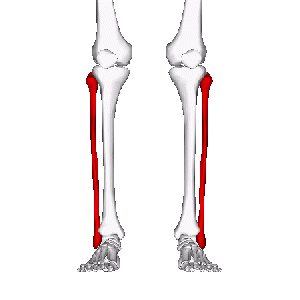
Fibula
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Leana Louw and Kim Jackson
Description[edit | edit source]
The lower leg is made up by two bones - the tibia and fibula. The fibula's role is to act as an attachment for muscles, as well as providing stability of the ankle joint.
Structure[edit | edit source]
The fibula is the thinner and posteriolaterally situated of the two lower leg bones. These two bones are connected by the tibiofibular syndesmosis, which includes the interosseous membrane.
Proximal: A enlarged pointed head and small neck form the proximal part of the fibula.
Shaft: The shaft is twisted in form and triangular in cross-section. It consists of the anterior, interosseous and posterior borders, as well as medial, posterior and lateral surfaces. It is the main area for muscle attachments.
Distal: The distal part of the fibula enlarges to form the lateral malleolus inferiolaterally and form part of the ankle joint.
Function[edit | edit source]
The fibula's role is to act as and attachment for muscles, as well as providing stability of the ankle joint. The fibula is a non-weight-bearing bone.
Articulations[edit | edit source]
Proximal: The fibular head articulates with the fibular facet on the lateral tibial condyle.
Distal: The lateral malleolus articulates with the to form the superior part of the ankle joint.
Muscle attachments[edit | edit source]
The fibula acts as an proximal attachment for the following muscles:
Extensor digitorum longus: Superior 3/4 of medial border
Extensor hallucis longus: Middle of anterior surface
Fibularis tertius: Inferior 1/3 of anterior surface
Fibularis longus: Fibular head and superior 2/3 of lateral surface
Fibularis brevis: Inferior 2/3 of lateral surface
Soleus: Fibular head (posterior) and superior 1/4 of posterior surface
Flexor hallucis longus: Inferior 2/3 of posterior surface
Flexor digitorum longus: Via tendon
Tibialis posterior: Posterior surface
*Take note that above only describes fibular attachments, and that all of these muscles also has other areas of attachments not mentioned in this page.
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x