Extensor Pollicis Longus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
It inserts at the base of distal phalanx of thumb via Lister's tubercle; that is the dorsal tubercle of radius. | It inserts at the base of distal phalanx of thumb via Lister's tubercle; that is the dorsal tubercle of the [[radius]]. | ||
=== Nerve === | === Nerve === | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
=== Artery === | === Artery === | ||
EPL blood supply is via the posterior interosseous artery and perforating branches of the anterior interosseous artery.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
* The EPL mainly hyper-/extends the interphalangeal joint of the distal phalanx of the thumb.<ref>Wikipedia. 2019. Available from:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extensor_pollicis_longus_muscle (accessed 10 October 2020)</ref> | * The EPL mainly hyper-/extends the interphalangeal joint of the distal phalanx of the thumb.<ref>Wikipedia. 2019. Available from:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extensor_pollicis_longus_muscle (accessed 10 October 2020)</ref> | ||
* It also serves as accessory extensors and adductors of the metacarpophalangeal of the proximal phalanx and carpometacarpal joints of the first metacarpal.<ref>Khan I. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Extensor Pollicis Longus Muscle. In: Varacallo M. editor. Statpearls, 2020. Available from:https://www.statpearls.com/articlelibrary/viewarticle/36135/ (accessed 10 October 2020)</ref> | * It also serves as accessory extensors and adductors of the metacarpophalangeal of the proximal phalanx and carpometacarpal joints of the first metacarpal.<ref name=":1">Khan I. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Extensor Pollicis Longus Muscle. In: Varacallo M. editor. Statpearls, 2020. Available from:https://www.statpearls.com/articlelibrary/viewarticle/36135/ (accessed 10 October 2020)</ref> | ||
* It may also assist in wrist joint extension.<ref>KenHub. Available from:https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/extensor-pollicis-longus-muscle (accessed 10 October 2020)</ref> | * It may also assist in [[Wrist and Hand|wrist joint]] extension.<ref name=":0">KenHub. Available from:https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/extensor-pollicis-longus-muscle (accessed 10 October 2020)</ref> | ||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
Tenosynovitis is a relatively common inflammatory irritation of the synovial sheath, after repetitive activities such as playing drum. | Tenosynovitis is a relatively common inflammatory irritation of the synovial sheath, after repetitive activities such as playing drum; this is termed drummers palsy.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Assessment == | == Assessment == | ||
== | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 10 October 2020
Original Editor - Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka
Top Contributors - Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka, Kim Jackson, Shaimaa Eldib and Aya Alhindi
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (10/10/2020)
Description[edit | edit source]
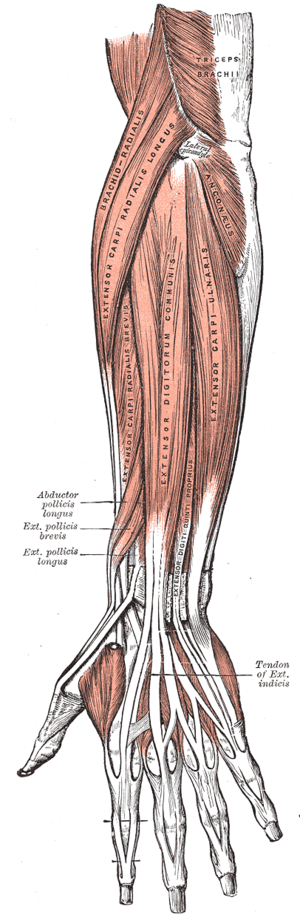
Extensor pollicis longus (EPL) is a long muscle located at the deep layer with extensor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis longus, extensor indicis, and supinator muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm.[1] It originates from the mid-third of the ulna, and interosseous membrane then courses down to the distal phalanx of the thumb. Though it is situated at the forearm, it is classified as part of the extrinsic muscles of the hand as it's function is seen in thumb movement.[2]
Origin[edit | edit source]
It originates from the mid-third of the ulna, and interosseous membrane
Insertion[edit | edit source]
It inserts at the base of distal phalanx of thumb via Lister's tubercle; that is the dorsal tubercle of the radius.
Nerve[edit | edit source]
It is innervated by the deep branch of the radial nerve via the posterior interosseous nerve (7th and 8th cervical nerve root).[3]
Artery[edit | edit source]
EPL blood supply is via the posterior interosseous artery and perforating branches of the anterior interosseous artery.[4][5]
Function[edit | edit source]
- The EPL mainly hyper-/extends the interphalangeal joint of the distal phalanx of the thumb.[6]
- It also serves as accessory extensors and adductors of the metacarpophalangeal of the proximal phalanx and carpometacarpal joints of the first metacarpal.[5]
- It may also assist in wrist joint extension.[4]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Tenosynovitis is a relatively common inflammatory irritation of the synovial sheath, after repetitive activities such as playing drum; this is termed drummers palsy.[4]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. 7th ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2014.
- ↑ Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AW, Gray H. Gray's anatomy for Students 2nd edition. Philadelphia : Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier, 2010.
- ↑ Department of Radiology; University of Washington. Available from: https://rad.washington.edu/muscle-atlas/extensor-pollicis-longus/ (accessed 10 October 2020)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 KenHub. Available from:https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/extensor-pollicis-longus-muscle (accessed 10 October 2020)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Khan I. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Extensor Pollicis Longus Muscle. In: Varacallo M. editor. Statpearls, 2020. Available from:https://www.statpearls.com/articlelibrary/viewarticle/36135/ (accessed 10 October 2020)
- ↑ Wikipedia. 2019. Available from:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extensor_pollicis_longus_muscle (accessed 10 October 2020)