Anterior Scalene: Difference between revisions
Wendy Walker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[Brachial plexus|" to "[[Brachial Plexus|") |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- | '''Original Editor ''' - [[User:Wendy Walker|Wendy Walker]] | ||
'''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
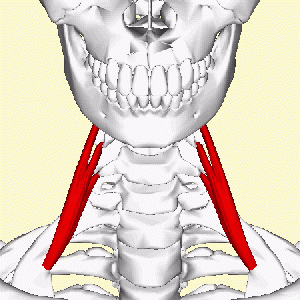
The anterior scalene, AKA scalenus anterior (scalenus anticus; Latin: musculus scalenus anterior) muscle is one of the lateral muscles of the neck, belonging to the scalene group. It is deeply placed, lying behind the [[Sternocleidomastoid|Sternocleidomastoid]]. | |||
It is located between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery | It is located between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery. The roots of the [[Brachial Plexus|brachial plexus]] pass posterior to it. The phrenic nerve crosses its anterior surface.<ref>Harry WG, Bennett JD, Guha SC. Scalene muscles and the brachial plexus: anatomical variations and their clinical significance. Clinical Anatomy: The Official Journal of the American Association of Clinical Anatomists and the British Association of Clinical Anatomists. 1997;10(4):250-2.</ref><br> [[Image:Scalenus anterior - animation04.gif|center|300x300px]]<br> | ||
[[Image:Scalenus anterior - animation04.gif]]<br> | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
Anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of [[Cervical Vertebrae|cervical vertebrae]] C3-C6 <ref name=":0">Sam Bernes.[https://teachmeanatomy.info/neck/muscles/scalene/ The Scalene Muscles] .Teach Me Anatomy.Accessed 28 April 2020. | |||
</ref> | |||
Anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of | |||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
By a narrow, flat tendon attaches into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first rib, and into the ridge on the upper surface of the rib in front of the subclavian groove. | |||
By a narrow, flat tendon into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first rib, and into the ridge on the upper surface of the rib in front of the subclavian groove. | |||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Anterior branches of the cervical nerves C5-C7. | |||
Anterior branches of the | |||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
Ascending cervical branch of the inferior thyroid artery. | |||
== Action and Function == | |||
Anterior scalene can perform individually or in synergistic group with other two scalenes ([[Middle Scalene|Middle]] and [[Posterior Scalene|Posterior]]) | |||
* Individually, bends the neck laterally on the same side - '''side flexor''' | |||
* In synergistic group: | |||
** Bilateral contraction causes anterior flexion of the neck - '''flexors''' | |||
** Ipsilateral contraction of the anterior scalene muscle primarily results in lateral flexion of the neck to the same side and elevation of the first rib during forced inspiration. | |||
** Elevate the 1st rib and are '''accessory muscles of respiration''' | |||
== Clinical Significance == | |||
Accessory muscles of respiration-The Scalene muscles help in elevation of the first and second ribs in increasing the intrathoracic volume.To aid in breathing,these muscles act as accessory muscles of respiration in patients with respiratory distress.The important clinical sign is the usage of accessory muscles in respiratory distress<ref name=":0" /> | |||
= | |||
== Referencest == | |||
<references /> | <references /><br> | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Cervical Spine - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Cervical_Spine]] | |||
[[Category:Muscles]] | |||
[[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | |||
[[Category:Cervical Spine - Muscles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:59, 8 March 2024
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors - Kim Jackson, Wendy Walker, Chrysolite Jyothi Kommu, Admin, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop and Milijana Delevic
Description[edit | edit source]
The anterior scalene, AKA scalenus anterior (scalenus anticus; Latin: musculus scalenus anterior) muscle is one of the lateral muscles of the neck, belonging to the scalene group. It is deeply placed, lying behind the Sternocleidomastoid.
It is located between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery. The roots of the brachial plexus pass posterior to it. The phrenic nerve crosses its anterior surface.[1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of cervical vertebrae C3-C6 [2]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
By a narrow, flat tendon attaches into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first rib, and into the ridge on the upper surface of the rib in front of the subclavian groove.
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Anterior branches of the cervical nerves C5-C7.
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Ascending cervical branch of the inferior thyroid artery.
Action and Function[edit | edit source]
Anterior scalene can perform individually or in synergistic group with other two scalenes (Middle and Posterior)
- Individually, bends the neck laterally on the same side - side flexor
- In synergistic group:
- Bilateral contraction causes anterior flexion of the neck - flexors
- Ipsilateral contraction of the anterior scalene muscle primarily results in lateral flexion of the neck to the same side and elevation of the first rib during forced inspiration.
- Elevate the 1st rib and are accessory muscles of respiration
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Accessory muscles of respiration-The Scalene muscles help in elevation of the first and second ribs in increasing the intrathoracic volume.To aid in breathing,these muscles act as accessory muscles of respiration in patients with respiratory distress.The important clinical sign is the usage of accessory muscles in respiratory distress[2]
Referencest[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Harry WG, Bennett JD, Guha SC. Scalene muscles and the brachial plexus: anatomical variations and their clinical significance. Clinical Anatomy: The Official Journal of the American Association of Clinical Anatomists and the British Association of Clinical Anatomists. 1997;10(4):250-2.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sam Bernes.The Scalene Muscles .Teach Me Anatomy.Accessed 28 April 2020.