Hand Exercises: Difference between revisions
Seba Mamdouh (talk | contribs) m (vocab correction) |
Seba Mamdouh (talk | contribs) m (format and vocab changes) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[File:Digit ROM Exercise Handout.jpg|thumb]] | [[File:Digit ROM Exercise Handout.jpg|thumb]] | ||
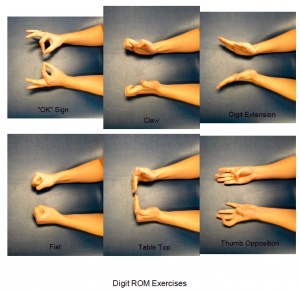
* '''Mobilizing''' '''exercise''' (Increase or maintain range of motion) | * '''Mobilizing''' '''exercise''' (Increase or maintain range of motion) | ||
* '''Strengthing''' '''exercise''' ( that use resistance from putty, a gel ball, or elastic band to strengthen hand and wrist muscles)<ref name=":0">Williams MA, Srikesavan C, Heine PJ, Bruce J, Brosseau L, Hoxey‐Thomas N, Lamb SE. Exercise for rheumatoid arthritis of the hand. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018(7).</ref> | * '''Strengthing''' '''exercise''' ( that use resistance from putty, a gel ball, or elastic band to strengthen hand and wrist muscles)<ref name=":0">Williams MA, Srikesavan C, Heine PJ, Bruce J, Brosseau L, Hoxey‐Thomas N, Lamb SE. Exercise for rheumatoid arthritis of the hand. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018(7).</ref> | ||
* '''Streaching''' '''exercise''' (to increase muscles flexibility of fingers and wrist) | |||
There are many conditions that may affect the hand and need exercise as an intervention to help patients to perform their ADL activities independently and increase the strength of handgrip. <ref>Ellegaard K, von Bülow C, Røpke A, Bartholdy C, Hansen IS, Rifbjerg-Madsen S, Henriksen M, Wæhrens EE. Hand exercise for women with rheumatoid arthritis and decreased hand function: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. Arthritis research & therapy. 2019 Dec 1;21(1):158.</ref> | There are many conditions that may affect the hand and need exercise as an intervention to help patients to perform their ADL activities independently and increase the strength of handgrip. <ref>Ellegaard K, von Bülow C, Røpke A, Bartholdy C, Hansen IS, Rifbjerg-Madsen S, Henriksen M, Wæhrens EE. Hand exercise for women with rheumatoid arthritis and decreased hand function: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. Arthritis research & therapy. 2019 Dec 1;21(1):158.</ref> | ||
=== ''<u>Example of conditions:</u>'' === | |||
'''[[Osteoarthritis]]''' is the most common joint disease and most frequently affects [[Hand Function|the hand]].<ref>Fife RS, Klippel J. Primer on the rheumatic diseases.</ref> This disease leads to pain in and around the affected [[Joint Classification|joints]] and to swelling, stiffness, deformity, and gradual loss of function. As a result, the ability to perform daily tasks may become impaired or lost.<ref>Stamm TA, Machold KP, Smolen JS, Fischer S, Redlich K, Graninger W, Ebner W, Erlacher L. Joint protection and home hand exercises improve hand function in patients with hand osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care & Research: Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology. 2002 Feb;47(1):44-9.</ref> A randomized controlled trail conducted in 2015 found that hand exercises were well tolerated and significantly improved activity performance, grip strength, pain and fatigue in women with Homeowners Association {HOA}<ref>Hennig T, Hæhre L, Hornburg VT, Mowinckel P, Norli ES, Kjeken I. Effect of home-based hand exercises in women with hand osteoarthritis: a randomised controlled trial. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2015 Aug 1;74(8):1501-8.</ref>. | '''[[Osteoarthritis]]''' is the most common joint disease and most frequently affects [[Hand Function|the hand]].<ref>Fife RS, Klippel J. Primer on the rheumatic diseases.</ref> This disease leads to pain in and around the affected [[Joint Classification|joints]] and to swelling, stiffness, deformity, and gradual loss of function. As a result, the ability to perform daily tasks may become impaired or lost.<ref>Stamm TA, Machold KP, Smolen JS, Fischer S, Redlich K, Graninger W, Ebner W, Erlacher L. Joint protection and home hand exercises improve hand function in patients with hand osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care & Research: Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology. 2002 Feb;47(1):44-9.</ref> A randomized controlled trail conducted in 2015 found that hand exercises were well tolerated and significantly improved activity performance, grip strength, pain and fatigue in women with Homeowners Association {HOA}<ref>Hennig T, Hæhre L, Hornburg VT, Mowinckel P, Norli ES, Kjeken I. Effect of home-based hand exercises in women with hand osteoarthritis: a randomised controlled trial. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2015 Aug 1;74(8):1501-8.</ref>. | ||
'''[[Rheumatoid Arthritis|Rheumatoid arthritis]]''' is the most common polyarthritis and affecting 0,24 to 1% of the population. Most of RA patients suffer from frequent problems for the hand and wrist like inflammation, [[Swan-Neck Deformity|deformity (swan neck deformity)]], pain, weakness, and restricted mobility, resulting in loss of function<ref name=":0" /><ref>Lamb SE, Williamson EM, Heine PJ, Adams J, Dosanjh S, Dritsaki M, Glover MJ, Lord J, McConkey C, Nichols V, Rahman A. Exercises to improve function of the rheumatoid hand (SARAH): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2015 Jan 31;385(9966):421-9.</ref>. | '''[[Rheumatoid Arthritis|Rheumatoid arthritis]]''' is the most common polyarthritis and affecting 0,24 to 1% of the population. Most of RA patients suffer from frequent problems for the hand and wrist like inflammation, [[Swan-Neck Deformity|deformity (swan neck deformity)]], pain, weakness, and restricted mobility, resulting in loss of function<ref name=":0" /><ref>Lamb SE, Williamson EM, Heine PJ, Adams J, Dosanjh S, Dritsaki M, Glover MJ, Lord J, McConkey C, Nichols V, Rahman A. Exercises to improve function of the rheumatoid hand (SARAH): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2015 Jan 31;385(9966):421-9.</ref>. | ||
=== Hand exercise === | === '''''<u>Hand exercise</u>''''' === | ||
{{#ev:youtube|GyCdT6hTgeA}} | {{#ev:youtube|GyCdT6hTgeA}} | ||
=== '' | === ''<u>iSARAH Hand Exercise</u>'' === | ||
It is a strengthening and stretching exercise program for the hand to help '''RA''' patients<ref name=":1">Hall AM, Copsey B, Williams M, Srikesavan C, Lamb SE, Sarah Trial Team. Mediating effect of changes in hand impairments on hand function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: exploring the mechanisms of an effective exercise program. Arthritis care & research. 2017 Jul;69(7):982-8.</ref>. A multi trial had been conducted in the UK as around 490 adult patients who suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, hand pain and dysfunction and they had been on a stable drug regime for at least 3 months, to either usual care or usual care plus a tailored strengthening and stretching hand exercise program<ref>Lamb SE, Williamson EM, Heine PJ, Adams J, Dosanjh S, Dritsaki M, Glover MJ, Lord J, McConkey C, Nichols V, Rahman A. Exercises to improve function of the rheumatoid hand (SARAH): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2015 Jan 31;385(9966):421-9.</ref><ref>Williams MA, Williamson EM, Heine PJ, Nichols V, Glover MJ, Dritsaki M, Adams J, Dosanjh S, Underwood M, Rahman A, McConkey C. Strengthening And stretching for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Hand (SARAH). A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.</ref>. The study concluded that using a tailored hand exercise program( iSARAH) is a worthwhile, low-cost intervention to provide as an adjunct to various drug regimens. <ref name=":1" /> | It is a strengthening and stretching exercise program for the hand to help '''RA''' patients<ref name=":1">Hall AM, Copsey B, Williams M, Srikesavan C, Lamb SE, Sarah Trial Team. Mediating effect of changes in hand impairments on hand function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: exploring the mechanisms of an effective exercise program. Arthritis care & research. 2017 Jul;69(7):982-8.</ref>. A multi trial had been conducted in the UK as around 490 adult patients who suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, hand pain and dysfunction and they had been on a stable drug regime for at least 3 months, to either usual care or usual care plus a tailored strengthening and stretching hand exercise program<ref>Lamb SE, Williamson EM, Heine PJ, Adams J, Dosanjh S, Dritsaki M, Glover MJ, Lord J, McConkey C, Nichols V, Rahman A. Exercises to improve function of the rheumatoid hand (SARAH): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2015 Jan 31;385(9966):421-9.</ref><ref>Williams MA, Williamson EM, Heine PJ, Nichols V, Glover MJ, Dritsaki M, Adams J, Dosanjh S, Underwood M, Rahman A, McConkey C. Strengthening And stretching for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Hand (SARAH). A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.</ref>. The study concluded that using a tailored hand exercise program( iSARAH) is a worthwhile, low-cost intervention to provide as an adjunct to various drug regimens. <ref name=":1" /> | ||
{{#ev:youtube|q1pNhMkJHhg}} | {{#ev:youtube|q1pNhMkJHhg}} | ||
Also, a qualitative longitudinal study<ref name=":2">Nichols VP, Williamson E, Toye F, Lamb SE. A longitudinal, qualitative study exploring sustained adherence to a hand exercise programme for rheumatoid arthritis evaluated in the SARAH trial. Disability and rehabilitation. 2017 Aug 28;39(18):1856-63.</ref> was conducted to explore the sustained adherence for hand exercise program( | Also, a qualitative longitudinal study<ref name=":2">Nichols VP, Williamson E, Toye F, Lamb SE. A longitudinal, qualitative study exploring sustained adherence to a hand exercise programme for rheumatoid arthritis evaluated in the SARAH trial. Disability and rehabilitation. 2017 Aug 28;39(18):1856-63.</ref> was conducted to explore the sustained adherence for hand exercise program(iSARAH)found that establishing a routine was an important step towards participants being able to exercise independently. Therapists provided participants with the skills to continue to exercise while dealing with changes in symptoms and schedules.<ref name=":2" /> | ||
The iSARAH program includes a total of 11 flexibility and strength exercises, supplemented with simple behavioral change support strategies recommended by health professionals to help patients adhere with their iSARAH exercises and make hand exercising a daily habit. Any health care professional can take the course of iSARAH hand program . Please follow this link: | The iSARAH program includes a total of 11 flexibility and strength exercises, supplemented with simple behavioral change support strategies recommended by health professionals to help patients adhere with their iSARAH exercises and make hand exercising a daily habit. Any health care professional can take the course of iSARAH hand program . Please follow this link: | ||
https://www.clahrc-oxford.nihr.ac.uk/blog/sarah-implementing-an-evidence-based-hand-exercise-programme-into-nhs-practice | <nowiki>https://www.clahrc-oxford.nihr.ac.uk/blog/sarah-implementing-an-evidence-based-hand-exercise-programme-into-nhs-practice</nowiki> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
[[Category:Hand - Interventions]] | [[Category:Hand - Interventions]] | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 12:29, 17 November 2022
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Hand Exercises are used as an intervention that aims to improve the mobility and strength of the hand in additionally,improving functional ability. Hand exercise may include:
- Mobilizing exercise (Increase or maintain range of motion)
- Strengthing exercise ( that use resistance from putty, a gel ball, or elastic band to strengthen hand and wrist muscles)[1]
- Streaching exercise (to increase muscles flexibility of fingers and wrist)
There are many conditions that may affect the hand and need exercise as an intervention to help patients to perform their ADL activities independently and increase the strength of handgrip. [2]
Example of conditions:[edit | edit source]
Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disease and most frequently affects the hand.[3] This disease leads to pain in and around the affected joints and to swelling, stiffness, deformity, and gradual loss of function. As a result, the ability to perform daily tasks may become impaired or lost.[4] A randomized controlled trail conducted in 2015 found that hand exercises were well tolerated and significantly improved activity performance, grip strength, pain and fatigue in women with Homeowners Association {HOA}[5].
Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common polyarthritis and affecting 0,24 to 1% of the population. Most of RA patients suffer from frequent problems for the hand and wrist like inflammation, deformity (swan neck deformity), pain, weakness, and restricted mobility, resulting in loss of function[1][6].
Hand exercise[edit | edit source]
iSARAH Hand Exercise[edit | edit source]
It is a strengthening and stretching exercise program for the hand to help RA patients[7]. A multi trial had been conducted in the UK as around 490 adult patients who suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, hand pain and dysfunction and they had been on a stable drug regime for at least 3 months, to either usual care or usual care plus a tailored strengthening and stretching hand exercise program[8][9]. The study concluded that using a tailored hand exercise program( iSARAH) is a worthwhile, low-cost intervention to provide as an adjunct to various drug regimens. [7]
Also, a qualitative longitudinal study[10] was conducted to explore the sustained adherence for hand exercise program(iSARAH)found that establishing a routine was an important step towards participants being able to exercise independently. Therapists provided participants with the skills to continue to exercise while dealing with changes in symptoms and schedules.[10]
The iSARAH program includes a total of 11 flexibility and strength exercises, supplemented with simple behavioral change support strategies recommended by health professionals to help patients adhere with their iSARAH exercises and make hand exercising a daily habit. Any health care professional can take the course of iSARAH hand program . Please follow this link:
https://www.clahrc-oxford.nihr.ac.uk/blog/sarah-implementing-an-evidence-based-hand-exercise-programme-into-nhs-practice
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Williams MA, Srikesavan C, Heine PJ, Bruce J, Brosseau L, Hoxey‐Thomas N, Lamb SE. Exercise for rheumatoid arthritis of the hand. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018(7).
- ↑ Ellegaard K, von Bülow C, Røpke A, Bartholdy C, Hansen IS, Rifbjerg-Madsen S, Henriksen M, Wæhrens EE. Hand exercise for women with rheumatoid arthritis and decreased hand function: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. Arthritis research & therapy. 2019 Dec 1;21(1):158.
- ↑ Fife RS, Klippel J. Primer on the rheumatic diseases.
- ↑ Stamm TA, Machold KP, Smolen JS, Fischer S, Redlich K, Graninger W, Ebner W, Erlacher L. Joint protection and home hand exercises improve hand function in patients with hand osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care & Research: Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology. 2002 Feb;47(1):44-9.
- ↑ Hennig T, Hæhre L, Hornburg VT, Mowinckel P, Norli ES, Kjeken I. Effect of home-based hand exercises in women with hand osteoarthritis: a randomised controlled trial. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2015 Aug 1;74(8):1501-8.
- ↑ Lamb SE, Williamson EM, Heine PJ, Adams J, Dosanjh S, Dritsaki M, Glover MJ, Lord J, McConkey C, Nichols V, Rahman A. Exercises to improve function of the rheumatoid hand (SARAH): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2015 Jan 31;385(9966):421-9.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Hall AM, Copsey B, Williams M, Srikesavan C, Lamb SE, Sarah Trial Team. Mediating effect of changes in hand impairments on hand function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: exploring the mechanisms of an effective exercise program. Arthritis care & research. 2017 Jul;69(7):982-8.
- ↑ Lamb SE, Williamson EM, Heine PJ, Adams J, Dosanjh S, Dritsaki M, Glover MJ, Lord J, McConkey C, Nichols V, Rahman A. Exercises to improve function of the rheumatoid hand (SARAH): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2015 Jan 31;385(9966):421-9.
- ↑ Williams MA, Williamson EM, Heine PJ, Nichols V, Glover MJ, Dritsaki M, Adams J, Dosanjh S, Underwood M, Rahman A, McConkey C. Strengthening And stretching for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Hand (SARAH). A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Nichols VP, Williamson E, Toye F, Lamb SE. A longitudinal, qualitative study exploring sustained adherence to a hand exercise programme for rheumatoid arthritis evaluated in the SARAH trial. Disability and rehabilitation. 2017 Aug 28;39(18):1856-63.