Spinalis Thoracis: Difference between revisions
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
=== Nerve === | === Nerve === | ||
Lateral branch of the posterior rami of spinal nerves | Lateral branch of the posterior rami of spinal nerves<ref name=":1" /> | ||
=== Artery === | === Artery === | ||
Posterior branch of posterior intercostal artery, deep cervical artery and muscular branches of vertebral artery. | Posterior branch of posterior intercostal artery, deep cervical artery and muscular branches of vertebral artery.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Spinalis thoracis works with the other spinalis and the | Spinalis thoracis works with the other spinalis and the other erector spinae muscles: [[Longissimus Thoracis|longissimus]] and [[Iliocostalis Thoracis|iliocostalis]] to produce thoracic extension as well as lateral flexion and rotation of the spine<ref name=":0" />. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 15:50, 30 November 2021
Original Editor - Abbey Wright
Top Contributors - Abbey Wright and Lucinda hampton
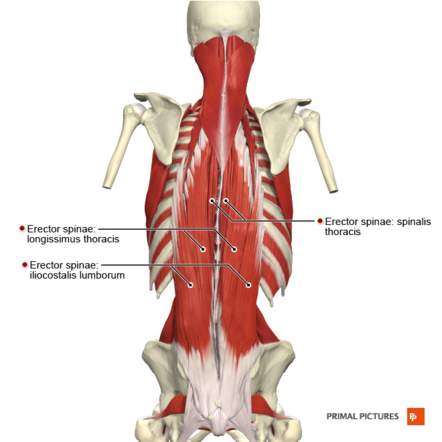
Description[edit | edit source]
Spinalis Thoracis belongs to the medial column of the erector spinae (Sacrospinalis) group of muscles.
It is the most prominent and well-organised portion of the spinalis muscle with spinalis capitis and spinalis cervicis superiorly.[1] With its muscle fibres running superiorly.
Origin[edit | edit source]
Spinous processes of T11-L2.[1][2]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Spinous processes of T2-T8.[2]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Lateral branch of the posterior rami of spinal nerves[2]
Artery[edit | edit source]
Posterior branch of posterior intercostal artery, deep cervical artery and muscular branches of vertebral artery.[2]
Function[edit | edit source]
Spinalis thoracis works with the other spinalis and the other erector spinae muscles: longissimus and iliocostalis to produce thoracic extension as well as lateral flexion and rotation of the spine[1].