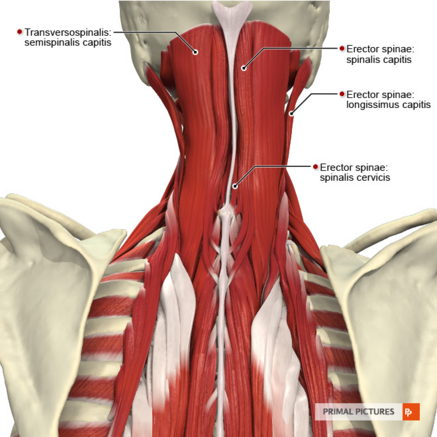
Spinalis Cervicis
Original Editor Oyemi Sillo
Lead Editors - Abbey Wright, Oyemi Sillo, Kim Jackson, 127.0.0.1, WikiSysop and Lucinda hampton
Description[edit | edit source]
The Spinalis muscle group are part of the the erector spinae (ES) group (the intermediate layer of the intrinsic back muscles). Spinalis Cervicis is the cervical portion of the spinalis muscle with spinalis capitis superiorly and spinalis thoracis inferiorly[1].
The Spinalis Cervicis is variably present.[1]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin: Variable origin on the spinous processes of the axis and sometimes the 3rd and 4th cervical spinous process.[2] [1]
Insertion: Lower part of ligamentum nuchae (C4 to C6) and spinous process of C7 to T2.[3][2]
Nerve Supply: Posterior rami of cervical and thoracic spinal nerves (C4 to T1). [2]
Blood Supply: Dorsal branches of the posterior intercostal arteries from the thoracic aorta.
Action[edit | edit source]
Spinalis works synergistically with the other members of the erector spinae group.
Specifically
- Bilaterally extend the cervical spine.
- Unilaterally laterally flex and rotate the cervical spine to ipsilateral (same) side.[2]
Function[edit | edit source]
Spinalis cervicis works with the other erector spinae muscles to produce extension, lateral flexion and rotation at the cervical spine level.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Radiopedia Erector Spinae Available:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/erector-spinae-group?lang=us (accessed 4.2.2022)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Spinalis Cervicis : Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics [Internet]. Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics. 2021 [cited 30 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.wheelessonline.com/bones/spine/spinalis-cervicis/
- ↑ spinalis muscle | anatomy [Internet]. Encyclopedia Britannica. 2021 [cited 30 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.britannica.com/science/spinalis-muscle