Musculocutaneous Nerve: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
== Movements produced == | == Movements produced == | ||
* Coracobrachialis - | * Coracobrachialis - flexes and adducts the [[Glenohumeral Joint|glenohumeral]] (GH) joint and acts to stabilise the humeral head in the [[Glenoid Labrum|glenoid]] fossa when the arm is hanging freely by side.<ref>Wikipedia. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coracobrachialis_muscle Coracobrachialis muscle.] Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coracobrachialis_muscle (last accessed 20.3.2019) </ref> | ||
* Brachialis- flexion of the [[Elbow|elbow joint]]. | * Brachialis- flexion of the [[Elbow|elbow joint]]. | ||
* Biceps Brachii- a weak abductor of GH joint when arm externally rotated | * Biceps Brachii- a weak abductor of GH joint when arm externally rotated, weak flexor of GH joint, helps to stabilise GH joint when weight carried in arm, supinator and flexor of the elbow joint.<ref>Wikipedia. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biceps Biceps Brachii]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biceps ( last accessed 20.3.2019)</ref> | ||
== Pathology/Injury<ref name=":0">Patient. [https://patient.info/doctor/musculocutaneous-nerve-lesion-c5-c6 Musculocutaneous nerve.] Available from: https://patient.info/doctor/musculocutaneous-nerve-lesion-c5-c6 (last accessed 20.3.2019)</ref><ref>Healthline. [https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/musculocutaneous-nerve#1 Musculocutaneous nerve]. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/musculocutaneous-nerve#1 (last accessed 20.3.2019)</ref> == | == Pathology/Injury<ref name=":0">Patient. [https://patient.info/doctor/musculocutaneous-nerve-lesion-c5-c6 Musculocutaneous nerve.] Available from: https://patient.info/doctor/musculocutaneous-nerve-lesion-c5-c6 (last accessed 20.3.2019)</ref><ref>Healthline. [https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/musculocutaneous-nerve#1 Musculocutaneous nerve]. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/musculocutaneous-nerve#1 (last accessed 20.3.2019)</ref> == | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
== Anatomical Variations == | == Anatomical Variations == | ||
Considerable anatomical variations present with this nerve. This may lead to clinical implications in | Considerable anatomical variations present with this nerve. This may lead to clinical implications in surgery, diagnosis.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Physiotherapy Techniques == | == Physiotherapy Techniques == | ||
=== Examination === | === Examination === | ||
Check strength of [[Biceps brachii|Biceps Brachii]], Corocobrachialis and [[Brachialis]] muscles . | * Check strength of [[Biceps brachii|Biceps Brachii]], Corocobrachialis and [[Brachialis]] muscles . | ||
Check sensation on lateral forearm | * Check sensation on lateral forearm | ||
See [[Nerve entrapment|Nerve Entrapement]] | * See [[Nerve entrapment|Nerve Entrapement]] | ||
Check for Differential Diagnoses- namely C5/6 [[Radiculopathy]]; [[Biceps Tendonitis|biceps Brachii]] distal insertion tear. | * Check for Differential Diagnoses- namely C5/6 [[Radiculopathy]]; [[Biceps Tendonitis|biceps Brachii]] distal insertion tear. | ||
=== Physiotherapeutic Techniques === | === Physiotherapeutic Techniques === | ||
Revision as of 13:19, 8 June 2020
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The Musculocutaneous nerve is a large branch of the Brachial Plexus.It is called musculocutaneous nerve as it supplies the muscles of the front of the arm and skin of lateral side of forearm.[1]
Root[edit | edit source]
Ventral rami of C5,C6,C7[1]
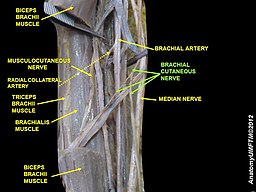
Course[edit | edit source]
The Musculocutaneous nerve is a terminal branch of the lateral cord of the Brachial Plexus. It emerges at the inferior border of Pectoralis minor muscle.It passes lateral to the axillary and upper part of brachial artery. It leaves the axilla to then pierce the Corocobrachialis near it humeral insertion to lie in the intermuscular septum between biceps brachii and brachialis muscles.Then it enters the elbow by piercing deep fascia and terminates as the Lateral Cutaneous nerve of the forearm.[1]
Branches[edit | edit source]
Motor branches are to
- Corocobrachialis
- Brachialis ( also has supply from Radial nerve)
- Biceps Brachii(both long head and short head)
Sensory branches are
- lateral cutaneous nerve to the lateral forearm (both front and back)
Articular branches
Movements produced[edit | edit source]
- Coracobrachialis - flexes and adducts the glenohumeral (GH) joint and acts to stabilise the humeral head in the glenoid fossa when the arm is hanging freely by side.[3]
- Brachialis- flexion of the elbow joint.
- Biceps Brachii- a weak abductor of GH joint when arm externally rotated, weak flexor of GH joint, helps to stabilise GH joint when weight carried in arm, supinator and flexor of the elbow joint.[4]
Pathology/Injury[5][6][edit | edit source]
Isolated injuries of the Musculocutaneous Nerve are rare. It may become injured by
- Brachial Plexus damage
- Compression injury eg weight lifting or sports involving lots of forarm flexing and supination.The biceps aponeurosis and tendon compress against the fascia of the brachialis muscle causing sensory loss below the elbow on the lateral side of the forearm.
- Dislocation of the shoulder
- Shoulder surgery
- Entrapment of the nerve at the elbow
Anatomical Variations[edit | edit source]
Considerable anatomical variations present with this nerve. This may lead to clinical implications in surgery, diagnosis.[5]
Physiotherapy Techniques[edit | edit source]
Examination[edit | edit source]
- Check strength of Biceps Brachii, Corocobrachialis and Brachialis muscles .
- Check sensation on lateral forearm
- Check for Differential Diagnoses- namely C5/6 Radiculopathy; biceps Brachii distal insertion tear.
Physiotherapeutic Techniques[edit | edit source]
see the following links
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Chaurasia BD. Human Anatomy.6th ed. Vol1,CBS Publisers and distributors Pvt Ltd.
- ↑ Osama Eqeel. Musculocutaneous nerve. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=46PTcikRi44 (last accessed 20.3.2019)
- ↑ Wikipedia. Coracobrachialis muscle. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coracobrachialis_muscle (last accessed 20.3.2019)
- ↑ Wikipedia. Biceps Brachii. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biceps ( last accessed 20.3.2019)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Patient. Musculocutaneous nerve. Available from: https://patient.info/doctor/musculocutaneous-nerve-lesion-c5-c6 (last accessed 20.3.2019)
- ↑ Healthline. Musculocutaneous nerve. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/musculocutaneous-nerve#1 (last accessed 20.3.2019)