Kleiger's Test: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) (Updated categories) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User: | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Khloud Shreif|Khloud Shreif]]<br> | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
== Purpose == | == Purpose == | ||
[[File:Interosseous membrane.JPG|thumb|339x339px]] | |||
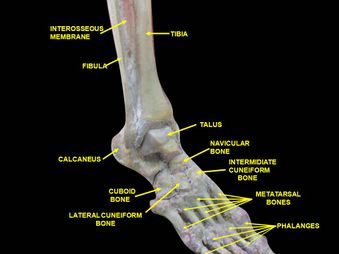
Kleiger's test or external rotation is used for the diagnosis of a medial [[Ankle Sprain|ankle sprain]], to assess the [[Medial ankle ligament|deltoid ligament]] sprain and inferior tibiofibular syndesmotic sprain<ref name=":0">Larkins L, Baker R, Baker J. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590109520300392?via%3Dihub Physical Examination of the Ankle: A Review of the Original Orthopedic Special Test Description and Scientific Validity of Common Tests for Ankle Examination]. Archives of Rehabilitation Research and Clinical Translation. 2020 Jul 8:100072.</ref>. | Kleiger's test or external rotation is used for the diagnosis of a medial [[Ankle Sprain|ankle sprain]], to assess the [[Medial ankle ligament|deltoid ligament]] sprain and inferior tibiofibular [[Syndesmotic Ankle Sprains|syndesmotic sprain]]<ref name=":0">Larkins L, Baker R, Baker J. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590109520300392?via%3Dihub Physical Examination of the Ankle: A Review of the Original Orthopedic Special Test Description and Scientific Validity of Common Tests for Ankle Examination]. Archives of Rehabilitation Research and Clinical Translation. 2020 Jul 8:100072.</ref>. | ||
== Technique == | == Technique == | ||
| Line 13: | Line 12: | ||
'''Test positive:''' if there is pain at the site of the interosseous membrane, or medially. Pain may radiate upward to the leg depending on the severity of the injury. | '''Test positive:''' if there is pain at the site of the interosseous membrane, or medially. Pain may radiate upward to the leg depending on the severity of the injury. | ||
{{#ev:youtube|AXPxMmChQj0|300}}<ref>Ortho EVAL Pal With Paul Marquis. Kleiger's test for High Ankle Sprain/Special Test for the Ankle. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AXPxMmChQj0[last accessed 26/2/2020]</ref> | |||
== Evidence == | == Evidence == | ||
Interrater reliability 0.75 according to kappa<ref>Alonso A, Khoury L, Adams R. Clinical tests for ankle syndesmosis injury: reliability and prediction of return to function. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 1998 Apr;27(4):276-84.</ref>. and a sensitivity of 25% and specificity of 84.8% when comparing the test with MRI finding<ref name=":0" />. | |||
With ankle dorsiflexion, the sensitivity of 75%, and the positive LR = 1.93<ref>Sman AD, Hiller CE, Rae K, Linklater J, Black DA, Nicholson LL, Burns J, Refshauge KM. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for ankle syndesmosis injury. British journal of sports medicine. 2015 Mar 1;49(5):323-9.</ref>. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Special Tests]] | |||
[[Category:Ankle - Ligaments]] | |||
[[Category:Ankle - Assessment and Examination]] | |||
[[Category:Ankle - Special Tests]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:10, 3 March 2021
Purpose[edit | edit source]
Kleiger's test or external rotation is used for the diagnosis of a medial ankle sprain, to assess the deltoid ligament sprain and inferior tibiofibular syndesmotic sprain[1].
Technique[edit | edit source]
Patient position: in a seated position, with knee hanging in 90 degrees, ankle relaxed.
Examiner: sitting at the level of the ankle to be tested with one hand stabilizing the leg from behind, the other hand grasp the ankle in neutral position then externally rotation of the foot. Nussbaum et al performed the test with the ankle fully dorsiflexed[1].
Test positive: if there is pain at the site of the interosseous membrane, or medially. Pain may radiate upward to the leg depending on the severity of the injury.
Evidence[edit | edit source]
Interrater reliability 0.75 according to kappa[3]. and a sensitivity of 25% and specificity of 84.8% when comparing the test with MRI finding[1].
With ankle dorsiflexion, the sensitivity of 75%, and the positive LR = 1.93[4].
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Larkins L, Baker R, Baker J. Physical Examination of the Ankle: A Review of the Original Orthopedic Special Test Description and Scientific Validity of Common Tests for Ankle Examination. Archives of Rehabilitation Research and Clinical Translation. 2020 Jul 8:100072.
- ↑ Ortho EVAL Pal With Paul Marquis. Kleiger's test for High Ankle Sprain/Special Test for the Ankle. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AXPxMmChQj0[last accessed 26/2/2020]
- ↑ Alonso A, Khoury L, Adams R. Clinical tests for ankle syndesmosis injury: reliability and prediction of return to function. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 1998 Apr;27(4):276-84.
- ↑ Sman AD, Hiller CE, Rae K, Linklater J, Black DA, Nicholson LL, Burns J, Refshauge KM. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for ankle syndesmosis injury. British journal of sports medicine. 2015 Mar 1;49(5):323-9.