Deltoid: Difference between revisions
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Shoulder]] [[Category:Muscles]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Shoulder]] [[Category:Muscles]] [[Category:Shoulder_Anatomy]] | ||
Revision as of 18:30, 25 May 2015
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors - Lucinda hampton, Sai Kripa, Wendy Walker, Naomi O'Reilly, Joao Costa, Chrysolite Jyothi Kommu, Kim Jackson, Andeela Hafeez, Vidya Acharya, WikiSysop, Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka, Wanda van Niekerk, Aminat Abolade, Admin, Evan Thomas and George Prudden
Description[edit | edit source]
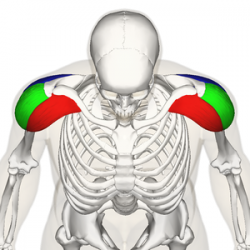
The Deltoid muscle is a large triangular shaped muscle which lies over the glenohumeral joint and which gives the shoulder its rounded contour. It is named after the Greek letter delta, which is shaped like an equilateral triangle. It comprises 3 distinct portions each of which produces a different movement of the glenohumeral joint, commonly named the anterior, mid (or lateral) and posterior heads.
Origin[edit | edit source]
Anterior fibres/head[edit | edit source]
Lateral third, anterior surface of the clavicle (close to the lateral fibres of pectoralis major).
Mid/lateral head[edit | edit source]
Acromion process, superior surface.
Posterior head[edit | edit source]
Spine of the scapula, posterior border.
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Fibres from all heads converge to insert into the deltoid tuberosity on the humerus.
The deltoid fascia is continuous with the brachial fascia and connects to the medial and lateral intermuscular septa[1].
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Axillary Nerve, C5 & 6, posterior cord of the brachial plexus.
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Deltoid receives its blood supply from the posterior circumflex humeral artery.
Action[edit | edit source]
All heads of deltoid work together to produce abduction of the shoulder joint.
In addition, the anterior fibres contribute to shoulder horizontal flexion, and internal rotation; the posterior fibres to horizontal extension, as well as external rotation.
Function[edit | edit source]
An important function of deltoid is the prevention of subluxation or even dislocation of the head of the humerus particularly when carrying a load.
Deltoid is the prime mover of shoulder abduction.
Resources[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ Rispoli, Damian M.; Athwal, George S.; Sperling, John W.; Cofield, Robert H. (2009). "The anatomy of the deltoid insertion". J Shoulder Elbow Surg 18: 386–390