Ulnar Nerve Entrapment: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[Muscle Strength" to "[[Muscle Strength Testing") |
||
| (47 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
' | == Introduction == | ||
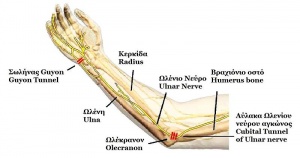
[[File:Ulnar nerve anatomy.JPG|thumb|Ulnar nerve]] | |||
[[Ulnar Nerve|Ulnar nerve]] entrapment occurs when the ulnar nerve is compressed. This typically occurs at two main sites: the [[elbow]] and the [[Wrist and Hand|wrist]]<ref>Jan Michael C. Lleva, Ke-Vin Chang.Ulnar Neuropathy. Available from: [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534226/ Ahttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534226/] (Accessed 30th March, 2019) | |||
</ref>. Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow is usually at the cubital tunnel ([https://www.physio-pedia.com/Cubital_Tunnel_Syndrome Cubital Tunnel Syndrome]). Ulnar nerve neuropathy at the elbow is the second most common entrapment neuropathy (the first most common is the median nerve at the [[Wrist and Hand|wrist]]).<ref>Lauretti L, D'Alessandris QG, De Simone C, Sop FY, Remore LM, Izzo A, et al. [https://www.jocn-journal.com/article/S0967-5868(17)30909-8/fulltext Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow. A surgical series and a systematic review of the literature.] Journal of Clinical Neuroscience. 2017;46:99-108.</ref> Ulnar nerve neuropathy less commonly occurs at Guyon’s canal in the wrist (Guyon’s canal syndrome/ulnar tunnel syndrome). | |||
Ulnar nerve entrapment | == Causes == | ||
Ulnar nerve [[Nerve entrapment|entrapment]] at the elbow ([https://www.physio-pedia.com/Cubital_Tunnel_Syndrome Cubital Tunnel Syndrome]) and wrist (Guyon's Canal Syndrome) occur due to repetitive compression, from leaning on the elbows or wrists ([https://www.physio-pedia.com/Cyclist%27s_palsy cyclist's palsy]) and prolonged elbow flexion. It can also occur from trauma, swelling, fractures, and vascular and bony pathologies/abnormalities. | |||
Guyon’s canal syndrome occurs when the ulnar nerve becomes entrapped between the hook of the hamate and the transverse carpal ligament. Guyon’s canal syndrome is considered an overuse injury which is commonly caused by direct pressure on a handlebar (i.e. [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Cyclist%27s_palsy bicycle handlebar], weight lifting, construction equipment) and therefore, is sometimes referred to as “handlebar palsy”. It can also result from excessive gripping, twisting, or repeated wrist and hand motions. Also, entrapment may develop if the hand is flexed and ulnar deviated for prolonged periods of time. | |||
The incidence of trauma leading to ulnar nerve compression is unknown; however ulnar neuropathy has been documented after distal humeral fractures and in up to 10% of elbow dislocations, and may also develop from any complex elbow or wrist trauma.<ref name="Svernlov et al" /> | |||
== Clinical Presentation<ref name="MD Guidelines">Neuropathy of Ulnar Nerve (Entrapment). MD Guidelines. http://www.mdguidelines.com/neuropathy-of-ulnar-nerve-entrapment/differential-diagnosis. Accessed March 15, 2011.</ref><ref name="WebMD">Ulnar Neuropathy. Emedicine from WebMD. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1141515-overview. Updated June 10, 2010. Accessed March 15, 2011.</ref><ref name="Palmer">Palmer BA, Hughes TB. Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. J Hand Surg. 2010: 35 (1): 153-163.</ref><ref name="emed">Nerve Entrapment Syndromes. Emedicine from WebMD. www.emedicine.medscape.com/article/249784-overview Updated July 31, 2009. Accessed March 15, 2011.</ref><ref name="aao">Ulnar Nerve Entrapment. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=a00069. Updated October 2007. Accessed March 15, 2011.</ref><ref name="Shin">Shin R, Ring D. The Ulnar Nerve in Elbow Trauma. J. Bone Jt. Surg. (Am.). 2007: 89: 1108-1116.</ref>== | |||
Symptoms of ulnar nerve entrapment include tingling in fingers 4 and 5, weak grip strength, [[Pain Mechanisms|pain]] and sensitivity on the ulnar side of the forearm, wrist and hand, muscle atrophy, clawing of digits 4 and 5 [[Benediction Hand (aka Benediction Sign or Preacher's Hand)|(sign of benediction)]]. | |||
[ | [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Cubital_Tunnel_Syndrome ''Cubital Tunnel Syndrome''] can present in different grades of severity:<ref name="Palmer" /> | ||
'''Grade I''': Mild symptoms including: | |||
*Intermittent paresthesia | |||
*Minor hypoesthesia of the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the fifth and medial aspect of fourth digits | |||
*No motor changes | |||
'''Grade II''': Moderate and persistent symptoms including: | |||
*Paresthesia | |||
*Hypoesthesia of the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the fifth and medial aspect of fourth digits | |||
*Mild weakness of ulnar innervated muscles | |||
*Early signs of muscular atrophy | |||
'''Grade III''': Severe symptoms including: | |||
*Paresthesia | |||
*Obvious loss of sensation of the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the fifth and medial aspect of fourth digits. | |||
*Significant functional and motor impairment | |||
*Muscle atrophy of the hand intrinsics | |||
*Possible digital clawing of fourth and fifth digits (Sign of Benediction) | |||
'''<sup></sup>'''''Guyon's Canal Syndrome'' symptoms include:<ref name="WebMD" /> | |||
#Muscular atrophy - Primarily the hypothenar muscles and interossei with muscle-sparing of the thenar group: | |||
''' | |||
'''<sup></sup>''' | |||
#Muscular atrophy - Primarily the hypothenar muscles and interossei with muscle sparing of the thenar group: | |||
#*weakened finger abduction and adduction (interossei) | #*weakened finger abduction and adduction (interossei) | ||
#*weakened thumb adductor (adductor pollicis) | #*weakened thumb adductor (adductor pollicis) | ||
#Sensory loss and pain | #Sensory loss and pain which may involve the palmar surface of the fifth digit and medial aspect of the fourth digit & the dorsum of medial aspect of the fourth finger and the dorsum of the fifth finger don’t have sensory loss. | ||
#Ulnar Claw may present (sign of Benediction) | |||
#Ulnar Claw may present (sign of Benediction) | |||
== Physical Therapy Examination == | |||
Guyon's Canal Syndrome: It is important t rule out other diagnoses which could refer to the elbow. Physical examination includes | |||
*ROM of the wrist and digits | *ROM of the wrist and digits | ||
*MMT of ulnar nerve muscles innervated distal to Guyon’s Canal | *[[Muscle Strength Testing|MMT]] of ulnar nerve muscles innervated distal to Guyon’s Canal | ||
*Sensory exam of the ulnar nerve cutaneous | *[[Sensation|Sensory exam]] of the ulnar nerve cutaneous distribution distal to Guyon’s Canal | ||
*Muscle wasting of intrinsic hand muscles | *Muscle wasting of intrinsic hand muscles | ||
Special Tests | '''Special Tests''' | ||
*Card test | *Card test | ||
*[[Froment’s Sign|Froment’s Sign]] | *[[Froment’s Sign|Froment’s Sign]] | ||
* | *[[Tinel’s Test|Tinnel's sign]] at Guyon’s canal | ||
*Ulnar neurodynamic test (ULTT3) may increase the patient’s symptoms | *Ulnar [[Neurodynamic Assessment|neurodynamic test]] (ULTT3) may increase the patient’s symptoms | ||
'''Diagnostic Tests for Ulnar Nerve Entrapment''' | |||
'''Diagnostic Tests for Ulnar Nerve | |||
*Imaging for OA, bone spurs, or bone cysts | *Imaging for OA, bone spurs, or bone cysts | ||
*Nerve Conduction Studies ( | *Nerve Conduction Studies (EMG) | ||
*If fracture/dislocation is suspected, plain film x-ray<br> | |||
*If fracture/dislocation is suspected, | |||
== Outcome Measures | == Outcome Measures == | ||
*[[DASH Outcome Measure|Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand]] - A 30 item questionnaire, targeted towards measuring the physical function and symptoms of patient | *[[DASH Outcome Measure|Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand]] - A 30 item questionnaire, targeted towards measuring the physical function and symptoms of the patient | ||
*Patient Specific Functional Scale (PSFS) - A questionnaire that is utilized to quantify activity limitations and measure functional outcomes of patients | *[[Patient Specific Functional Scale|Patient-Specific Functional Scale]] (PSFS) - A questionnaire that is utilized to quantify activity limitations and measure functional outcomes of patients | ||
*[[DASH Outcome Measure|DASH Outcome Measure]] - A questionnaire that measures a patient’s functional ability and severity of their symptoms | *[[DASH Outcome Measure|DASH Outcome Measure]] - A questionnaire that measures a patient’s functional ability and severity of their symptoms | ||
*Upper Extremity Functional Index (UEFI) - A questionnaire of 20 items regarding severity of difficulty performing activities throughout the day<br> | *[[Upper Extremity Functional Index]] (UEFI) - A questionnaire of 20 items regarding the severity of difficulty performing activities throughout the day<br> | ||
== Management / Interventions | == Physical Therapy Management / Interventions == | ||
*The Impairment-based approach can be used to address deficits in strength, ROM, and the attainment of functional goals | |||
*The source of the pain should be treated in conjunction with the impairments. | |||
*Following treatment, reassess the functional task that produced pain to determine effective treatment outcome | |||
*Administer a home exercise program that aims to treat the same impairments and function tasks | |||
<br>In a study conducted by Svernlov and colleagues, three treatments were compared for individuals with cubital tunnel syndrome.<ref name="Svernlov et al">Svernlov B, Larsson M, Rehn K, Adolfsson L. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6589621/ Conservative treatment of the cubital tunnel syndrome]. J Hand Surg Eur. 2009;34(2):201-207.</ref> All three groups had positive outcomes, with the control group improving just as much as the intervention groups.<ref name="Svernlov et al" /> | |||
#Splint group protocol | #'''Splint group protocol'''<sup> </sup> - An elbow brace was worn every night for a period of three months and the brace prevented elbow flexion beyond 45 degrees.<ref name="Svernlov et al" /> | ||
#'''Nerve gliding protoco'''l<sup> </sup> - Patients were instructed to complete nerve gliding exercises two times per day in six different positions and hold them for 30 seconds for three repetitions with a 1-minute break in between each repetition. Patients were instructed to complete these exercises until the next visit, which occurred 1-2 weeks later. The frequency of the exercises were increased to three times per day, holding the exercise for one minute each day for a period of three months if there were no symptoms at the next visit.<ref name="Svernlov et al" /> | |||
#'''Control group protocol'''<sup> </sup>- The control group only received education<ref name="Svernlov et al" /> | |||
According to a case report by Coppieters and colleagues, joint mobilizations of the elbow, thoracic spine and rib thrust manipulations, and ulnar nerve sliding/tension techniques for six sessions were associated with improvements of decreased elbow pain and considerable improvement scores on a neck questionnaire up to a ten month follow-up.<ref name="Coppieters et al">Coppieters MW, Bartholomeeusen KE, Stappaerts KH. Incorporating nerve0gliding techniques in the conservative management of cubital tunnel. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2004;27(9):560-568</ref> The patient reported a history of symptoms for two months prior to starting physical therapy.<ref name="Coppieters et al" /><sup> </sup>The protocol used in this study can be seen by accessing the link in the case study section below. | According to a case report by Coppieters and colleagues, joint mobilizations of the elbow, thoracic spine and rib thrust manipulations, and ulnar nerve sliding/tension techniques for six sessions were associated with improvements of decreased elbow pain and considerable improvement scores on a neck questionnaire up to a ten month follow-up.<ref name="Coppieters et al">Coppieters MW, Bartholomeeusen KE, Stappaerts KH. Incorporating nerve0gliding techniques in the conservative management of cubital tunnel. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2004;27(9):560-568</ref> The patient reported a history of symptoms for two months prior to starting physical therapy.<ref name="Coppieters et al" /><sup> </sup>The protocol used in this study can be seen by accessing the link in the case study section below. | ||
{{#ev:youtube|0zC3VvYg1sM|300}} | {{#ev:youtube|0zC3VvYg1sM|300}}<ref> Physical Therapy Nation. Clinician Education: How To Teach A Patient Upper Limb Nerve Gliding (Ulnar Nerve). Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0zC3VvYg1sM [last accessed 24/10/2020]</ref> | ||
Guyon’s Canal Syndrome and other ulnar nerve sites: | Guyon’s Canal Syndrome and other ulnar nerve sites: | ||
== Differential Diagnosis == | |||
== Differential Diagnosis | |||
The cervical spine and shoulder regions should be examined to rule out diagnoses that can refer to the elbow.<br>There are numerous differential diagnoses for ulnar nerve entrapment such as: | The cervical spine and shoulder regions should be examined to rule out diagnoses that can refer to the elbow.<br>There are numerous differential diagnoses for ulnar nerve entrapment such as:<ref name="WebMD" /> | ||
*Elbow fracture/dislocation | *Elbow fracture/dislocation | ||
*Cervical Radiculopathy | *[[Cervical Radiculopathy]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS)|Thoracic Outlet Syndrome]] | ||
*[[Peripheral Arterial Disease|Peripheral Vascular Disease]] | *[[Peripheral Arterial Disease|Peripheral Vascular Disease]] | ||
*Ulnar collateral ligament injury | *[[Medial Collateral Ligament of the Elbow|Ulnar collateral ligament]] injury | ||
*[[Rheumatoid Arthritis|Rheumatoid Arthritis]] | *[[Rheumatoid Arthritis|Rheumatoid Arthritis]] | ||
*Medial Epicondylalgia | *Medial Epicondylalgia | ||
| Line 217: | Line 107: | ||
*Peripheral polyneuropathy<br> | *Peripheral polyneuropathy<br> | ||
== | == Highlights for Physical Therapy == | ||
*Special tests that are utilized in the diagnosis of ulnar nerve entrapment have extremely high sensitivity of .98 and above and therefore are extremely useful in ruling in diagnosis. | *Special tests that are utilized in the diagnosis of ulnar nerve entrapment have extremely high sensitivity of .98 and above and therefore are extremely useful in ruling in diagnosis.<ref name="Spinner">Spinner RJ. Outcomes for Peripheral Nerve Entrapment. Clin Neurosurg. 2006; 53: 285-294.</ref> | ||
*Conservative treatment is effective about 50% of the time, while surgical intervention is effective 60-95% of the time | *Conservative treatment is effective about 50% of the time<ref name="Svernlov et al" />, while surgical intervention is effective 60-95% of the time | ||
*Conservative management has been proven effective when incorporating splinting and manual therapy including neural glides and joint mobilizations | *Conservative management has been proven effective when incorporating splinting and manual therapy including neural glides and joint mobilizations; though a recent study has highlighted more studies are needed to know when to treat conservatively or to opt for surgery.<ref>Caliandro P, La Torre G, Padua R, Giannini F, Padua L.Treatment for ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;11:CD006839.</ref> | ||
*Patient’s seeking conservative treatment earlier rather than waiting have a thirty percent greater chance of avoiding surgery<br> | *Patient’s seeking conservative treatment earlier rather than waiting have a thirty percent greater chance of avoiding surgery<br> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
<br> | |||
[[Category:Hand]] | |||
[[Category:Elbow]] | |||
[[Category:Nerves]] | |||
[[Category:Neuropathy]] | |||
[[Category:Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Elbow - Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Hand - Conditions]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:27, 12 April 2021
Original Editor Trevor Bradshaw ; and Robert Bardinas; as part of the Temple University Evidence-Based Practice Project
Top Contributors - Vanessa Rhule, Trevor Bradshaw, Nikhil Benhur Abburi, Admin, Robert Bardinas, Kim Jackson, Aimee Tow, Rachael Lowe, WikiSysop, Noah Lahjouji, Simisola Ajeyalemi, Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka, Scott A Burns, Laura Ritchie, Fasuba Ayobami, Lauren Kwant, Amanda Ager and Anas Mohamed
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs when the ulnar nerve is compressed. This typically occurs at two main sites: the elbow and the wrist[1]. Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow is usually at the cubital tunnel (Cubital Tunnel Syndrome). Ulnar nerve neuropathy at the elbow is the second most common entrapment neuropathy (the first most common is the median nerve at the wrist).[2] Ulnar nerve neuropathy less commonly occurs at Guyon’s canal in the wrist (Guyon’s canal syndrome/ulnar tunnel syndrome).
Causes[edit | edit source]
Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow (Cubital Tunnel Syndrome) and wrist (Guyon's Canal Syndrome) occur due to repetitive compression, from leaning on the elbows or wrists (cyclist's palsy) and prolonged elbow flexion. It can also occur from trauma, swelling, fractures, and vascular and bony pathologies/abnormalities.
Guyon’s canal syndrome occurs when the ulnar nerve becomes entrapped between the hook of the hamate and the transverse carpal ligament. Guyon’s canal syndrome is considered an overuse injury which is commonly caused by direct pressure on a handlebar (i.e. bicycle handlebar, weight lifting, construction equipment) and therefore, is sometimes referred to as “handlebar palsy”. It can also result from excessive gripping, twisting, or repeated wrist and hand motions. Also, entrapment may develop if the hand is flexed and ulnar deviated for prolonged periods of time.
The incidence of trauma leading to ulnar nerve compression is unknown; however ulnar neuropathy has been documented after distal humeral fractures and in up to 10% of elbow dislocations, and may also develop from any complex elbow or wrist trauma.[3]
Clinical Presentation[4][5][6][7][8][9][edit | edit source]
Symptoms of ulnar nerve entrapment include tingling in fingers 4 and 5, weak grip strength, pain and sensitivity on the ulnar side of the forearm, wrist and hand, muscle atrophy, clawing of digits 4 and 5 (sign of benediction).
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome can present in different grades of severity:[6]
Grade I: Mild symptoms including:
- Intermittent paresthesia
- Minor hypoesthesia of the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the fifth and medial aspect of fourth digits
- No motor changes
Grade II: Moderate and persistent symptoms including:
- Paresthesia
- Hypoesthesia of the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the fifth and medial aspect of fourth digits
- Mild weakness of ulnar innervated muscles
- Early signs of muscular atrophy
Grade III: Severe symptoms including:
- Paresthesia
- Obvious loss of sensation of the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the fifth and medial aspect of fourth digits.
- Significant functional and motor impairment
- Muscle atrophy of the hand intrinsics
- Possible digital clawing of fourth and fifth digits (Sign of Benediction)
Guyon's Canal Syndrome symptoms include:[5]
- Muscular atrophy - Primarily the hypothenar muscles and interossei with muscle-sparing of the thenar group:
- weakened finger abduction and adduction (interossei)
- weakened thumb adductor (adductor pollicis)
- Sensory loss and pain which may involve the palmar surface of the fifth digit and medial aspect of the fourth digit & the dorsum of medial aspect of the fourth finger and the dorsum of the fifth finger don’t have sensory loss.
- Ulnar Claw may present (sign of Benediction)
Physical Therapy Examination[edit | edit source]
Guyon's Canal Syndrome: It is important t rule out other diagnoses which could refer to the elbow. Physical examination includes
- ROM of the wrist and digits
- MMT of ulnar nerve muscles innervated distal to Guyon’s Canal
- Sensory exam of the ulnar nerve cutaneous distribution distal to Guyon’s Canal
- Muscle wasting of intrinsic hand muscles
Special Tests
- Card test
- Froment’s Sign
- Tinnel's sign at Guyon’s canal
- Ulnar neurodynamic test (ULTT3) may increase the patient’s symptoms
Diagnostic Tests for Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
- Imaging for OA, bone spurs, or bone cysts
- Nerve Conduction Studies (EMG)
- If fracture/dislocation is suspected, plain film x-ray
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
- Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand - A 30 item questionnaire, targeted towards measuring the physical function and symptoms of the patient
- Patient-Specific Functional Scale (PSFS) - A questionnaire that is utilized to quantify activity limitations and measure functional outcomes of patients
- DASH Outcome Measure - A questionnaire that measures a patient’s functional ability and severity of their symptoms
- Upper Extremity Functional Index (UEFI) - A questionnaire of 20 items regarding the severity of difficulty performing activities throughout the day
Physical Therapy Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
- The Impairment-based approach can be used to address deficits in strength, ROM, and the attainment of functional goals
- The source of the pain should be treated in conjunction with the impairments.
- Following treatment, reassess the functional task that produced pain to determine effective treatment outcome
- Administer a home exercise program that aims to treat the same impairments and function tasks
In a study conducted by Svernlov and colleagues, three treatments were compared for individuals with cubital tunnel syndrome.[3] All three groups had positive outcomes, with the control group improving just as much as the intervention groups.[3]
- Splint group protocol - An elbow brace was worn every night for a period of three months and the brace prevented elbow flexion beyond 45 degrees.[3]
- Nerve gliding protocol - Patients were instructed to complete nerve gliding exercises two times per day in six different positions and hold them for 30 seconds for three repetitions with a 1-minute break in between each repetition. Patients were instructed to complete these exercises until the next visit, which occurred 1-2 weeks later. The frequency of the exercises were increased to three times per day, holding the exercise for one minute each day for a period of three months if there were no symptoms at the next visit.[3]
- Control group protocol - The control group only received education[3]
According to a case report by Coppieters and colleagues, joint mobilizations of the elbow, thoracic spine and rib thrust manipulations, and ulnar nerve sliding/tension techniques for six sessions were associated with improvements of decreased elbow pain and considerable improvement scores on a neck questionnaire up to a ten month follow-up.[10] The patient reported a history of symptoms for two months prior to starting physical therapy.[10] The protocol used in this study can be seen by accessing the link in the case study section below.
Guyon’s Canal Syndrome and other ulnar nerve sites:
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The cervical spine and shoulder regions should be examined to rule out diagnoses that can refer to the elbow.
There are numerous differential diagnoses for ulnar nerve entrapment such as:[5]
- Elbow fracture/dislocation
- Cervical Radiculopathy
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Ulnar collateral ligament injury
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Medial Epicondylalgia
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Alcohol (Ethanol) Related Neuropathy
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Pancoast Tumor
- Primary Bone Tumors
- Peripheral polyneuropathy
Highlights for Physical Therapy[edit | edit source]
- Special tests that are utilized in the diagnosis of ulnar nerve entrapment have extremely high sensitivity of .98 and above and therefore are extremely useful in ruling in diagnosis.[12]
- Conservative treatment is effective about 50% of the time[3], while surgical intervention is effective 60-95% of the time
- Conservative management has been proven effective when incorporating splinting and manual therapy including neural glides and joint mobilizations; though a recent study has highlighted more studies are needed to know when to treat conservatively or to opt for surgery.[13]
- Patient’s seeking conservative treatment earlier rather than waiting have a thirty percent greater chance of avoiding surgery
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Jan Michael C. Lleva, Ke-Vin Chang.Ulnar Neuropathy. Available from: Ahttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534226/ (Accessed 30th March, 2019)
- ↑ Lauretti L, D'Alessandris QG, De Simone C, Sop FY, Remore LM, Izzo A, et al. Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow. A surgical series and a systematic review of the literature. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience. 2017;46:99-108.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Svernlov B, Larsson M, Rehn K, Adolfsson L. Conservative treatment of the cubital tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Eur. 2009;34(2):201-207.
- ↑ Neuropathy of Ulnar Nerve (Entrapment). MD Guidelines. http://www.mdguidelines.com/neuropathy-of-ulnar-nerve-entrapment/differential-diagnosis. Accessed March 15, 2011.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Ulnar Neuropathy. Emedicine from WebMD. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1141515-overview. Updated June 10, 2010. Accessed March 15, 2011.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Palmer BA, Hughes TB. Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. J Hand Surg. 2010: 35 (1): 153-163.
- ↑ Nerve Entrapment Syndromes. Emedicine from WebMD. www.emedicine.medscape.com/article/249784-overview Updated July 31, 2009. Accessed March 15, 2011.
- ↑ Ulnar Nerve Entrapment. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=a00069. Updated October 2007. Accessed March 15, 2011.
- ↑ Shin R, Ring D. The Ulnar Nerve in Elbow Trauma. J. Bone Jt. Surg. (Am.). 2007: 89: 1108-1116.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Coppieters MW, Bartholomeeusen KE, Stappaerts KH. Incorporating nerve0gliding techniques in the conservative management of cubital tunnel. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2004;27(9):560-568
- ↑ Physical Therapy Nation. Clinician Education: How To Teach A Patient Upper Limb Nerve Gliding (Ulnar Nerve). Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0zC3VvYg1sM [last accessed 24/10/2020]
- ↑ Spinner RJ. Outcomes for Peripheral Nerve Entrapment. Clin Neurosurg. 2006; 53: 285-294.
- ↑ Caliandro P, La Torre G, Padua R, Giannini F, Padua L.Treatment for ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;11:CD006839.