Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Definition/Description == | == Definition/Description == | ||
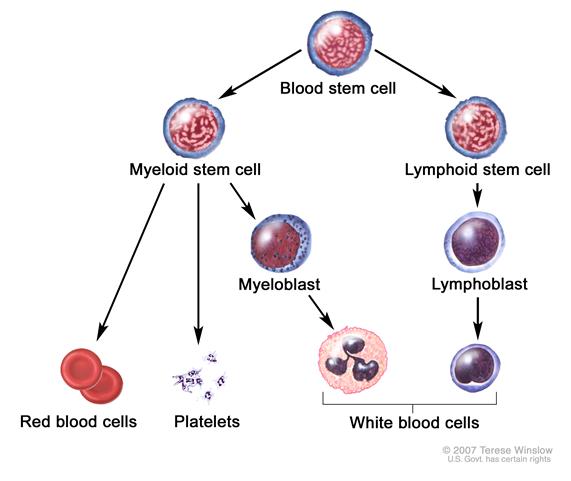
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer involving the blood and bone marrow. The main cell involved in this disorder is myeloid stem cells which can become either red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. In this disorder, Myeloid stem cells become a type of immature white blood cell called myeloblasts. These myeloblasts never become healthy white blood cells. Abnormal red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets begin to crowd in the bone marrow to prevent healthy cells from forming.<ref name="National Cancer Institute">National Cancer Institute. Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treatment. National Cancer Institute at the National Institute of Health. December 26, 2013. Available at http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/adultAML/Patient/page1, Accessed March 11, 2014</ref> <br> | Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer involving the blood and bone marrow. The main cell involved in this disorder is myeloid stem cells which can become either red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. In this disorder, Myeloid stem cells become a type of immature white blood cell called myeloblasts. These myeloblasts never become healthy white blood cells. Abnormal red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets begin to crowd in the bone marrow to prevent healthy cells from forming.<ref name="National Cancer Institute">National Cancer Institute. Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treatment. National Cancer Institute at the National Institute of Health. December 26, 2013. Available at http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/adultAML/Patient/page1, Accessed March 11, 2014</ref> <br> | ||
[[Image:Multiple Myeloma pic.jpg|center|Blood Cell Development Process]] | |||
== Prevalence == | == Prevalence == | ||
Revision as of 17:17, 11 March 2014
Original Editors - Kevin Mooney & Erik Rice from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.
Top Contributors - Kevin Mooney, Erik Rice, Lucinda hampton, Elaine Lonnemann, Vidya Acharya, Kim Jackson, Shaimaa Eldib, WikiSysop, Wendy Walker, George Prudden and Sarah Haerinck
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer involving the blood and bone marrow. The main cell involved in this disorder is myeloid stem cells which can become either red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. In this disorder, Myeloid stem cells become a type of immature white blood cell called myeloblasts. These myeloblasts never become healthy white blood cells. Abnormal red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets begin to crowd in the bone marrow to prevent healthy cells from forming.[1]
Prevalence[edit | edit source]
add text here
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
add text here
Associated Co-morbidities[edit | edit source]
add text here
Medications[edit | edit source]
add text here
Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values[edit | edit source]
add text here
Etiology/Causes[edit | edit source]
add text here
Systemic Involvement[edit | edit source]
add text here
Medical Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
add text here
Physical Therapy Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
add text here
Alternative/Holistic Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
add text here
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
add text here
Case Reports/ Case Studies[edit | edit source]
add links to case studies here (case studies should be added on new pages using the case study template)
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
see tutorial on Adding PubMed Feed
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: addfeedhere|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ National Cancer Institute. Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treatment. National Cancer Institute at the National Institute of Health. December 26, 2013. Available at http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/adultAML/Patient/page1, Accessed March 11, 2014