Aldosterone Receptor Antagonist: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Lucinda hampton moved page Aldosterone Receptor Antagonist Diuretics in the treatment of congestive heart failure to Aldosterone Receptor Antagonist: more appropriate) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Lauren Pulliam Southern|Lauren Pulliam Southern]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | |||
== Introduction == | |||
[[File:Kidney and adrenal gland.jpeg|thumb|Kidney and adrenal gland]] | |||
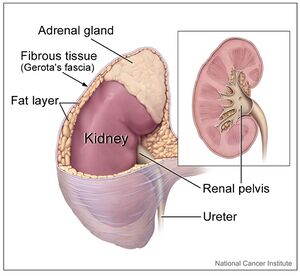
Aldosterone receptor antagonists are a class of drugs which block the effects of aldosterone. Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid [[Hormones|hormone]] in the body and is produced in the adrenal cortex of the [[Adrenal Glands|adrenal gland]]. | |||
Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption by the [[kidney]]<nowiki/>s, salivary glands, sweat glands and colon. At the same time, it increases the excretion of hydrogen and potassium ions. | |||
Aldosterone receptor antagonists block the effects of aldosterone, preventing the the reabsorption of sodium, which encourages water loss. This leads to a decrease in [[Blood Pressure|blood pressure]] and a reduction in fluid around the [[Anatomy of the Human Heart|heart]]. | |||
# Aldosterone receptor antagonists may be used in the treatment of [[Hypertension|high blood pressure]] or [[Heart Failure|heart failure]]. They also have a weak [[Diuretics|diuretic]] action. | |||
# Aldosterone receptor antagonists have been shown to reduce heart failure-related hospitalisations, prolong life, and improve exercise tolerance and [[Quality of Life|quality of life]].<ref name=":1">Heart Failure Matters ALDOSTERONE RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS OR MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST (MRAS) Available:https://www.heartfailurematters.org/what-your-doctor-can-do/aldosterone-receptor-antagonists-or-mineralocorticoid-receptor-antagonist-mras/#animated-journey (accessed 7.4.2022)</ref> | |||
This 2 minute video is a good introduction to Aldosterone receptor antagonists | |||
{{#ev:youtube|v=4uU2ivM_dZU}}<ref> | |||
UTMC Pharmacy. Aldosterone Receptor Antagonist . Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4uU2ivM_dZU [last accessed 7.4.2022]</ref> | |||
== Polypharmacy == | |||
Aldosterone receptor antagonists are proven to be beneficial in heart failure patients even if they are already on [[Angiotensin Inhibitors and Blockers for Treating Hypertension|angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors]] or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). <ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Common ARAs == | |||
Two common aldosterone receptor antagonists are<ref name=":0">Lainscak M, Pelliccia F, Rosano G, Vitale C, Schiariti M, Greco C, Speziale G, Gaudio C (2015). Safety profile of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: Spironolactone and eplerenone. Int J Cardiol. 200, 25-9</ref> | |||
* Spironolactone: taken orally with doses of 12.5-25 mg per day and has a long half-life of 13-17 hours<ref>U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Aldactone spironolactone tablets, USP. Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/012151s062lbl.pdf. Last accessed 11/29/18.</ref>. | |||
7. Sica DA. Diuretic-related side effects: development and treatment. J Clin Hypertens. 2004;6:532–540. | * Eplerenone is also taken orally with doses of 50 mg twice daily with a half-life of 4 hours<ref>U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). INSPRA eplerenone tablets. Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2002/21437lbl.pdf. Last accessed 11/29/18.</ref> and both are excreted by via the liver and kidneys<ref>Nappi JM, Sieg A (2011). Aldosterone and aldosterone receptor antagonists in patients with chronic heart failure. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 7, 353-63.</ref>. | ||
== Adverse Effects == | |||
Due to the prevention of potassium secretion into the distal tubule both these drugs are associated with an adverse effect of: | |||
* [[Hyperkalemia]] due to them being potassium sparing diuretics. | |||
* Gynecomastia and breast pain in men because it tends to bind to progesterone and androgen receptors<ref name=":0" />. The newer drugs don’t have this effect<ref name=":1" />. | |||
== Physiotherapy - Implications == | |||
[[File:Angina.jpg|thumb|215x215px|Angina]] | |||
These drugs can sometimes affect kidney function and can also increase potassium levels (hyperkalemia). Hyperkalemia affects the cardiac conductive tissue and can cause serious [[Heart Arrhythmias|arrhythmias]] ( eg [[Ventricular Fibrillation|ventricular fibrillation]], [[Cardiac Arrest|asystolic arrest]]). It important to check for any irregular heartbeats if the patient begins complaining of chest pains or [[Dyspnoea|shortness of breath]]<ref>Sica DA. Diuretic-related side effects: development and treatment. J Clin Hypertens. 2004;6:532–540.</ref>. This is especially important for patients who also use ACE inhibitors or ARBs. | |||
In addition to monitoring the patient’s [[Vital Signs|vitals]] before, during and after treatment, patients should be educated on lifestyle changes to help decrease their mortality. | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Cardiovascular Disease]] | |||
[[Category:Pharmacology]] | |||
[[Category:Pharmacology for Cardiovascular Disease]] | |||
Latest revision as of 02:49, 7 April 2022
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Aldosterone receptor antagonists are a class of drugs which block the effects of aldosterone. Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid hormone in the body and is produced in the adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland.
Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption by the kidneys, salivary glands, sweat glands and colon. At the same time, it increases the excretion of hydrogen and potassium ions.
Aldosterone receptor antagonists block the effects of aldosterone, preventing the the reabsorption of sodium, which encourages water loss. This leads to a decrease in blood pressure and a reduction in fluid around the heart.
- Aldosterone receptor antagonists may be used in the treatment of high blood pressure or heart failure. They also have a weak diuretic action.
- Aldosterone receptor antagonists have been shown to reduce heart failure-related hospitalisations, prolong life, and improve exercise tolerance and quality of life.[1]
This 2 minute video is a good introduction to Aldosterone receptor antagonists
Polypharmacy[edit | edit source]
Aldosterone receptor antagonists are proven to be beneficial in heart failure patients even if they are already on angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). [1]
Common ARAs[edit | edit source]
Two common aldosterone receptor antagonists are[3]
- Spironolactone: taken orally with doses of 12.5-25 mg per day and has a long half-life of 13-17 hours[4].
- Eplerenone is also taken orally with doses of 50 mg twice daily with a half-life of 4 hours[5] and both are excreted by via the liver and kidneys[6].
Adverse Effects[edit | edit source]
Due to the prevention of potassium secretion into the distal tubule both these drugs are associated with an adverse effect of:
- Hyperkalemia due to them being potassium sparing diuretics.
- Gynecomastia and breast pain in men because it tends to bind to progesterone and androgen receptors[3]. The newer drugs don’t have this effect[1].
Physiotherapy - Implications[edit | edit source]
These drugs can sometimes affect kidney function and can also increase potassium levels (hyperkalemia). Hyperkalemia affects the cardiac conductive tissue and can cause serious arrhythmias ( eg ventricular fibrillation, asystolic arrest). It important to check for any irregular heartbeats if the patient begins complaining of chest pains or shortness of breath[7]. This is especially important for patients who also use ACE inhibitors or ARBs.
In addition to monitoring the patient’s vitals before, during and after treatment, patients should be educated on lifestyle changes to help decrease their mortality.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Heart Failure Matters ALDOSTERONE RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS OR MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST (MRAS) Available:https://www.heartfailurematters.org/what-your-doctor-can-do/aldosterone-receptor-antagonists-or-mineralocorticoid-receptor-antagonist-mras/#animated-journey (accessed 7.4.2022)
- ↑ UTMC Pharmacy. Aldosterone Receptor Antagonist . Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4uU2ivM_dZU [last accessed 7.4.2022]
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lainscak M, Pelliccia F, Rosano G, Vitale C, Schiariti M, Greco C, Speziale G, Gaudio C (2015). Safety profile of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: Spironolactone and eplerenone. Int J Cardiol. 200, 25-9
- ↑ U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Aldactone spironolactone tablets, USP. Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/012151s062lbl.pdf. Last accessed 11/29/18.
- ↑ U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). INSPRA eplerenone tablets. Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2002/21437lbl.pdf. Last accessed 11/29/18.
- ↑ Nappi JM, Sieg A (2011). Aldosterone and aldosterone receptor antagonists in patients with chronic heart failure. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 7, 353-63.
- ↑ Sica DA. Diuretic-related side effects: development and treatment. J Clin Hypertens. 2004;6:532–540.