Bacterial Infections
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Vidya Acharya, Rucha Gadgil and Nupur Smit Shah
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Bacteria are found everywhere, in any climate and location throughout the world. Some are airborne and others are most prevalent in water, soil, plants, animals, and even people. Many strains of bacteria are harmless and some are even beneficial, such as those found in the human gastrointestinal tract to aid digestion and produce vitamins. There are few (less than 1% of all bacteria types) that cause illness in humans. Some bacteria can be quite dangerous, resulting in salmonella, pneumonia, or meningitis[1].
- The global problem of infectious and deadly diseases caused by bacteria are presently major scientific and medical issues.
- Bacterial infections have a large impact on public health.
- As a general rule, bacterial infections are easier to treat than viral infections, since we have an extensive army of antimicrobial agents with activity against bacteria.
- Bacterial resistance to antimicrobials is a rapidly growing problem with potentially devastating consequences.[2]
- The most deadly bacterial disease contracted by human beings is mycobacterium tuberculosis, the world's leading infectious disease with more than 1,700,000 deaths per year. As much as 13% of cases are resistant to most antibiotics, and about 6% are resistant or unresponsive to essentially all treatment[1].
Structure[edit | edit source]
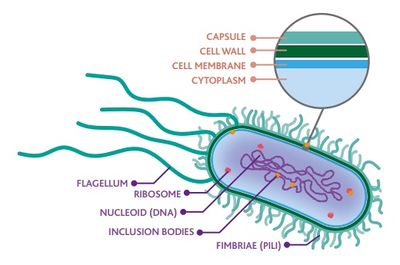
Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms that carry their genetic information in a double-stranded circular molecule of DNA. Some species also contain small circular plasmids of additional DNA. The cell cytoplasm contains ribosomes and there is both a cell membrane and, in all species except Mycoplasma, a complex cell wall. External to the cell wall, some bacteria have capsules, flagella, or pili. Bacteria normally reproduce by binary fission. Under the proper conditions, some bacteria can divide and multiply rapidly. Consequently, some infections require only a small number of organisms to cause potentially overwhelming infection.
Bacteria are classified
- Gram-positive or Gram-negative based on the characteristics of their cell wall, as seen under a microscope after stains have been administered, a procedure called Gram staining, that was developed in 1882 by Hans Christian Gram (see Figure 2 ). Most, but not all, bacteria fall into one of these two categories. Clinically, one of the main differences between gram-positive and gram-negative organisms is that gram-negative bacteria tend to produce an endotoxin that can cause tissue destruction, shock, and death. The two classes of bacteria differ in their antibiotic susceptibilities as well.
- Aerobic or Anaerobic, based on their growth responses in the presence and absence of oxygen[2].
All of the human organs are susceptible to bacterial infection.
Mode of Action[edit | edit source]
Each species of bacteria has a predilection to infect certain organs and not others. eg. Neisseria meningitidis normally infects the meninges (covering) of the central nervous system, it is not, however, a cause of skin infection.
Disease can be caused by the
- Destruction of the body's cells by the organism
- Body's immune response to the infection. Antibiotics may be of little or no use when the disease manifestations are a result of the body's attempts to rid itself of the bacteria. The systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), usually caused by a bacterial infection, is an overwhelming inflammatory response to infection, manifested by the release of large numbers of cytokines and presenting with signs of infection and early signs of hemodynamic instability. If allowed to progress, SIRS patients can go on to develop sepsis, with multiorgan failure and death. Once the cascade of events has begun, even the strongest antibiotics are often powerless to stop this progression[2].
The immune response is the way in which your body recognizes and defends itself against bacteria, viruses, and other substances that are foreign and harmful. It is the job of the immune system to protect our bodies from harmful invaders by recognizing and responding to antigens. See the Immune System
Most Deadly Bacterial Infections[edit | edit source]
1. Anthrax
2. Tetanus
3. Leptospirosis
4. Tuberculosis
5. Pneumonia
6. Cholera
7. Botulism
8. Pseudomonas Infection
9. MRSA Infection
10. E.Coli Infection
11. Meningitis
12. Gonorrhea
13. Bubonic Plague
14. Syphilis[3]
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Among the top causes of mortality in the world
- Lower respiratory infection is the third most common and diarrhea is the sixth (both often caused by bacteria).
- Tuberculosis is the seventh most common cause of death.
Measures to prevent infection have a dramatic impact on morbidity and mortality. Prevention is especially important in this age of increasing antibiotic resistance, because treatment can be so difficult to achieve.
- There are three major principals of control of bacterial infection: Eliminate or contain the source of infection, interrupt the chain of transmission, and protect the host against infection or disease.
- In addition, there is increasing recognition that elimination of important cofactors, such as air pollution from vehicles or from indoor cooking, can markedly reduce the incidence of bacterial infections.
- Which measure is most effective often depends on the reservoir for the infection.
- Prevention of infection, e.g., through a vaccine, is generally called primary prevention, treatment of infected people to prevent symptomatic infection is called secondary prevention, and treatment of infected people to prevent transmission to other humans is called tertiary prevention[2].
Antibiotic resistance[edit | edit source]
- Antibiotic resistance is one of the biggest threats to global health, food security, and development today.
- Antibiotic resistance can affect anyone, of any age, in any country.
- Antibiotic resistance occurs naturally, but misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals is accelerating the process.
- A growing number of infections – such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, gonorrhoea, and salmonellosis – are becoming harder to treat as the antibiotics used to treat them become less effective.
- Antibiotic resistance leads to longer hospital stays, higher medical costs and increased mortality.[4]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 World Atlas What's The Deadliest Bacterial Disease? Available from:https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/what-s-the-deadliest-bacterial-disease.html (last accessed 10.11.2020)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Doron S, Gorbach SL. Bacterial Infections: Overview. International Encyclopedia of Public Health. 2008:273.Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7149789/ (last accessed 10.11.2020)
- ↑ "Top 14 Most Infectious and Deadliest Diseases Caused By Bacteria," in Bio Explorer, November 10, 2020, Available from:https://www.bioexplorer.net/bacterial-diseases.html/(last accessed 10.11.2020)
- ↑ WHO Antibiotic resistance Available from:https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance (last accessed 10.11.2020)