Gemellus Inferior: Difference between revisions
(Information updated and added. Citations added) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:User Name|Nikhil Benhur Abburi]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:User Name|Nikhil Benhur Abburi]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
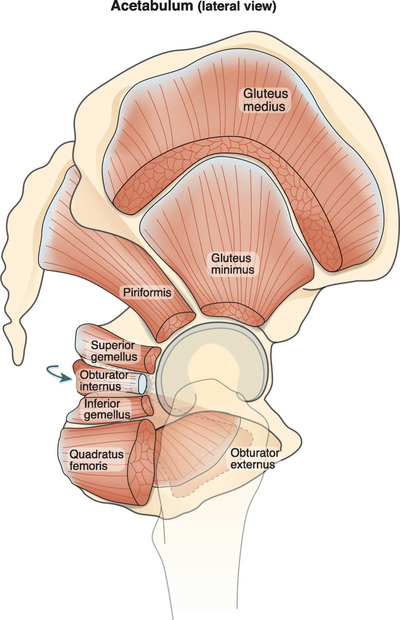
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[File:Gluteal muscles gemelli.webp|alt=|thumb|620x620px]] | |||
Gemellus inferior is the second of the '''gemelli''' '''muscles.'''<ref>Miniato MA, Varacallo M. Anatomy, Back, Lumbosacral Trunk. InStatPearls [Internet] 2019 Mar 9. StatPearls Publishing.</ref> It lies inferior to [[Gemellus Superior|gemellus superior]] and the [[Obturator Internus|Obturator internus]] tendon <ref>Häggström, Mikael (2014). "Medical gallery of Mikael Häggström 2014". ''WikiJournal of Medicine'' '''1''' (2). DOI:[https://doi.org/10.15347/wjm/2014.008 10.15347/wjm/2014.008]. ISSN [https://www.worldcat.org/issn/2002-4436 2002-4436]</ref>. It is a triangle-shaped muscle<ref name=":0">Lezak B, Massel DH. A[[Natomy, bony pelvis and lower limhttps://europepmc.org/article/NBK/nbk557420#free-full-textb, gemelli muscles|natomy, bony pelvis and lower limb, gemelli muscles]].</ref> found in the deep gluteal space<ref name=":1">Carro LP, Hernando MF, Cerezal L, Navarro IS, Fernandez AA, Castillo AO. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5193530/ Deep gluteal space problems: piriformis syndrome, ischiofemoral impingement and sciatic nerve release.] Muscles, ligaments and tendons journal. 2016 Jul;6(3):384.</ref>. The inferior gemellus joins the [[Gemellus Superior|superior gemellus]] and [[Obturator Internus|obturator internus]] as a conjoined tendon, the triceps coxae<ref name=":0" />. | Gemellus inferior is the second of the '''gemelli''' '''muscles.'''<ref>Miniato MA, Varacallo M. Anatomy, Back, Lumbosacral Trunk. InStatPearls [Internet] 2019 Mar 9. StatPearls Publishing.</ref> It lies inferior to [[Gemellus Superior|gemellus superior]] and the [[Obturator Internus|Obturator internus]] tendon <ref>Häggström, Mikael (2014). "Medical gallery of Mikael Häggström 2014". ''WikiJournal of Medicine'' '''1''' (2). DOI:[https://doi.org/10.15347/wjm/2014.008 10.15347/wjm/2014.008]. ISSN [https://www.worldcat.org/issn/2002-4436 2002-4436]</ref>. It is a triangle-shaped muscle<ref name=":0">Lezak B, Massel DH. A[[Natomy, bony pelvis and lower limhttps://europepmc.org/article/NBK/nbk557420#free-full-textb, gemelli muscles|natomy, bony pelvis and lower limb, gemelli muscles]].</ref> found in the deep gluteal space<ref name=":1">Carro LP, Hernando MF, Cerezal L, Navarro IS, Fernandez AA, Castillo AO. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5193530/ Deep gluteal space problems: piriformis syndrome, ischiofemoral impingement and sciatic nerve release.] Muscles, ligaments and tendons journal. 2016 Jul;6(3):384.</ref>. The inferior gemellus joins the [[Gemellus Superior|superior gemellus]] and [[Obturator Internus|obturator internus]] as a conjoined tendon, the triceps coxae<ref name=":0" />. | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 12 February 2023
Description[edit | edit source]
Gemellus inferior is the second of the gemelli muscles.[1] It lies inferior to gemellus superior and the Obturator internus tendon [2]. It is a triangle-shaped muscle[3] found in the deep gluteal space[4]. The inferior gemellus joins the superior gemellus and obturator internus as a conjoined tendon, the triceps coxae[3].
Origin[edit | edit source]
Ischial tuberosity[3] and lower part of lesser sciatic notch.
Insertion[edit | edit source]
The inferior gemellus, together with the superior gemellus and obturator internus, insert on the greater trochanter of femur.[3]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
The nerve to Quadratus Femoris innervates the inferior gemellus (L4, L5, S1)[3][5].
Artery[edit | edit source]
It is supplied by the inferior gluteal artery[3].
Function[edit | edit source]
The two gemelli's primary function is to externally (laterally) rotate and extend the hip[3]. It also contributes to hip abduction while the hip is in flexion[3].
Clinical significance[edit | edit source]
Gemelli-obturator syndrome occurs when there is a dynamic compression of the sciatic nerve during stretching of the gemelii-obturator complex[3][4]. It is a rare condition and is a possible diagnosis for deep gluteal syndrome.[4]Symptoms include pain and/or dysesthesias in the hip, buttock or posterior thigh, with or without non-discogenic radicular pain[4].
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Miniato MA, Varacallo M. Anatomy, Back, Lumbosacral Trunk. InStatPearls [Internet] 2019 Mar 9. StatPearls Publishing.
- ↑ Häggström, Mikael (2014). "Medical gallery of Mikael Häggström 2014". WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.008. ISSN 2002-4436
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Lezak B, Massel DH. Anatomy, bony pelvis and lower limb, gemelli muscles.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Carro LP, Hernando MF, Cerezal L, Navarro IS, Fernandez AA, Castillo AO. Deep gluteal space problems: piriformis syndrome, ischiofemoral impingement and sciatic nerve release. Muscles, ligaments and tendons journal. 2016 Jul;6(3):384.
- ↑ Honma S, Jun Y, Horiguchi M. The human gemelli muscles and their nerve supplies. Kaibogaku zasshi. Journal of anatomy. 1998 Aug;73(4):329-35.
- ↑ Kenhub - Learn human anatomy. Functions of the gemelli muscles (preview) - 3D Human Anatomy | Kenhub. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SWuoa-XJPXg [last accessed 25/07/2019]