ICRC Physiotherapy Standards Rehab Cycle
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (13/09/2021)
Original Editors - Add your name/s here if you are the original editor/s of this page. User Name
Top Contributors - Kim Jackson
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
- Professional Standards in (ICRC) Physiotherapy
- ICRC Physiotherapy Standards Project Cycle
- ICRC Physiotherapy Standards Rehab Cycle
Introduction[edit | edit source]
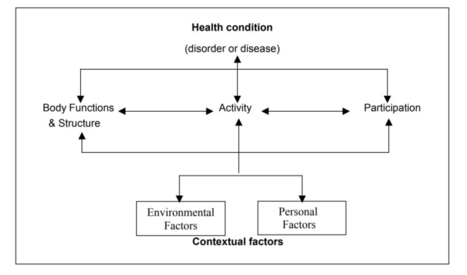
A number of PT standards are related to the rehab cycle of an individual patient or service user. It is advised to apply the ICF-Model for rehab cycle and for any intervention with a rehabilitation user. Click HERE for more information and for an e-learning module on ICF visit this LINK.
See the tools and documents accompanying different steps of the rehab cycle.
Assess and Analyse[edit | edit source]
The assessment process is an important step in the rehab cycle. Information collected during an assessment can guide clinical reasoning and, by evaluating a person's individual needs, enhance the the rehabilitation experience as well as identifying gaps in service provision that can aid the improvement of physiotherapy services.
Assessment can be considered to be the first step in the rehabilitation process. It is a continuous process, where information is gathered through various sources. The information once gathered is interpreted and the main aim is to identify key problems and then formulate a treatment plan which is relevant to the individual.
It is important to perform a good quality assessment, as the quality of care given is based on the assessment. This assessment should identify any additional factors that may contribute to the service users/patients presenting problems. The assessment process will assist the physiotherapist to recognize his/her own expertise and limitations, and where necessary refer to other disciplines as indicated.
The key elements of the assessment process require the gathering information from relevant sources, medical notes, investigations. Important sources that are required to develop a deep understanding of the person and situation include:
- Demographics - After taking the demographic information (which could also be retrieved by the general file), it is important to ask for the service user/patient informed consent. Oral consent should be received by every service user/patient prior to assessment/treatment and can be written in certain contexts.
- Assessment - It is not always feasible to gather information required at one time, assessments may be ongoing, depending on the complexity of the problem. The purpose is to establish the service user/patient’s physical, psychological and social needs and perceptions of their needs through the interview. It is also desirable to get an insight into the person’s expectations of their assessment and subsequent treatment.
It is important to keep a clear, structured format of the assessment, for example using the SOAP note format. SOAP is an acronym for:
- Subjective - What the patient says about the problem / intervention.
- Objective - The therapists objective observations and treatment interventions (e.g. ROM, Outcome Measures)
- Analysis - The therapists analysis of the various components of the assessment.
- Plan - How the treatment will be developed to the reach the goals or objectives.
Subjective Assessment[edit | edit source]
Assessment and Treatment Guidance [Word doc]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Outcomes measures for an individual user must be chosen according to their health condition and rehabilitation goals. There are generic outcome measures that should be performed with each user. When measuring health and disability we advise using the Manual for WHO Disability Assessment Schedule (WHODAS 2.0) for this purpose.
For more consistency we also advise a few simple outcomes measures for the following health conditions and clinical pictures :
- Lower limb conditions (due to amputation, fracture, stroke, incomplete SCI, Polio, old age, etc.)
- Upper limb conditions (due to amputation, fracture, stroke etc.)
- Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) - (ICRC (ARAT) Link)
- Watch the video : ARAT Test
- Any condition
- Functionality
Note - You are encouraged to individually select and use additional outcome measures for and with each user. Remember: measuring outcome is not a goal in itself (it's the outcome that counts, not the measuring) – keep it short and simple!
Formulate and Plan [edit | edit source]
Check out the Goal Setting in Rehabilitation (Physiopedia)
Make sure your goals are SMART
PTS Assessment and Treatment Guidance .docx [Document missing https://icrc.scenari.eu/public/Health/Health_Wiki/PTS/PTS%20Assessment%20and%20Treatment%20Guidance%20.docx]
For further reading
Bovend Eerdt SMART guide.pdf [Document missing https://icrc.scenari.eu/public/Health/Health_Wiki/PTS/Bovend%20Eerdt%20SMART%20guide.pdf]
Evidence based practice WCPT keynote.pdf
Herbert Evidence based physiotherapy.pdf [Document missing https://icrc.scenari.eu/public/Health/Health_Wiki/PTS/Herbert%20Evidence%20based%20physiotherapy.pdf@1]
How to make SMART goals [Powerpoint Presentation]
Physio network - Infographics
Physio network - Free resources
Implement and Monitor[edit | edit source]
www.physiotherapyexercises.com
For further reading
Rehabilitation exercise diary.pdf
Evaluate and Learn[edit | edit source]
Check out the documents from the Assess and Analyse
Service User Feedback Tool [Word Doc]
Resources[edit | edit source]
International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health - Beginners' Guide
International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health - Practical Manual
References[edit | edit source]