Shower and Toilet Chairs: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[Assistive Technology: Self Care and Environment Products" to "[[Technological Aids for Self-Care and Environmental Adaptations") |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Robin Tacchetti|Robin Tacchetti]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Robin Tacchetti|Robin Tacchetti]] based on the course by [https://members.physio-pedia.com/course_tutor/dana-mather/ Dana Mather]<br> | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Mobility is | Mobility is an essential component of many activities of daily living (ADL). Bathroom tasks such as toileting and showering can become difficult when mobility is limited. Research shows that older adults ranked showering as the most difficult ADL, with toileting the third most difficult.<ref name=":0">De-Rosende-Celeiro I, Torres G, Seoane-Bouzas M, Ávila A. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6453482/ Exploring the use of assistive products to promote functional independence in self-care activities in the bathroom]. Plos one. 2019 Apr 8;14(4):e0215002.</ref> People with disabilities and health care practitioners also report that independent toileting is essential to avoid feelings associated with a loss of self-esteem.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
Assistive technology bathroom adaptations can help individuals who experience difficulty with toileting and showering. Examples of assistive technology for personal hygiene and toileting include grab bars, nonslip mats, bath transfer benches and raised toilet seats.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1">Guay M, Latulippe K, Auger C, Giroux D, Séguin-Tremblay N, Gauthier J, Genest C, Morales E, Vincent C. [https://www.jmir.org/2020/8/e16175/ Self-selection of bathroom-assistive technology: development of an electronic decision support system] (Hygiene 2.0). Journal of medical internet research. 2020 Aug 10;22(8):e16175.</ref> Using assistive devices can increase independence, physical stability, confidence and safety.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2">Meng H, Peterson LJ, Feng L, Dobbs D, Hyer K. [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2333721419885291 The Use of Mobility Devices and Personal Assistance: A Joint Modeling Approach]. Gerontology and Geriatric Medicine. 2019 Oct;5:2333721419885291.</ref> In addition, assistive technology can ease the load on caregivers and health care workers.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
* | === Shower and Toilet Chairs === | ||
* | Many individuals across the lifespan, from children to adults and older adults, may benefit from a shower or toilet chair, including those with the following:<ref name=":3">World Health Organization. Training in Assistive Products (TAP). 2020. Available from https://www.gate-tap.org/all-modules/</ref> | ||
* | |||
* | * Difficulty standing or cannot stand | ||
* Gets dizzy or tired during shower time | |||
* At risk for falls or afraid of falling | |||
* Difficulty sitting down and standing up and/or squatting | |||
=== Shower Chairs === | === Shower Chairs === | ||
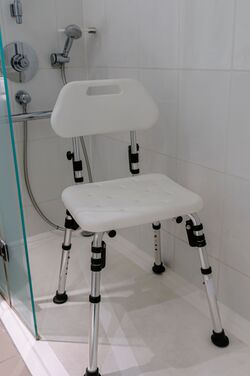
Shower stools and chairs are useful for individuals who need to sit down while washing | [[File:Showerchair.jpg|thumb|376x376px|Shower chair|alt=]] | ||
Shower stools and chairs are useful for individuals who need to sit down while washing because of limited balance, strength or mobility. A shower stool or chair should:<ref name=":3" /> | |||
* carry the weight of the user | * Be able to carry the weight of the user | ||
* brakes if they have wheels | * Have brakes if they have wheels and rubber stoppers if they have legs | ||
* rust resistant | * Be rust resistant | ||
* water resistant | * Be water resistant | ||
* durable and strong | * Be durable and strong | ||
* smooth finish | * Have a smooth finish | ||
Optional features include:<ref name=":3" /> | |||
* | * Padding on the seat | ||
* | * Armrests and backrests | ||
* | * Castor wheels with brakes | ||
=== Toilet Chair === | === Toilet Chair === | ||
A raised toilet chair is helpful for individuals who have difficulty squatting or bending. | A raised toilet chair is helpful for individuals who have difficulty squatting or bending. They are typically placed over the existing toilet. A raised toilet chair should:<ref name=":3" /> | ||
[[File:Toilet chair.jpg|thumb| | [[File:Toilet chair.jpg|thumb|Raised toilet chair]] | ||
* carry the weight of the user | * Be able to carry the weight of the user | ||
* height adjustable legs | * Have height adjustable legs | ||
* brakes if they have wheels | * Have brakes if they have wheels and rubber stoppers if they have legs | ||
* rust resistant | * Be rust resistant | ||
* water resistant | * Be water resistant | ||
* durable and strong | * Be durable and strong | ||
* smooth finish | * Have a smooth finish | ||
Optional features include:<ref name=":3" /> | |||
* | * Padding on seat and armrests | ||
* | * Height adjustable armrests | ||
* | * Height adjustable and swing away footrests | ||
* | * Backrest with padding | ||
* | * A removable bucket | ||
* | * Castor wheels that swivel or turn | ||
== Pressure Ulcers == | |||
== Pressure | Before fitting someone with a shower or toilet chair, ensure they do not currently have or are at risk for a [[Pressure Ulcers|pressure ulcer.]] If an individual has a current wound that would contact the chair, they should avoid using this assistive device until the wound is fully healed. Individuals at risk for a pressure ulcer include: | ||
Before fitting someone with a shower or toilet chair, ensure they do not currently have or are at risk for a [[Pressure Ulcers|pressure | |||
* | * Someone who has had a previous wound | ||
* | * Someone with decreased sensation in their thighs, back or buttocks | ||
* | * Someone who cannot easily shift their weight | ||
* | * Frail or thin individuals | ||
At risk individuals should use a chair with a padded surface.<ref name=":3" /> | At risk individuals should use a chair with a padded surface.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
| Line 58: | Line 60: | ||
* [https://www.myotspot.com/adaptive-equipment/ My OT Spot: Our List of “Must-Know” Adaptive Equipment for OT Practitioners] | * [https://www.myotspot.com/adaptive-equipment/ My OT Spot: Our List of “Must-Know” Adaptive Equipment for OT Practitioners] | ||
* [[Dressing Aids]] | * [[Dressing Aids]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Technological Aids for Self-Care and Environmental Adaptations|Self-Care and Assistive Products]] | ||
=== References === | === References === | ||
Latest revision as of 14:27, 29 February 2024
Top Contributors - Robin Tacchetti, Jess Bell and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Mobility is an essential component of many activities of daily living (ADL). Bathroom tasks such as toileting and showering can become difficult when mobility is limited. Research shows that older adults ranked showering as the most difficult ADL, with toileting the third most difficult.[1] People with disabilities and health care practitioners also report that independent toileting is essential to avoid feelings associated with a loss of self-esteem.[1]
Assistive technology bathroom adaptations can help individuals who experience difficulty with toileting and showering. Examples of assistive technology for personal hygiene and toileting include grab bars, nonslip mats, bath transfer benches and raised toilet seats.[1][2] Using assistive devices can increase independence, physical stability, confidence and safety.[1][2][3] In addition, assistive technology can ease the load on caregivers and health care workers.[3]
Shower and Toilet Chairs[edit | edit source]
Many individuals across the lifespan, from children to adults and older adults, may benefit from a shower or toilet chair, including those with the following:[4]
- Difficulty standing or cannot stand
- Gets dizzy or tired during shower time
- At risk for falls or afraid of falling
- Difficulty sitting down and standing up and/or squatting
Shower Chairs[edit | edit source]
Shower stools and chairs are useful for individuals who need to sit down while washing because of limited balance, strength or mobility. A shower stool or chair should:[4]
- Be able to carry the weight of the user
- Have brakes if they have wheels and rubber stoppers if they have legs
- Be rust resistant
- Be water resistant
- Be durable and strong
- Have a smooth finish
Optional features include:[4]
- Padding on the seat
- Armrests and backrests
- Castor wheels with brakes
Toilet Chair[edit | edit source]
A raised toilet chair is helpful for individuals who have difficulty squatting or bending. They are typically placed over the existing toilet. A raised toilet chair should:[4]
- Be able to carry the weight of the user
- Have height adjustable legs
- Have brakes if they have wheels and rubber stoppers if they have legs
- Be rust resistant
- Be water resistant
- Be durable and strong
- Have a smooth finish
Optional features include:[4]
- Padding on seat and armrests
- Height adjustable armrests
- Height adjustable and swing away footrests
- Backrest with padding
- A removable bucket
- Castor wheels that swivel or turn
Pressure Ulcers[edit | edit source]
Before fitting someone with a shower or toilet chair, ensure they do not currently have or are at risk for a pressure ulcer. If an individual has a current wound that would contact the chair, they should avoid using this assistive device until the wound is fully healed. Individuals at risk for a pressure ulcer include:
- Someone who has had a previous wound
- Someone with decreased sensation in their thighs, back or buttocks
- Someone who cannot easily shift their weight
- Frail or thin individuals
At risk individuals should use a chair with a padded surface.[4]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- Shirley Ryan Ability Lab: 10 Tips from an OT to Make Your Bathroom Safer for Aging in Place
- My OT Spot: Our List of “Must-Know” Adaptive Equipment for OT Practitioners
- Dressing Aids
- Self-Care and Assistive Products
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 De-Rosende-Celeiro I, Torres G, Seoane-Bouzas M, Ávila A. Exploring the use of assistive products to promote functional independence in self-care activities in the bathroom. Plos one. 2019 Apr 8;14(4):e0215002.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Guay M, Latulippe K, Auger C, Giroux D, Séguin-Tremblay N, Gauthier J, Genest C, Morales E, Vincent C. Self-selection of bathroom-assistive technology: development of an electronic decision support system (Hygiene 2.0). Journal of medical internet research. 2020 Aug 10;22(8):e16175.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Meng H, Peterson LJ, Feng L, Dobbs D, Hyer K. The Use of Mobility Devices and Personal Assistance: A Joint Modeling Approach. Gerontology and Geriatric Medicine. 2019 Oct;5:2333721419885291.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 World Health Organization. Training in Assistive Products (TAP). 2020. Available from https://www.gate-tap.org/all-modules/