Madelung's Deformity: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) (corrected grammar error) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Shwe Shwe U Marma|Shwe Shwe U Marma]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
* | |||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User:Shwe Shwe U Marma|Shwe Shwe U Marma]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
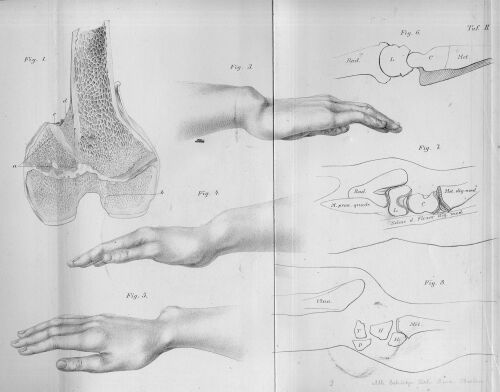
Madelung’s deformity is a condition of the [[Wrist and Hand|wrist]] characterized by a shortened distal [[radius]] with volar–ulnar curvature and a dorsally prominent distal [[ulna]].<ref>Dubey A, Fajardo M, Green S, Lee SK. [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1753193409346070 Madelung’s deformity: a review]. Journal of Hand Surgery (European Volume). 2010 Mar;35(3):174-81.</ref> | Madelung’s deformity is a condition of the [[Wrist and Hand|wrist]] characterized by a shortened distal [[radius]] with volar–ulnar curvature and a dorsally prominent distal [[ulna]].<ref>Dubey A, Fajardo M, Green S, Lee SK. [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1753193409346070 Madelung’s deformity: a review]. ''Journal of Hand Surgery'' (European Volume). 2010 Mar;35(3):174-81.</ref>This condition could be congenital(multiple osteochondrom)<ref>[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31192035/ Nakamura T. Madelung's Deformity. J Wrist Surg. 2019 Jun;8(3):175. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1688992. Epub 2019 Jun 3. PMID: 31192035; PMCID: PMC6546497.]</ref> or acquired as a result of a trauma to the growth plate (traumatic early closure of the epiphysis or Salter-Harris fracture (type V). <ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK580535/ Madelung Deformity Tara A. Saxena, Janay Mckie StatPearls, 5 2022] | ||
[[File:Madelung's Deformity.jpg|center|thumb| | |||
A Vickers’ [[ligament]] is the feature to differentiate Madelung’s deformity from Madelung-like deformities.<ref>Prasad N, Venkatesh M. [https://www.ijcmsr.com/uploads/1/0/2/7/102704056/ijcmsr_456.pdf Madelung Deformity of the Wrist: A Classic Presentation]. International Journal of Contemporary Medicine Surgery and Radiology. 2020;5:C4-5</ref> | </ref> | ||
==== Aetiology ==== | |||
This condition is caused by an abnormal ligament discovered by Vickers and Nielsen<ref>[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1402266/ Vickers D, Nielsen G. Madelung deformity: surgical prophylaxis (physiolysis) during the late growth period by resection of the dyschondrosteosis lesion. J Hand Surg Br. 1992 Aug;17(4):401-7. doi: 10.1016/s0266-7681(05)80262-1. PMID: 1402266.]</ref>. This ligament,5mm in diameter lies anterior to the volar-ulnar corner of the distal radial metaphysis, crosses the physis and inserts onto the lunate<ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8056710/ Farr S, Martínez-Alvarez S, Little KJ, Henstenburg J, Ristl R, Stauffer A, Soldado F, Zlotolow DA. The prevalence of Vickers' ligament in Madelung's deformity: a retrospective multicentre study of 75 surgical cases. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2021 May;46(4):384-390. doi: 10.1177/1753193420981522. Epub 2021 Jan 17. Erratum in: J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2021 Jan 27;:1753193421993305. PMID: 33459142; PMCID: PMC8056710.]</ref>. It is found more in females and is usually associated with a mesomelic form of dwarfism known as Leri-Weill dyschondrosteosis<ref>[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26341718/ Kozin SH, Zlotolow DA. Madelung Deformity. J Hand Surg Am. 2015 Oct;40(10):2090-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.03.033. Epub 2015 Sep 1. PMID: 26341718.]</ref> or caused by mutation in the Short-stature homeobox (SHOX) gene (haploinsufficiency) which may lead to skeletal dysplasia such as the Madelung's Deformity<ref>[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25220427/ Frederiksen AL, Hansen S, Brixen K, Frost M. Increased cortical area and thickness in the distal radius in subjects with SHOX-gene mutation. Bone. 2014 Dec;69:23-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 8. PMID: 25220427.]</ref>. The volar ulnar corner of the distal radius is a critical point located between the radial calcar, distal ulna, and carpus and it is responsible for maintaining stability while transferring force from the carpus<ref>[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35837591/ Chiri W, MacLean SB, Clarnette J, Eardley-Harris N, White J, Bain GI. Anatomical and Clinical Concepts in Distal Radius Volar Ulnar Corner fractures. J Wrist Surg. 2022 Jul 12;11(3):238-249. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1748674. PMID: 35837591; PMCID: PMC9276061.]</ref>.Due to the position of the Vickman's ligament of crossing the volar-ulnar part of the distal radial metaphysis it restricts movements of the wrist and causing reduced stability of the wrist joint<ref>[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35837591/ Kozin SH, Zlotolow DA. Madelung Deformity. J Hand Surg Am. 2015 Oct;40(10):2090-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.03.033. Epub 2015 Sep 1. PMID: 26341718.]</ref>. [[File:Madelung's Deformity.jpg|center|thumb|500x500px|Madelung's deformity]] | |||
A Vickers’ [[ligament]] is the feature to differentiate Madelung’s deformity from Madelung-like deformities.<ref>Prasad N, Venkatesh M. [https://www.ijcmsr.com/uploads/1/0/2/7/102704056/ijcmsr_456.pdf Madelung Deformity of the Wrist: A Classic Presentation]. ''International Journal of Contemporary Medicine Surgery and Radiology''. 2020;5:C4-5</ref> | |||
== Epidemiology == | == Epidemiology == | ||
Predominantly adolescent females are affected by a ratio of 4:1 | * Predominantly adolescent females are affected by a ratio of 4:1 and it does not usually manifest until 10-14 years of age<ref>[https://radiopaedia.org/articles/madelung-deformity Madelung deformity Henry Knipe, Frank Gaillard] | ||
= | [https://radiopaedia.org/articles/madelung-deformity Radiopaedia.org, 11 2009]</ref>, The deformity often occurs bilaterally<ref name=":02">Thomson C, Hawkes D, Nixon M. [http://www.journaloforthoplasticsurgery.com/index.php/JOPS/article/view/54/29 Madelung’s Deformity: Diagnosis, Classification and Treatment]. ''Journal of Orthoplastic Surgery''. 2020 Apr 17;4(1):1-1.</ref> Madelung deformity is relatively rare, with a prevalence of less than 2% of pediatric hand deformities, therefore less than 0.03% of the total population<ref>[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16473675/ Arora AS, Chung KC. Otto W. Madelung and the recognition of Madelung's deformity. J Hand Surg Am. 2006 Feb;31(2):177-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2005.09.001. PMID: 16473675.]</ref>. It is common in patients with short stature as this stature is mostly attributed to the mutation in the ''SHOX'' gene.<ref>[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32295321/ Gürsoy S, Hazan F, Aykut A, Nalbantoğlu Ö, Korkmaz HA, Demir K, Özkan B, Çoğulu Ö. Detection of ''SHOX'' Gene Variations in Patients with Skeletal Abnormalities with or without Short Stature. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020 Nov 25;12(4):358-365. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2020.2019.0001. Epub 2020 Apr 16. PMID: 32295321; PMCID: PMC7711637.]</ref> "In a study done, the mean age for patients who presented with Madelung's deformity was 22.5 years with a range from 10 years to 64 years and (77%) were female<ref name=":2">[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11727381/ Schmidt-Rohlfing B, Schwöbel B, Pauschert R, Niethard FU. Madelung deformity: clinical features, therapy and results. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2001 Oct;10(4):344-8. PMID: 11727381.]</ref> | ||
== Pathogenesis == | == Pathogenesis == | ||
Premature growth plate arrest at the medial volar aspect of the distal radius causes Madelung deformity. Repetitive traumatic pressure may result in Madelung-like deformity. Mutation or absence of the short stature homeobox (SHOX) gene is thought to be the cause of congenital | Premature growth plate arrest at the medial volar aspect of the distal radius causes Madelung deformity. Repetitive traumatic pressure may result in Madelung-like deformity. Mutation or absence of the short stature homeobox (SHOX) gene is thought to be the cause of congenital Madelung deformity.Congenital Madelung deformity can occur as a part of Leri-Weill dyschondrosteosis (LWD) or Turner syndrome.<ref>Tranmer A, Laub Jr D. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4993032/ Madelung deformity]. ''Eplasty''. 2016;16.</ref> | ||
Congenital | |||
=== '''Clinical Features''' === | |||
*Initially asymptomatic, progressive clinical deformity | |||
*Pain at wrist | |||
*Limited range of motion | |||
*Decreased wrist extension and supination; the distal ulna is prominent and dorsally dislocated<ref>[https://www.jpeds.com/article/S0022-3476(00)90028-3/fulltext Madelung's deformity as a presenting sign of turner's syndrome R. P. Schwartz,T. E. Sumner Journal of Pediatrics, 136, 4, 4 2000]</ref> | |||
*Obvious hand-wrist deformity<ref name=":2" /> | |||
*Distal radial abnormality or carpal subluxation<ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6546486/ Babu S, Turner J, Seewoonarain S, Chougule S. Madelung's Deformity of the Wrist-Current Concepts and Future Directions. J Wrist Surg. 2019 Jun;8(3):176-179. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1685488. Epub 2019 Apr 22. PMID: 31192036; PMCID: PMC6546486.]</ref> | |||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Radiology investigations such as the X-ray and MRI | |||
Key Features to note on an X-Ray are; | |||
# increased dorsal and radial convexity of the distal radius | |||
# increased volar and ulnar tilt of the distal radial articular surface | |||
# widened interosseous space | |||
# relative dorsal position of the ulnar head | |||
# pyramiding of the carpus<ref name=":0">Thomson C, Hawkes D, Nixon M. [http://www.journaloforthoplasticsurgery.com/index.php/JOPS/article/view/54/29 Madelung’s Deformity: Diagnosis, Classification and Treatment]. ''Journal of Orthoplastic Surgery''. 2020 Apr 17;4(1):1-1.</ref> | |||
=== | === MRI === | ||
MRI is done | MRI is done on the patients who need the surgical release of Vickers’ ligament to prevent deformity progression.<ref name=":1">Knutsen EJ, Goldfarb CA. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4152440/ Madelung's deformity]. ''Hand''. 2014 Sep;9(3):289-91.</ref> | ||
== Differential Diagnosis == | == Differential Diagnosis == | ||
* Turner syndrome | * Turner syndrome | ||
* Nail-patella syndrome | * Nail-patella syndrome | ||
* Hereditary, multiple | * Hereditary, multiple exostoses | ||
* Ollier’s disease | * Ollier’s disease | ||
* [[Achondroplasia]] | * [[Achondroplasia]] | ||
* Multiple epiphyseal dysplasias | * Multiple epiphyseal dysplasias | ||
* Mucopolysaccharidoses (Hurler and Morquio syndrome)<ref> | * Mucopolysaccharidoses (Hurler and Morquio syndrome)<ref>Kakarla S. [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334069794_Madelung_and_pseudo_Madelung_deformities-Pictorial_essay Madelung and pseudo Madelung deformities-Pictorial essay]. ''Journal of Medical and Scientific Research''. 2019;7:1-6</ref> | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
=== | === Physiotherapy Management === | ||
The aim is physiotherapy's management is to relieve pain,improve the range of motion of the wrist joint, prevent deformity and increase the functional capacity and dexterity of the wrist. | |||
* | |||
* | # Pain management | ||
* | #* Cold | ||
#* whirlpool immersion | |||
#* Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) | |||
# Volar [[splint]]<ref>Shahi P, Sudan A, Sehgal A, Meher D, Meena U. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7306668/ Madelung Deformity of the Wrist Managed Conservatively]. ''Cureus''. 2020 May;12(5).</ref> is used to immobilize tissue injuries which could be traumatic or non-traumatic conditions of the hand and the wrist<ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482429/ Volar Splinting Courtney A. Bethel, Menachem M. Meller StatPearls, 7 2022]</ref> | |||
# Range of Motion exercises as limited pronation and supination suggests the need of exercise to help maintaining and/or increasing the power of involved muscles, i.e.- pronators and supinators<ref>Brooks TJ. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC155529/ Madelung deformity in a collegiate gymnast: a case report]. ''Journal of Athletic Training''. 2001 Apr;36(2):170.</ref> | |||
# Exercises with Dexterity box | |||
# Passive movement and Stretching. | |||
# Muscle Strengthening | |||
=== | === Medical and Surgical Management === | ||
* Radial or ulnar [[osteotomy]] | * Radial or ulnar [[osteotomy]] | ||
* Use of oral analgesics | |||
* Vickers’ ligament resection | * Vickers’ ligament resection | ||
* Ulnar epiphysiodesis<ref>Bebing M, de Courtivron B, Pannier S, Journeau P, Fitoussi F, Morin C, Violas P. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1877056820302486 Madelung's deformity in children: Clinical and radiological results from a French national multicentre retrospective study]. Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research. 2020 Nov 1;106(7):1339-43.</ref> | * Ulnar epiphysiodesis<ref>Bebing M, de Courtivron B, Pannier S, Journeau P, Fitoussi F, Morin C, Violas P. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1877056820302486 Madelung's deformity in children: Clinical and radiological results from a French national multicentre retrospective study]. ''Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research''. 2020 Nov 1;106(7):1339-43.</ref> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 11:20, 23 July 2023
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Madelung’s deformity is a condition of the wrist characterized by a shortened distal radius with volar–ulnar curvature and a dorsally prominent distal ulna.[1]This condition could be congenital(multiple osteochondrom)[2] or acquired as a result of a trauma to the growth plate (traumatic early closure of the epiphysis or Salter-Harris fracture (type V). [3]
Aetiology[edit | edit source]
This condition is caused by an abnormal ligament discovered by Vickers and Nielsen[4]. This ligament,5mm in diameter lies anterior to the volar-ulnar corner of the distal radial metaphysis, crosses the physis and inserts onto the lunate[5]. It is found more in females and is usually associated with a mesomelic form of dwarfism known as Leri-Weill dyschondrosteosis[6] or caused by mutation in the Short-stature homeobox (SHOX) gene (haploinsufficiency) which may lead to skeletal dysplasia such as the Madelung's Deformity[7]. The volar ulnar corner of the distal radius is a critical point located between the radial calcar, distal ulna, and carpus and it is responsible for maintaining stability while transferring force from the carpus[8].Due to the position of the Vickman's ligament of crossing the volar-ulnar part of the distal radial metaphysis it restricts movements of the wrist and causing reduced stability of the wrist joint[9].
A Vickers’ ligament is the feature to differentiate Madelung’s deformity from Madelung-like deformities.[10]
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
- Predominantly adolescent females are affected by a ratio of 4:1 and it does not usually manifest until 10-14 years of age[11], The deformity often occurs bilaterally[12] Madelung deformity is relatively rare, with a prevalence of less than 2% of pediatric hand deformities, therefore less than 0.03% of the total population[13]. It is common in patients with short stature as this stature is mostly attributed to the mutation in the SHOX gene.[14] "In a study done, the mean age for patients who presented with Madelung's deformity was 22.5 years with a range from 10 years to 64 years and (77%) were female[15]
Pathogenesis[edit | edit source]
Premature growth plate arrest at the medial volar aspect of the distal radius causes Madelung deformity. Repetitive traumatic pressure may result in Madelung-like deformity. Mutation or absence of the short stature homeobox (SHOX) gene is thought to be the cause of congenital Madelung deformity.Congenital Madelung deformity can occur as a part of Leri-Weill dyschondrosteosis (LWD) or Turner syndrome.[16]
Clinical Features[edit | edit source]
- Initially asymptomatic, progressive clinical deformity
- Pain at wrist
- Limited range of motion
- Decreased wrist extension and supination; the distal ulna is prominent and dorsally dislocated[17]
- Obvious hand-wrist deformity[15]
- Distal radial abnormality or carpal subluxation[18]
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Radiology investigations such as the X-ray and MRI
Key Features to note on an X-Ray are;
- increased dorsal and radial convexity of the distal radius
- increased volar and ulnar tilt of the distal radial articular surface
- widened interosseous space
- relative dorsal position of the ulnar head
- pyramiding of the carpus[19]
MRI[edit | edit source]
MRI is done on the patients who need the surgical release of Vickers’ ligament to prevent deformity progression.[20]
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- Turner syndrome
- Nail-patella syndrome
- Hereditary, multiple exostoses
- Ollier’s disease
- Achondroplasia
- Multiple epiphyseal dysplasias
- Mucopolysaccharidoses (Hurler and Morquio syndrome)[21]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Physiotherapy Management[edit | edit source]
The aim is physiotherapy's management is to relieve pain,improve the range of motion of the wrist joint, prevent deformity and increase the functional capacity and dexterity of the wrist.
- Pain management
- Cold
- whirlpool immersion
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
- Volar splint[22] is used to immobilize tissue injuries which could be traumatic or non-traumatic conditions of the hand and the wrist[23]
- Range of Motion exercises as limited pronation and supination suggests the need of exercise to help maintaining and/or increasing the power of involved muscles, i.e.- pronators and supinators[24]
- Exercises with Dexterity box
- Passive movement and Stretching.
- Muscle Strengthening
Medical and Surgical Management[edit | edit source]
- Radial or ulnar osteotomy
- Use of oral analgesics
- Vickers’ ligament resection
- Ulnar epiphysiodesis[25]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Dubey A, Fajardo M, Green S, Lee SK. Madelung’s deformity: a review. Journal of Hand Surgery (European Volume). 2010 Mar;35(3):174-81.
- ↑ Nakamura T. Madelung's Deformity. J Wrist Surg. 2019 Jun;8(3):175. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1688992. Epub 2019 Jun 3. PMID: 31192035; PMCID: PMC6546497.
- ↑ Madelung Deformity Tara A. Saxena, Janay Mckie StatPearls, 5 2022
- ↑ Vickers D, Nielsen G. Madelung deformity: surgical prophylaxis (physiolysis) during the late growth period by resection of the dyschondrosteosis lesion. J Hand Surg Br. 1992 Aug;17(4):401-7. doi: 10.1016/s0266-7681(05)80262-1. PMID: 1402266.
- ↑ Farr S, Martínez-Alvarez S, Little KJ, Henstenburg J, Ristl R, Stauffer A, Soldado F, Zlotolow DA. The prevalence of Vickers' ligament in Madelung's deformity: a retrospective multicentre study of 75 surgical cases. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2021 May;46(4):384-390. doi: 10.1177/1753193420981522. Epub 2021 Jan 17. Erratum in: J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2021 Jan 27;:1753193421993305. PMID: 33459142; PMCID: PMC8056710.
- ↑ Kozin SH, Zlotolow DA. Madelung Deformity. J Hand Surg Am. 2015 Oct;40(10):2090-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.03.033. Epub 2015 Sep 1. PMID: 26341718.
- ↑ Frederiksen AL, Hansen S, Brixen K, Frost M. Increased cortical area and thickness in the distal radius in subjects with SHOX-gene mutation. Bone. 2014 Dec;69:23-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 8. PMID: 25220427.
- ↑ Chiri W, MacLean SB, Clarnette J, Eardley-Harris N, White J, Bain GI. Anatomical and Clinical Concepts in Distal Radius Volar Ulnar Corner fractures. J Wrist Surg. 2022 Jul 12;11(3):238-249. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1748674. PMID: 35837591; PMCID: PMC9276061.
- ↑ Kozin SH, Zlotolow DA. Madelung Deformity. J Hand Surg Am. 2015 Oct;40(10):2090-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.03.033. Epub 2015 Sep 1. PMID: 26341718.
- ↑ Prasad N, Venkatesh M. Madelung Deformity of the Wrist: A Classic Presentation. International Journal of Contemporary Medicine Surgery and Radiology. 2020;5:C4-5
- ↑ Madelung deformity Henry Knipe, Frank Gaillard Radiopaedia.org, 11 2009
- ↑ Thomson C, Hawkes D, Nixon M. Madelung’s Deformity: Diagnosis, Classification and Treatment. Journal of Orthoplastic Surgery. 2020 Apr 17;4(1):1-1.
- ↑ Arora AS, Chung KC. Otto W. Madelung and the recognition of Madelung's deformity. J Hand Surg Am. 2006 Feb;31(2):177-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2005.09.001. PMID: 16473675.
- ↑ Gürsoy S, Hazan F, Aykut A, Nalbantoğlu Ö, Korkmaz HA, Demir K, Özkan B, Çoğulu Ö. Detection of SHOX Gene Variations in Patients with Skeletal Abnormalities with or without Short Stature. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020 Nov 25;12(4):358-365. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2020.2019.0001. Epub 2020 Apr 16. PMID: 32295321; PMCID: PMC7711637.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Schmidt-Rohlfing B, Schwöbel B, Pauschert R, Niethard FU. Madelung deformity: clinical features, therapy and results. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2001 Oct;10(4):344-8. PMID: 11727381.
- ↑ Tranmer A, Laub Jr D. Madelung deformity. Eplasty. 2016;16.
- ↑ Madelung's deformity as a presenting sign of turner's syndrome R. P. Schwartz,T. E. Sumner Journal of Pediatrics, 136, 4, 4 2000
- ↑ Babu S, Turner J, Seewoonarain S, Chougule S. Madelung's Deformity of the Wrist-Current Concepts and Future Directions. J Wrist Surg. 2019 Jun;8(3):176-179. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1685488. Epub 2019 Apr 22. PMID: 31192036; PMCID: PMC6546486.
- ↑ Thomson C, Hawkes D, Nixon M. Madelung’s Deformity: Diagnosis, Classification and Treatment. Journal of Orthoplastic Surgery. 2020 Apr 17;4(1):1-1.
- ↑ Knutsen EJ, Goldfarb CA. Madelung's deformity. Hand. 2014 Sep;9(3):289-91.
- ↑ Kakarla S. Madelung and pseudo Madelung deformities-Pictorial essay. Journal of Medical and Scientific Research. 2019;7:1-6
- ↑ Shahi P, Sudan A, Sehgal A, Meher D, Meena U. Madelung Deformity of the Wrist Managed Conservatively. Cureus. 2020 May;12(5).
- ↑ Volar Splinting Courtney A. Bethel, Menachem M. Meller StatPearls, 7 2022
- ↑ Brooks TJ. Madelung deformity in a collegiate gymnast: a case report. Journal of Athletic Training. 2001 Apr;36(2):170.
- ↑ Bebing M, de Courtivron B, Pannier S, Journeau P, Fitoussi F, Morin C, Violas P. Madelung's deformity in children: Clinical and radiological results from a French national multicentre retrospective study. Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research. 2020 Nov 1;106(7):1339-43.