Allodynia
Overview[edit | edit source]
Allodynia is defined as pain resulting from a stimulus, such as a light touch of the skin, that would not normally provoke pain[1]. For example, brushing a feather against the arm causes pain where it should only cause a sensation. Allodynia is a type of neuropathic (nerve) pain and is categorized into three types: dynamic (or mechanical) when pain results from an object moving across the skin, thermal which results from mild changes in temperature, or tactile (or static) which results from gentle touch or pressure. There is ultimately an error in the nerve communication network.
Etiology[edit | edit source]
The exact etiology behind allodynia is unknown. Allodynia is considered a symptom, not a disease. It may be a patient's chief complaint. Allodynia is the phenomenon of a non-painful stimulus producing a sharp pain response, which implies an error in neuronal conduction. The mechanism behind this error is also unclear. The strongest evidence that exists thus far, suggests that sensory neuronal fibers may stimulate pain pathways, possibly due to an error in long-term potentiation. However, studies exist that suggest that superficial sensory components may also have involvement. There is also evidence that different mental states can affect the perception of allodynia. The use of the analogy of "crisscrossed" fibers, the actual location of the crisscrossing can vary and may be located almost anywhere along the peripheral to the central nervous system tract. Allodynia can involve both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system via sensitization, and the mechanism behind the inappropriate pain sensations can evolve over time; this might partially explain the existing contradictory studies - they may all be measuring allodynia with neuronal confusion at different locations[2].
Listed below are some of the most common diseases associated with allodynia:
- Fibromyalgia
- Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Diabetic Neuropathic Pain
- Migraine Associated Allodynia
Differential Diagnoses[edit | edit source]
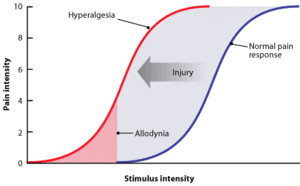
Treatment[edit | edit source]
There are multiple ways that healthcare providers can help treat allodynia. Providers can either treat the condition that is causing allodynia or try to reduce the pain. Oral and topical medications can be prescribed. Some oral medications that can help manage allodynia include anticonvulsants (used to treat seizures), triptans (used to treat migraines), and some antidepressants. Topical creams that can help manage allodynia will typically have lidocaine or capsaicin as the active ingredient. Counseling may be recommended if signs of depression are detected. Biofeedback, mindfulness training, and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy can change the way a person responds to pain. Physical therapists can help manage allodynia with desensitization and/or mirror therapy. A nerve block injection may be recommended to reduce pain in a specific nerve or nerve groups. Surgery may be needed if these treatments are unsuccessful in managing allodynia. The surgeon implants a device that will deliver electricity directly to the spinal cord to stimulate it. These low levels of electricity help reduce pain.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Allodynia cannot not be directly prevented, however, one can lower the risk of acquiring a condition that causes allodynia. Risk management includes exercising regularly, monitoring health via checkups, maintaining a healthy weight, staying up-to-date on vaccines, and having a balanced diet.
References[edit | edit source]
see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ 4. Definition of ALLODYNIA [Internet]. Merriam-webster.com. 2017 [cited 2022 Apr 9]. Available from: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/allodynia
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 1. He Y, Kim PY. Allodynia [Internet]. PubMed. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2016 [cited 2022 Apr 9]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537129/
- ↑ Garvey, J., Abolade, A., Etherton, J., Jackson, K., Hampton, L., Thomas, E., Van der Stockt, T., Lopez, L., & Lowe, R. (2016, April 1). Pain Behaviours. Physio-Pedia.com. File:Allodynia.gif
- ↑ 3. Medical Definition of HYPERALGESIA [Internet]. www.merriam-webster.com. [cited 2022 Apr 9]. Available from: https://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/hyperalgesia






