Achilles Tenotomy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Rachael Lowe (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div><div align="justify"> | </div><div align="justify"> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
After the final manipulation it is time to correct the equinus. | After the final manipulation in [[Ponseti method|management of clubfoot]] it is time to correct the equinus. At this stage the total midfoot [[Pirani Score|Pirani score]] is usually 0, the cavus, adductus, and varus are all corrected, the lateral head of talus is fully covered, and the foot is 50 - 70° abducted. In a few cases the equinus can be corrected by manipulation, but in 90% the [[achilles tendon]] is too tight and a tenotomy is needed. Over 90% of cases need a tenotomy<ref name=":0" />. | ||
The tenotomy corrects the rigid equinus. It is a complete cut through of the Achilles tendon, not a tendon lengthening. It creates a very small incision - it is known as a percutaneous (“through the skin”) tenotomy. | The tenotomy corrects the rigid equinus. It is a complete cut through of the Achilles tendon, not a tendon lengthening. It creates a very small incision - it is known as a percutaneous (“through the skin”) tenotomy. It is necessary because although tissues yield to gentle stretch, collagen of the achilles tendon is more restrictive than the joint capsule and ligaments and does not respond to stretching as predictably. <ref name=":0">Africa Clubfoot Training Project. Chapter 7 Africa Clubfoot Training Basic & Advanced Clubfoot Treatment Provider Courses - Participant Manual. University of Oxford: Africa Clubfoot Training Project, 2017.</ref> In infants the tendon heals sufficiently in 3 weeks.<blockquote>Remember: In most cases tenotomy is needed</blockquote> | ||
It is necessary because although tissues yield to gentle stretch, collagen of the | |||
== Indication for Tenotomy == | == Indication for Tenotomy == | ||
Are the following all present? | Are the following all present? | ||
* Talar Head Covered (Pirani Midfoot Score Usually = 0) | * Talar Head Covered (Pirani Midfoot Score Usually = 0) | ||
* Foot Abducts to 50 - 70 Degrees | * Foot Abducts to 50 - 70 Degrees | ||
* Heel in Valgus or at least Neutral | * Heel in Valgus or at least Neutral | ||
In some rare cases when the above criteria are reached, the | If yes, proceed to tenotomy. | ||
If no, the foot may need more manipulation and casting. | |||
In some rare cases when the above criteria are reached, the achilles tendon will not be tight, and if it allows Dorsiflexion to greater than 15° then tenotomy can be avoided. <blockquote>Remember: Cover Talus before Tenotomy</blockquote> | |||
== Considerations == | == Considerations == | ||
Communicate with surgeon BEFORE tenotomy | * Communicate with surgeon BEFORE tenotomy. | ||
* Anticipate date through Pirani Scores, using graph if possible. | |||
* Allow time for questions from parents. | |||
* Decide on holding / casting roles. | |||
* Measure the foot to organize a brace, which will be needed next visit. | |||
* Paperwork and informed consent of parent or caregiver. | |||
* Clinic environment: calm, quiet, baby feeding <ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Equipment required == | |||
Achilles tenotomy can be done in the Ponseti clinic under local anaesthetic, some teams opt to perform achilles tenotomy in theatre. The following equipment is required: | |||
* Sterile Area, linen or paper sterile field | |||
* Antiseptic | |||
* Small Syringe with small gauge needle (25g or Smaller - An insulin syringe is perfect) | |||
* Local anaesthesia Lignocaine 1 - 2% (inject 0.5–1ml) | |||
* Gloves | |||
* <nowiki>#</nowiki>15 Blade | |||
* Sterile Gauze | |||
* Timer to time 5 minutes (Pressure over Wound), or until Bleeding Stops | |||
* The right size underwrap and padding need to be ready | |||
* 2 Trained People: 1 to perform the tenotomy and 1 to Assist <ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Equipment | |||
Sterile Area, linen or paper sterile field | |||
Antiseptic | |||
Small Syringe with small gauge needle (25g or Smaller - An insulin syringe is perfect) | |||
Local anaesthesia Lignocaine 1 - 2% (inject 0.5–1ml) | |||
Gloves | |||
<nowiki>#</nowiki>15 Blade | |||
Sterile Gauze | |||
Timer to time 5 minutes (Pressure over Wound), or until Bleeding Stops | |||
The right size underwrap and padding need to be ready | |||
2 Trained People: | |||
== Procedure == | == Procedure == | ||
This may be done in the clinic by an | This may be done in the clinic by an orthopaedic surgeon or an experienced and trained clinician. Two people are required, one person to hold the foot and one person to perform the tenotomy. The person holding the foot grips the leg below the knee and the midfoot, with the child’s knee in extension. A generous antiseptic prep of the heel and ankle is applied, extending medially and laterally. A small amount of local anaesthetic is placed medial to the achilles tendon 1cm proximal to its insertion. If too much anaesthetic is used the tendon is difficult to feel. | ||
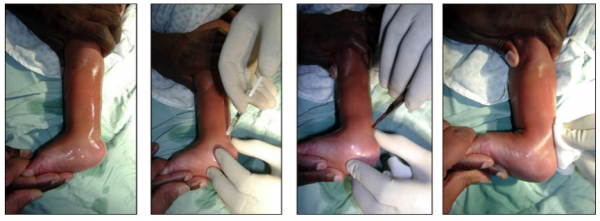
Insert the knife (a number 15 scalpel or beaver blade works well) on the medial side, parallel to and beneath (anterior to) the tendon approximately 1cm above its insertion into the calcaneum. Turn the sharp edge of the knife to the tendon and perform the tenotomy. The “release” obtained after a complete tenotomy is easily felt. Often there is a “pop” sound. 10 - 20 degrees of additional dorsiflexion will be obtained.[[File:Achilles Tenotomy.png|none|thumb|600x600px|Pictures from left: | Insert the knife (a number 15 scalpel or beaver blade works well) on the medial side, parallel to and beneath (anterior to) the tendon approximately 1cm above its insertion into the calcaneum. Turn the sharp edge of the knife to the tendon and perform the tenotomy. The “release” obtained after a complete tenotomy is easily felt. Often there is a “pop” sound. 10 - 20 degrees of additional dorsiflexion will be obtained.[[File:Achilles Tenotomy.png|none|thumb|600x600px|Pictures from left: | ||
| Line 79: | Line 56: | ||
Clean skin with alcohol to remove the betadine. Place a sterile dressing over the wound. Apply firm pressure for 5 mins (or until bleeding stops) over the incision site. Apply the post-tenotomy cast: keep knee in 90 degrees flexion. Wrap with under-cast padding. Place a well-moulded above-knee plaster cast with the foot in maximum dorsiflexion (at least 15 degrees) and 50-70 degrees of abduction (with no eversion). This last cast should be worn for 3 weeks. The patient should remain in the department for 1 hour to check for bleeding and circulation.<ref name=":0" />{{#ev:youtube|0dhB0dx8sgM|600}} | Clean skin with alcohol to remove the betadine. Place a sterile dressing over the wound. Apply firm pressure for 5 mins (or until bleeding stops) over the incision site. Apply the post-tenotomy cast: keep knee in 90 degrees flexion. Wrap with under-cast padding. Place a well-moulded above-knee plaster cast with the foot in maximum dorsiflexion (at least 15 degrees) and 50-70 degrees of abduction (with no eversion). This last cast should be worn for 3 weeks. The patient should remain in the department for 1 hour to check for bleeding and circulation.<ref name=":0" />{{#ev:youtube|0dhB0dx8sgM|600}} | ||
== Effectiveness of | == Effectiveness of tenotomy == | ||
Some clinicians have expressed concerns about performing a complete tenotomy (completely severing) of the Achilles tendon, fearing this procedure will cause damage. However, an ultrasound study on children who had undergone Achilles tenotomy as part of their clubfoot treatment showed tendon re-growth; most tendons were clinically intact after 3 weeks and after 6 weeks all were intact.<ref>Barker S, Lavy C (2006) Correlation of clinical and ultrasonographical findings after Achilles tenotomy in idiopathic club foot. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 88-B (3): 377-379</ref> | Some clinicians have expressed concerns about performing a complete tenotomy (completely severing) of the Achilles tendon, fearing this procedure will cause damage. However, an ultrasound study on children who had undergone Achilles tenotomy as part of their clubfoot treatment showed tendon re-growth; most tendons were clinically intact after 3 weeks and after 6 weeks all were intact.<ref>Barker S, Lavy C (2006) Correlation of clinical and ultrasonographical findings after Achilles tenotomy in idiopathic club foot. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 88-B (3): 377-379</ref> Percutaneous tendo Achilles tenotomy is safe, inexpensive, effective, and an easy office procedure used to expedite the correction of equinus deformity in idiopathic clubfeet with a very low complication rate.<ref>Riyaz Ahmad Dar, Mohd Shafi Bhat, Mohmad Yaseen Rather, Ansar ul Haq, Shera Ifran Ali. [https://www.ejmanager.com/mnstemps/83/83-1426055533.pdf Percutaneous Tendo Achilles Tenotomy in the management of Equinus Deformity in conservatively treated CTEV]. SEAJCRR 2015, JAN-FEB 4 (1) | ||
Percutaneous tendo Achilles tenotomy is safe, inexpensive, effective, and an easy office procedure used to expedite the correction of equinus deformity in idiopathic clubfeet with a very low complication rate.<ref> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|} | |} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
Tenotomy in older children is a controversial area. A study of older children (7-11 years old) who had achilles tenotomies performed reported that none of the participants had weakness of the gastrocnemius or soleus muscles.<ref name=":1">Khan S & Kumar A (2010) Ponseti’s manipulation in neglected clubfoot in children more than 7 years of age: a prospective evaluation of 25 feet with long term follow-up. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics B 19: 385-389</ref> However, the maximum age when tenotomy can be used has not been established, it has been suggested that a lengthening procedure using three incisions could be used in place of complete tenotomy in older children.<ref name=":1" /> This topic needs further investigation. | |||
== Management | == Errors during tenotomy == | ||
'''Premature equinus correction''' - Attempts to correct the equinus before the heel varus and foot supination are corrected will result in a rocker-bottom deformity. Equinus through the subtalar joint can be corrected only if the calcaneus abducts. Tenotomy is indicated after cavus, adductus, and varus are fully corrected.<div align="justify"> | |||
'''Failure to perform a complete tenotomy''' - The sudden lengthening with a “pop” or “snap” signals a complete tenotomy. Failure to achieve this may indicate an incomplete tenotomy. Repeat the tenotomy maneuver to ensure a complete tenotomy if there is no “pop” or “snap.” <ref>Lynn Staheli, Ignacio Ponseti, & Others. Clubfoot: Ponseti Management, 3rd Edition. Global Help, 2009. p13-15 | |||
</ref><div align="justify"> | |||
== Management post tenotomy == | |||
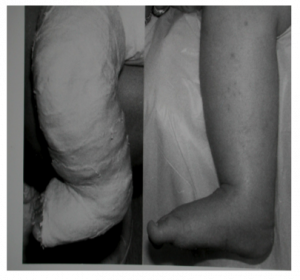
The cast after tenotomy stays on for 3 weeks. Prior to the tenotomy it is important to ensure to order the brace and book a the brace fitting. The foot must be in a dorsiflexed and abducted position to fit into brace. The last cast is applied with the foot in 50-70 degrees of abduction and at least 15 degrees of dorsiflexion. After removal of the last cast 3 weeks later there is correction of cavus, adductus, varus, and equinus (CAVE).[[File:28.png|none|thumb|300x300px]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 10 November 2017
Original Editor - Africa Clubfoot Training Team as part of ICRC and GCI Clubfoot Content Development Project
Top Contributors - Naomi O'Reilly, Daniele Barilla, Kim Jackson, Rucha Gadgil, Rachael Lowe, Simisola Ajeyalemi, Chelsea Mclene, Olajumoke Ogunleye and Meaghan Rieke
Introduction[edit | edit source]
After the final manipulation in management of clubfoot it is time to correct the equinus. At this stage the total midfoot Pirani score is usually 0, the cavus, adductus, and varus are all corrected, the lateral head of talus is fully covered, and the foot is 50 - 70° abducted. In a few cases the equinus can be corrected by manipulation, but in 90% the achilles tendon is too tight and a tenotomy is needed. Over 90% of cases need a tenotomy[1].
The tenotomy corrects the rigid equinus. It is a complete cut through of the Achilles tendon, not a tendon lengthening. It creates a very small incision - it is known as a percutaneous (“through the skin”) tenotomy. It is necessary because although tissues yield to gentle stretch, collagen of the achilles tendon is more restrictive than the joint capsule and ligaments and does not respond to stretching as predictably. [1] In infants the tendon heals sufficiently in 3 weeks.Remember: In most cases tenotomy is needed
Indication for Tenotomy[edit | edit source]
Are the following all present?
- Talar Head Covered (Pirani Midfoot Score Usually = 0)
- Foot Abducts to 50 - 70 Degrees
- Heel in Valgus or at least Neutral
If yes, proceed to tenotomy.
If no, the foot may need more manipulation and casting.
In some rare cases when the above criteria are reached, the achilles tendon will not be tight, and if it allows Dorsiflexion to greater than 15° then tenotomy can be avoided.Remember: Cover Talus before Tenotomy
Considerations[edit | edit source]
- Communicate with surgeon BEFORE tenotomy.
- Anticipate date through Pirani Scores, using graph if possible.
- Allow time for questions from parents.
- Decide on holding / casting roles.
- Measure the foot to organize a brace, which will be needed next visit.
- Paperwork and informed consent of parent or caregiver.
- Clinic environment: calm, quiet, baby feeding [1]
Equipment required[edit | edit source]
Achilles tenotomy can be done in the Ponseti clinic under local anaesthetic, some teams opt to perform achilles tenotomy in theatre. The following equipment is required:
- Sterile Area, linen or paper sterile field
- Antiseptic
- Small Syringe with small gauge needle (25g or Smaller - An insulin syringe is perfect)
- Local anaesthesia Lignocaine 1 - 2% (inject 0.5–1ml)
- Gloves
- #15 Blade
- Sterile Gauze
- Timer to time 5 minutes (Pressure over Wound), or until Bleeding Stops
- The right size underwrap and padding need to be ready
- 2 Trained People: 1 to perform the tenotomy and 1 to Assist [1]
Procedure[edit | edit source]
This may be done in the clinic by an orthopaedic surgeon or an experienced and trained clinician. Two people are required, one person to hold the foot and one person to perform the tenotomy. The person holding the foot grips the leg below the knee and the midfoot, with the child’s knee in extension. A generous antiseptic prep of the heel and ankle is applied, extending medially and laterally. A small amount of local anaesthetic is placed medial to the achilles tendon 1cm proximal to its insertion. If too much anaesthetic is used the tendon is difficult to feel.
Insert the knife (a number 15 scalpel or beaver blade works well) on the medial side, parallel to and beneath (anterior to) the tendon approximately 1cm above its insertion into the calcaneum. Turn the sharp edge of the knife to the tendon and perform the tenotomy. The “release” obtained after a complete tenotomy is easily felt. Often there is a “pop” sound. 10 - 20 degrees of additional dorsiflexion will be obtained.Effectiveness of tenotomy[edit | edit source]
Some clinicians have expressed concerns about performing a complete tenotomy (completely severing) of the Achilles tendon, fearing this procedure will cause damage. However, an ultrasound study on children who had undergone Achilles tenotomy as part of their clubfoot treatment showed tendon re-growth; most tendons were clinically intact after 3 weeks and after 6 weeks all were intact.[2] Percutaneous tendo Achilles tenotomy is safe, inexpensive, effective, and an easy office procedure used to expedite the correction of equinus deformity in idiopathic clubfeet with a very low complication rate.[3]
Tenotomy in older children is a controversial area. A study of older children (7-11 years old) who had achilles tenotomies performed reported that none of the participants had weakness of the gastrocnemius or soleus muscles.[4] However, the maximum age when tenotomy can be used has not been established, it has been suggested that a lengthening procedure using three incisions could be used in place of complete tenotomy in older children.[4] This topic needs further investigation.
Errors during tenotomy[edit | edit source]
Premature equinus correction - Attempts to correct the equinus before the heel varus and foot supination are corrected will result in a rocker-bottom deformity. Equinus through the subtalar joint can be corrected only if the calcaneus abducts. Tenotomy is indicated after cavus, adductus, and varus are fully corrected.Management post tenotomy[edit | edit source]
The cast after tenotomy stays on for 3 weeks. Prior to the tenotomy it is important to ensure to order the brace and book a the brace fitting. The foot must be in a dorsiflexed and abducted position to fit into brace. The last cast is applied with the foot in 50-70 degrees of abduction and at least 15 degrees of dorsiflexion. After removal of the last cast 3 weeks later there is correction of cavus, adductus, varus, and equinus (CAVE).References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Africa Clubfoot Training Project. Chapter 7 Africa Clubfoot Training Basic & Advanced Clubfoot Treatment Provider Courses - Participant Manual. University of Oxford: Africa Clubfoot Training Project, 2017.
- ↑ Barker S, Lavy C (2006) Correlation of clinical and ultrasonographical findings after Achilles tenotomy in idiopathic club foot. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 88-B (3): 377-379
- ↑ Riyaz Ahmad Dar, Mohd Shafi Bhat, Mohmad Yaseen Rather, Ansar ul Haq, Shera Ifran Ali. Percutaneous Tendo Achilles Tenotomy in the management of Equinus Deformity in conservatively treated CTEV. SEAJCRR 2015, JAN-FEB 4 (1)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Khan S & Kumar A (2010) Ponseti’s manipulation in neglected clubfoot in children more than 7 years of age: a prospective evaluation of 25 feet with long term follow-up. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics B 19: 385-389
- ↑ Lynn Staheli, Ignacio Ponseti, & Others. Clubfoot: Ponseti Management, 3rd Edition. Global Help, 2009. p13-15