Pulmonary Bullae: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
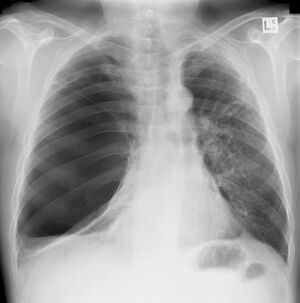
[[File:Giant-pulmonary-bulla.jpg|thumb|Large bulla R lung, absence of lung markings.]] | [[File:Giant-pulmonary-bulla.jpg|thumb|Large bulla R lung, absence of lung markings.]] | ||
A pulmonary bulla is an air-filled space, greater than 1 cm in diameter, that develops within the lung due to [[Emphysema|emphysematous]] damage of the [[Lung Anatomy|lung]] | A pulmonary bulla is an air-filled space, greater than 1 cm in diameter, that develops within the lung due to [[Emphysema|emphysematous]] damage of the [[Lung Anatomy|lung]]. Pulmonary emphysema itself causes destruction of the distal lung design with lasting expansion of the [[Alveoli|alveolar]] space distal to the terminal bronchiole. Significantly 80% percent of patients presenting with bullae suffer from emphysema, a subset of [[COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)|chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).]] | ||
== Pathology == | == Pathology == | ||
The development of lung bullae is heterogenis. Most commonly they are COPD-related emphysematous bullae, whilst ventilator-associated lung bullae are a rarity. | The development of lung bullae is heterogenis. Most commonly they are COPD-related emphysematous bullae, whilst [[Ventilation and Weaning|ventilator]]-associated lung bullae are a rarity. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Management options are manifold, for example | Management options are manifold, for example; simply treating the underlying disease; ventilation strategies to prevent progression of the bullous lung disease; and surgical or bronchoscopic intervention. <ref>Ruan SY, Huang CT, Chien JY, Kuo YW, Yu CJ. [https://rc.rcjournal.com/content/56/10/1614 Non-surgical management of giant lung bullae during mechanical ventilation]. Respiratory care. 2011 Oct 1;56(10):1614-6.Available:https://rc.rcjournal.com/content/56/10/1614 (accessed 28.4.2023)</ref> | ||
== Physiotherapy == | == Physiotherapy == | ||
Revision as of 06:04, 28 April 2023
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton
Introduction[edit | edit source]
A pulmonary bulla is an air-filled space, greater than 1 cm in diameter, that develops within the lung due to emphysematous damage of the lung. Pulmonary emphysema itself causes destruction of the distal lung design with lasting expansion of the alveolar space distal to the terminal bronchiole. Significantly 80% percent of patients presenting with bullae suffer from emphysema, a subset of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Pathology[edit | edit source]
The development of lung bullae is heterogenis. Most commonly they are COPD-related emphysematous bullae, whilst ventilator-associated lung bullae are a rarity.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Management options are manifold, for example; simply treating the underlying disease; ventilation strategies to prevent progression of the bullous lung disease; and surgical or bronchoscopic intervention. [1]
Physiotherapy[edit | edit source]
Treatment will involves a respiratory therapists.
- Clients need to be educated on the correct use of inhaler and the use of spacers in conjunction with inhalers.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation is also an important element of treatment.
- Telehealth may have a role as a cost-effectiveness resource, however this still requires further evaluation.[2]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Ruan SY, Huang CT, Chien JY, Kuo YW, Yu CJ. Non-surgical management of giant lung bullae during mechanical ventilation. Respiratory care. 2011 Oct 1;56(10):1614-6.Available:https://rc.rcjournal.com/content/56/10/1614 (accessed 28.4.2023)
- ↑ Siddiqui NA, Mansour MK, Nookala V. Bullous emphysema. InStatPearls [Internet] 2021 Jul 26. StatPearls Publishing.Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537243/ (accessed 28.4.2023)