source]
HELLP syndrome has the potential to quickly turn life-threatening for both mother and fetus. Therefore the recommendation is always to hospitalize patients for strict monitoring of laboratory values.
- During hospitalization, patients should be treated as severely pre-eclamptic and should receive magnesium sulfate for seizure prophylaxis along with blood pressure control.
- Maternal-fetal monitoring should be performed throughout each step of management as typically, immediate delivery is recommended for true HELLP patients
- Those with stable maternal-fetal conditions between 24 to 34 weeks gestation a recommendation is to give corticosteroids then deliver 24 hours after the last dose. See also Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Steroid administration is not only beneficial to the fetus for lung maturity but also for improvement of laboratory values in patients, particularly in elevating platelet counts.
- Some patients may benefit from transfusions of red cells, platelets, and plasma[3].
[Chart courtesy of Journal of The American Family Physician: HELLP Syndrome[4]]
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
HELLP syndrome is a life-threatening condition. Early diagnosis and treatment, along with maternal and neonatal intensive care, can help to reduce the mortality in HELLP syndrome.
- The mortality rate of women with HELLP syndrome is 0%-24%, with a perinatal death rate of up to 37% (poor perinatal prognosis is because of placental abruption, intrauterine hypoxia and asphyxia, prematurity, and low birth weight).
Maternal death occurs due to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), placental abruption, postpartum hemorrhage, or acute renal failure.
- DIC occurs in 15% to 62.5% of the cases.
- Placental abruption occurs in 11% to 25% of women with HELLP syndrome.
- Postpartum hemorrhage occurs in 12.5% to 40%
- Acute renal failure in 36% to 50% of the cases.
Patients with HELLP syndrome have a 19%-27% risk of developing HELLP syndrome in subsequent pregnancies[3].
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
Due to the severity and risk of maternal mortality, conservative management is not recommended in the treatment of HELLP syndrome.[5]
- Abdominal weakness and deconditioning may be seen in patients after a caesarean section.
- Most patients are advised to wait 4-6 weeks before resuming physical activity and exercise.[6]
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
HELLP Syndrome my be misdiagnosed as any of the below conditions:[5]
- Viral Hepatitis
- Cholangitis
- Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
- Haemolytic uremic syndrome
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Case Report[edit | edit source]
- Subscapular Liver Hematoma in HELLP Syndrome: Case Report.[7] [view article in Gastroenterology Research]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Rare Diseases hellp syndrome Available: https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/8528/hellp-syndrome (accessed 5.9.2021)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Radiopedia HELLP syndrome Available:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hellp-syndrome (accessed 6.10.2021)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Khalid F, Tonismae T. HELLP Syndrome. StatPearls [Internet]. 2020 Jul 31.Available:https://www.statpearls.com/articlelibrary/viewarticle/22684/ (accessed 5.10.2021)
- ↑ Padden MO. HELLP syndrome: recognition and perinatal management. American family physician. 1999 Sep;60(3):829-36.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Haram, K. Svendsen, E. Abildgaard, U. The HELLP syndrome: Clinical issues and management. A Review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth [serial online]. 2009; 9:8.
- ↑ Cesarean Birth; Post Partum Patient Education Material: Ohio State University Medical Center. Can be located online at http://medicalcenter.osu.edu/PatientEd/Materials/PDFDocs/women-in/post-par/cesarean.pdf. Accessed 25 March 2011.
- ↑ Kapan M. Evsen MS. Gumas M.. Onder A. Tekbas G., Subscapular Liver Hematoma in HELLP Syndrome: Case Report. Gastroenterology Research. June 2010. 3(3). 144-146.