Spinalis Capitis: Difference between revisions
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) (content added) |
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
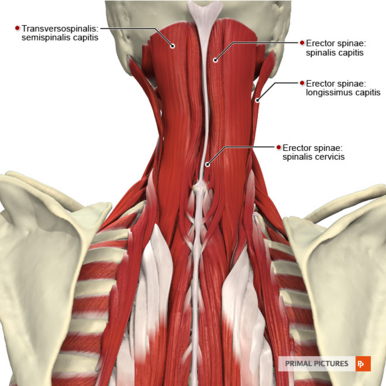
Spinalis Capitis (or Spinalis Colli) belongs to the medial column of the [[Erector Spinae|erector spinae]] (Sacrospinalis) group of muscles.<ref name="gray">Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.</ref> It is the most superior of the spinalis group of muscles with [[Spinalis Cervicis|spinalis cervicis]] and thoracis lying inferiorly in the cervical and thoracic spine. | Spinalis Capitis (or Spinalis Colli) belongs to the medial column of the [[Erector Spinae|erector spinae]] (Sacrospinalis) group of muscles.<ref name="gray">Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.</ref> It is the most superior of the spinalis group of muscles with [[Spinalis Cervicis|spinalis cervicis]] and thoracis lying inferiorly in the cervical and thoracic spine. | ||
The spinalis muscles are a group of flat fascicles of varying lengths.<ref name=":0">Spinalis muscle [Internet]. Kenhub. 2021 [cited 30 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/spinalis-muscle</ref> | The spinalis muscles are a group of flat fascicles of varying lengths.<ref name=":0">Spinalis muscle [Internet]. Kenhub. 2021 [cited 30 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/spinalis-muscle</ref> | ||
It is known as spinalis capitis due to its attachments to the head (cranium).<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 30 November 2021
Original Editor Oyemi Sillo
Lead Editors - Abbey Wright, Lucinda hampton, Oyemi Sillo, Kim Jackson and WikiSysop
Description[edit | edit source]
Spinalis Capitis (or Spinalis Colli) belongs to the medial column of the erector spinae (Sacrospinalis) group of muscles.[1] It is the most superior of the spinalis group of muscles with spinalis cervicis and thoracis lying inferiorly in the cervical and thoracic spine.
The spinalis muscles are a group of flat fascicles of varying lengths.[2]
It is known as spinalis capitis due to its attachments to the head (cranium).[2]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Spinous process of C7 -T1.[2]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Near the midline between superior and inferior nuchal lines of occipital bone.
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Dorsal rami of cervical spinal nerves (C1 to C3).
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
The muscle receives a blood supply from muscular branches of the vertebral artery via the subclavian and also from muscular branches of the occipital artery via the external carotid artery.
Action[edit | edit source]
Extension of the vertebral column and head.
Function[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Spinalis muscle [Internet]. Kenhub. 2021 [cited 30 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/spinalis-muscle